J Breast Cancer.
2016 Mar;19(1):61-67. 10.4048/jbc.2016.19.1.61.
Analysis of TRRAP as a Potential Molecular Marker and Therapeutic Target for Breast Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Breast Surgery, Affiliated Tumor Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin, China. pangdasir2015@126.com
- 2Northern (China) Translational Medicine Research and Cooperation Center, Heilongjiang Academy of Medical Sciences, Harbin, China.
- KMID: 2176322
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2016.19.1.61
Abstract
- PURPOSE
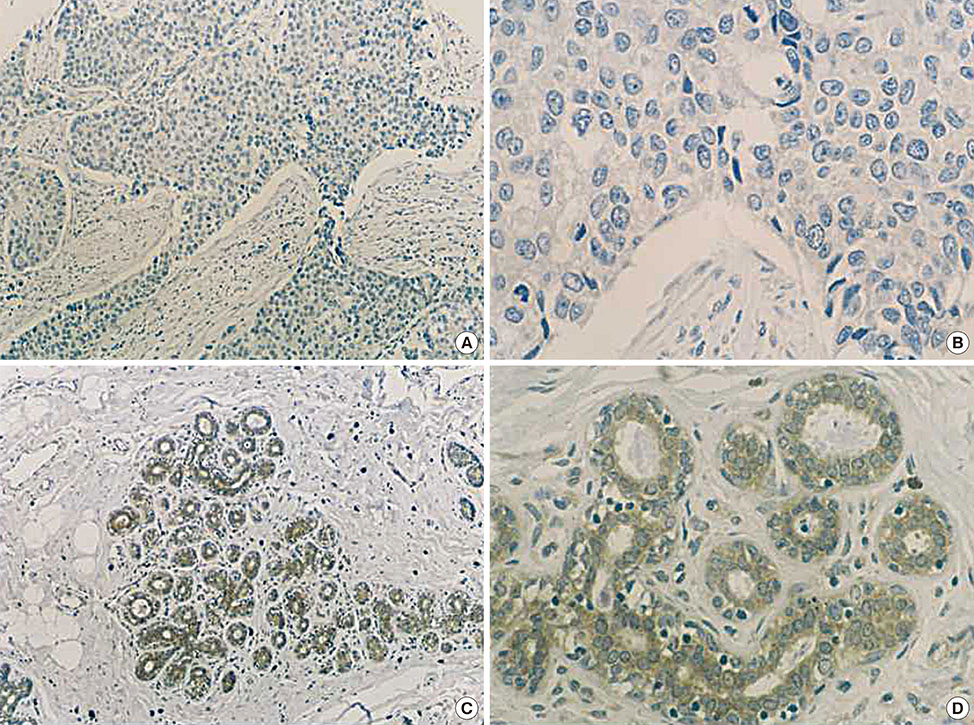
This study was designed to assess the protein levels of transformation/transcription domain-associated protein (TRRAP) in invasive ductal breast carcinomas, and investigated the association between TRRAP and the clinicopathological features of breast cancer.
METHODS
We examined TRRAP protein expression in 470 breast cancer tissues and normal breast tissues by tissue microarray to study the correlation between TRRAP expression and clinicopathological features. This was analyzed using the chi-square test. Kaplan-Meier survival curves and log-rank tests were applied to analyze the survival status. Cox regression was applied for multivariate analysis of prognosis.
RESULTS
The data demonstrated that expression of TRRAP was significantly lower in breast carcinomas (36.6%) than in corresponding normal breast tissues (50.8%). In addition, TRRAP protein levels negatively correlated with tumor size, and indicated poor differentiation, increased nodal involvement, and low p53-positive rates. Analysis of survival revealed that lower TRRAP expression correlated with shorter survival time. Univariate analyses identified TRRAP and progesterone receptor as independent protective factors for breast cancer prognosis. However, Ki-67, tumor size, and nodal involvement appeared to be independent risk factors.
CONCLUSION
The findings indicate a significant correlation between TRRAP protein levels and adverse prognosis in breast cancer. Therefore, TRRAP could be a prognostic biomarker for breast cancer. In addition, TRRAP is also a predictive biomarker of breast cancer treatment.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013; 63:11–30.
Article2. Hebbes TR, Thorne AW, Crane-Robinson C. A direct link between core histone acetylation and transcriptionally active chromatin. EMBO J. 1988; 7:1395–1402.
Article3. Bannister AJ, Kouzarides T. Regulation of chromatin by histone modifications. Cell Res. 2011; 21:381–395.
Article4. Lane AA, Chabner BA. Histone deacetylase inhibitors in cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27:5459–5468.
