J Adv Prosthodont.
2009 Mar;1(1):31-36. 10.4047/jap.2009.1.1.31.
A comparison of the implant stability among various implant systems: clinical study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Esthetic Restorative Dentistry, Korea University, Korea.
- 2Department of Prosthodontics, Institute for Clinical Dental Research, Korea University, Korea.
- 3Department of Prosthodontics, Ansan Hospital, College of Medicine, Korea University, Korea. koprosth@unitel.co.kr
- KMID: 2176338
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jap.2009.1.1.31
Abstract
- PURPOSE
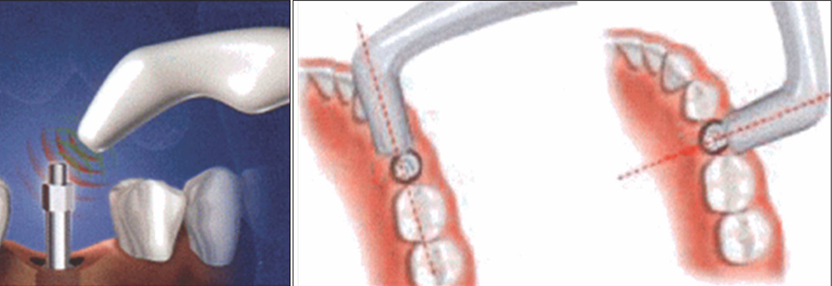
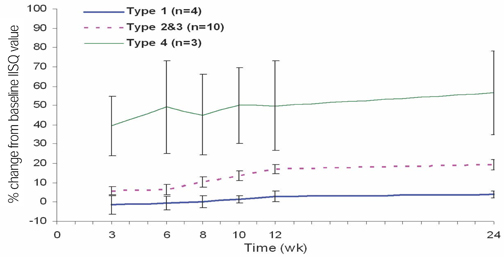
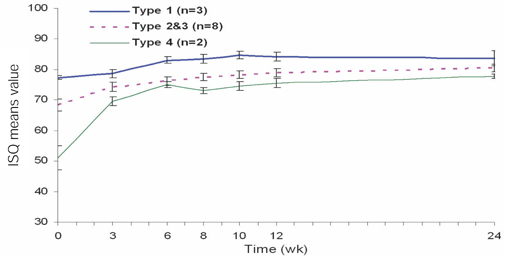
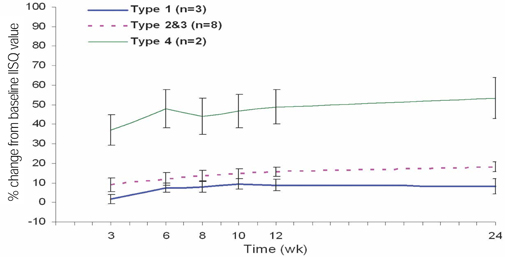
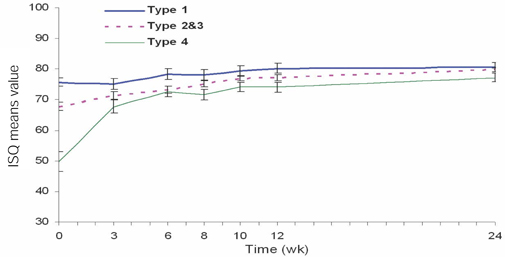
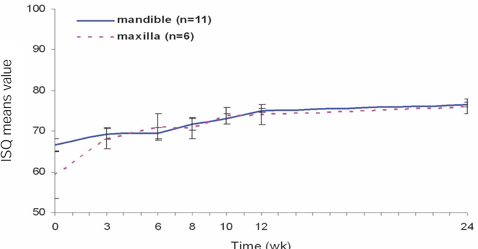
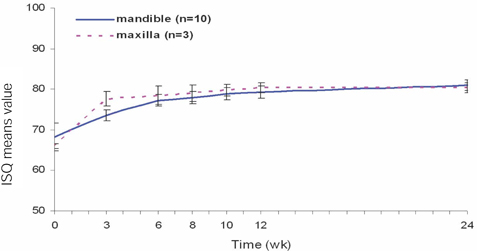
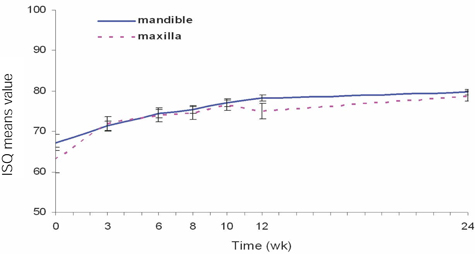
To determine the change in stability of single-stage, three different design of implant systems in humans utilizing resonance frequency analysis for early healing period (24 weeks), without loading. MATERIAL AND METHODS: Twenty-five patients were included into this study. A total of 45 implants, three different design of implant systems (group A,C,R) were placed in the posterior maxilla or mandible. The specific transducer for each implant system was used. ISQ (implant stability quotient) reading were obtained for each implant at the time of surgery, 3, 6, 8, 10, 12, 24 weeks postoperatively. Data were analyzed for different implant type, bone type, healing time, anatomical locations. RESULTS: For each implant system, a two-factor mixed-model ANOVA demonstrated that a significant effect on ISQ values (group A = 0.0022, C = 0.017, R = 0.0018). For each implant system, in a two-factor mixed model ANOVA, and two-sample t-test, the main effect of jaw position (P > .005) on ISQ values were not significant. CONCLUSIONS: All the implant groups A, C and R, the change patterns of ISQ over time differed by bone type. Implant stability increased greatly between week 0 and week six and showed slow increase between week six and six months (plateau effect).