Article5. Glozak MA, Seto E. Histone deacetylases and cancer. Oncogene. 2007; 26:5420–5432.
Article6. Emanuele S, Lauricella M, Tesoriere G. Histone deacetylase inhibitors: apoptotic effects and clinical implications (Review). Int J Oncol. 2008; 33:637–646.
Article7. Li H, Cuenin C, Murr R, Wang ZQ, Herceg Z. HAT cofactor Trrap regulates the mitotic checkpoint by modulation of Mad1 and Mad2 expression. EMBO J. 2004; 23:4824–4834.
Article8. Murr R, Loizou JI, Yang YG, Cuenin C, Li H, Wang ZQ, et al. Histone acetylation by Trrap-Tip60 modulates loading of repair proteins and repair of DNA double-strand breaks. Nat Cell Biol. 2006; 8:91–99.
Article9. Murr R, Vaissière T, Sawan C, Shukla V, Herceg Z. Orchestration of chromatin-based processes: mind the TRRAP. Oncogene. 2007; 26:5358–5372.
Article10. McMahon SB, Van Buskirk HA, Dugan KA, Copeland TD, Cole MD. The novel ATM-related protein TRRAP is an essential cofactor for the c-Myc and E2F oncoproteins. Cell. 1998; 94:363–374.
Article11. Oishi H, Kitagawa H, Wada O, Takezawa S, Tora L, Kouzu-Fujita M, et al. An hGCN5/TRRAP histone acetyltransferase complex co-activates BRCA1 transactivation function through histone modification. J Biol Chem. 2006; 281:20–26.
Article12. Charles NA, Holland EC. TRRAP and the maintenance of stemness in gliomas. Cell Stem Cell. 2010; 6:6–7.
Article13. Matkovic B, Juretic A, Separovic V, Novosel I, Separovic R, Gamulin M, et al. Immunohistochemical analysis of ER, PR, HER-2, CK 5/6, p63 and EGFR antigen expression in medullary breast cancer. Tumori. 2008; 94:838–844.
Article14. Cheang MC, Chia SK, Voduc D, Gao D, Leung S, Snider J, et al. Ki67 index, HER2 status, and prognosis of patients with luminal B breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2009; 101:736–750.
Article15. Remmele W, Stegner HE. Recommendation for uniform definition of an immunoreactive score (IRS) for immunohistochemical estrogen receptor detection (ER-ICA) in breast cancer tissue. Pathologe. 1987; 8:138–140.16. Kruse JP, Gu W. Modes of p53 regulation. Cell. 2009; 137:609–622.
Article17. Levine AJ, Oren M. The first 30 years of p53: growing ever more complex. Nat Rev Cancer. 2009; 9:749–758.
Article18. Brooks CL, Gu W. The impact of acetylation and deacetylation on the p53 pathway. Protein Cell. 2011; 2:456–462.
Article19. Li AG, Piluso LG, Cai X, Gadd BJ, Ladurner AG, Liu X. An acetylation switch in p53 mediates holo-TFIID recruitment. Mol Cell. 2007; 28:408–421.
Article20. Zhang H, Luo M, Jin Z, Wang D, Sun M, Zhao X, et al. Expression and clinicopathological significance of FSIP1 in breast cancer. Oncotarget. 2015; 6:10658–10666.
Article21. Mantelingu K, Kishore AH, Balasubramanyam K, Kumar GV, Altaf M, Swamy SN, et al. Activation of p300 histone acetyltransferase by small molecules altering enzyme structure: probed by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. J Phys Chem B. 2007; 111:4527–4534.
Article22. Dastjerdi MN, Salahshoor MR, Mardani M, Hashemibeni B, Roshankhah S. The effect of CTB on P53 protein acetylation and consequence apoptosis on MCF-7 and MRC-5 cell lines. Adv Biomed Res. 2013; 2:24.
Article23. Sterner DE, Berger SL. Acetylation of histones and transcription-related factors. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2000; 64:435–459.
Article24. Khaleel SS, Andrews EH, Ung M, DiRenzo J, Cheng C. E2F4 regulatory program predicts patient survival prognosis in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2014; 16:486.
Article25. Reis-Filho JS, Tutt AN. Triple negative tumours: a critical review. Histopathology. 2008; 52:108–118.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Significance of p-AKT1 as a Prognostic Marker and Therapeutic Target in Patients With Hormone Receptor-Positive and Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-2-Positive Early Breast Cancer
- Hormone Therapy for Metastatic Breast Cancer
- Heat Shock Protein as Molecular Targets for Breast Cancer Therapeutics
- Circulating Tumor Cells: Detection Methods and Potential Clinical Application in Breast Cancer
- Hormone Treatment for Breast Cancer