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Retrospective study of implant stability according to the implant length, diameter and position
Ji-Hye Kim, Jin-Yong Jeon, Yu-Ri Heo, Mee-Kyoung Son
J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2013;51(4):269-275. doi: 10.4047/jkap.2013.51.4.269.
Reference
-
1. Brånemark PI. An introduction to osseointegration. Quintessence. 1985. 11–53.2. Davies JE. Understanding peri-implant endosseous healing. J Dent Educ. 2003. 67:932–949.3. Cochran DL, Buser D, ten Bruggenkate CM, Weingart D, Taylor TM, Bernard JP, Peters F, Simpson JP. The use of reduced healing times on ITI implants with a sandblasted and acid-etched (SLA) surface: early results from clinical trials on ITI SLA implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2002. 13:144–153.4. Meredith N. Assessment of implant stability as a prognostic determinant. Int J Prosthodont. 1998. 11:491–501.5. Nedir R, Bischof M, Szmukler-Moncler S, Bernard JP, Samson J. Predicting osseointegration by means of implant primary stability. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2004. 15:520–528.6. Meredith N. The application of modal vibration analysis to study bone healing in vivo. J Dent Res. 1994. 73:793.7. Meredith N, Alleyne D, Cawley P. Quantitative determination of the stability of the implant-tissue interface using resonance frequency analysis. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1996. 7:261–267.8. Meredith N, Book K, Friberg B, Jemt T, Sennerby L. Resonance frequency measurements of implant stability in vivo. A cross-sectional and longitudinal study of resonance frequency measurements on implants in the edentulous and partially dentate maxilla. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1997. 8:226–233.9. Meredith N, Shagaldi F, Alleyne D, Sennerby L, Cawley P. The application of resonance frequency measurements to study the stability of titanium implants during healing in the rabbit tibia. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1997. 8:234–243.10. Friberg B, Sennerby L, Meredith N, Lekholm U. A comparison between cutting torque and resonance frequency measurements of maxillary implants. A 20-month clinical study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1999. 28:297–303.11. Friberg B, Sennerby L, Linden B, Gröndahl K, Lekholm U. Stability measurements of one-stage Brånemark implants during healing in mandibles. A clinical resonance frequency analysis study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1999. 28:266–272.12. Valderrama P, Oates TW, Jones AA, Simpson J, Schoolfield JD, Cochran DL. Evaluation of two different resonance frequency devices to detect implant stability: a clinical trial. J Periodontol. 2007. 78:262–272.13. Trisi P, Rao W. Bone classification: clinical-histomorphometric comparison. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1999. 10:1–7.14. Roberts WE. Bone tissue interface. J Dent Educ. 1988. 52:804–809.15. Davies JE. Understanding peri-implant endosseous healing. J Dent Educ. 2003. 67:932–949.16. Cochran DL, Schenk RK, Lussi A, Higginbottom FL, Buser D. Bone response to unloaded and loaded titanium implants with a sandblasted and acid-etched surface: a histometric study in the canine mandible. J Biomed Mater Res. 1998. 40:1–11.17. Cochran DL. A comparison of endosseous dental implant surfaces. J Periodontol. 1999. 70:1523–1539.18. Esposito M, Hirsch JM, Lekholm U, Thomsen P. Biological factors contributing to failures of osseointegrated oral implants. (II). Etiopathogenesis. Eur J Oral Sci. 1998. 106:721–764.19. Huang HM, Chiu CL, Yeh CY, Lee SY. Factors influencing the resonance frequency of dental implants. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2003. 61:1184–1188.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of initial implant stability measured by Resonance Frequency Analysis between different implant systems
- A Two-year Retrospective Study on the Clinical Success of the Korean Implant Systems
- The effect of osteotome technique on primary implant stability according to implant fixture diameter
- Evaluation of Dental Implant Stability with or without Photoactivated Surface Treatment
- The evaluation of implant stability measured by resonance frequency analysis in different bone types