J Korean Acad Conserv Dent.
2010 Mar;35(2):96-105. 10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.2.096.
The remineralization aspect of enamel according to change of the degree of saturation of the organic acid buffering solution in pH 5.5
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dentistry, the Graduate School, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea. chanyoungl@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2176297
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.2.096
Abstract
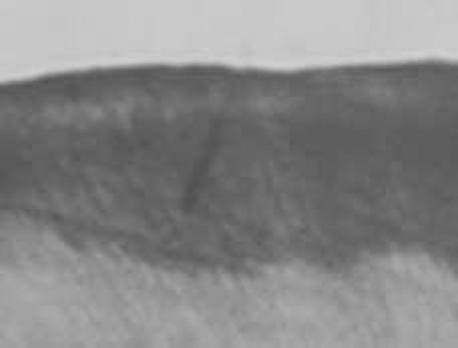
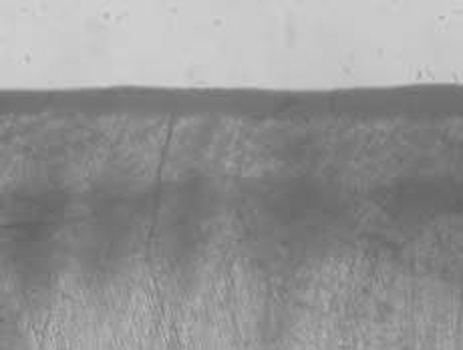
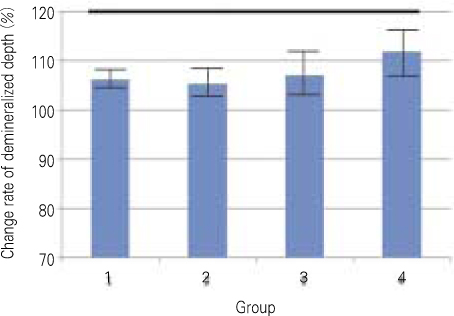
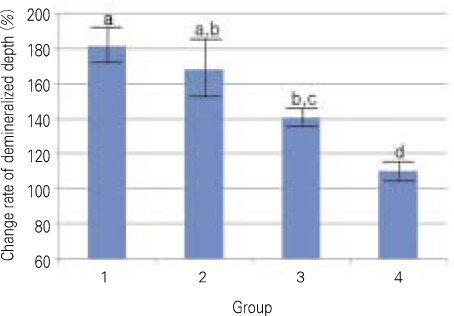
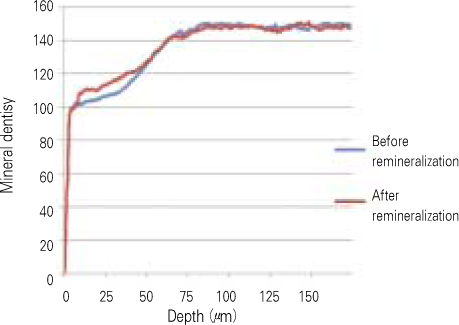
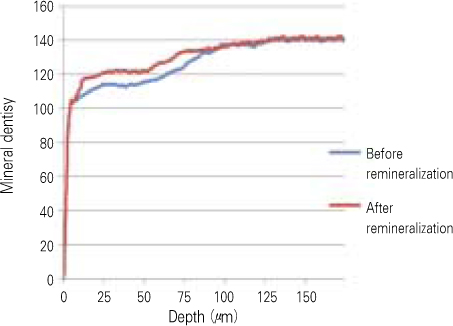
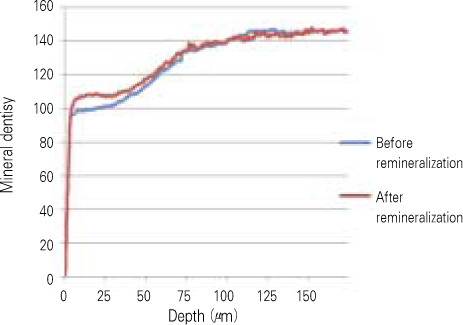
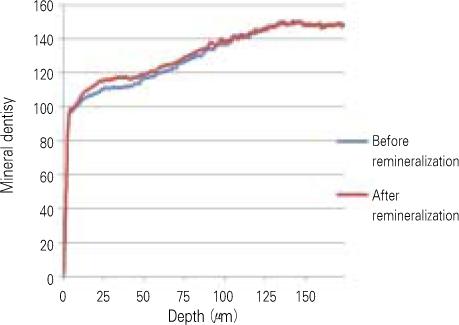
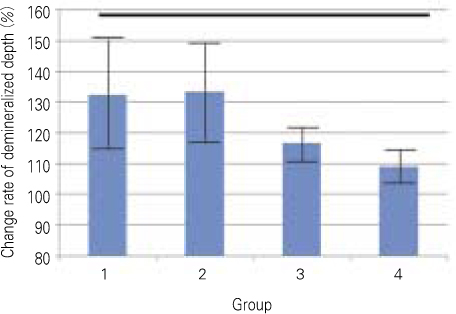
- The purpose of this study is to observe and compare the remineralization tendencies of artificial enamel caries lesion by remineralization solutions of different degree of saturations at pH 5.5, using a polarizing microscope and computer programs (Photoshop, Image pro plus, Scion Image, Excel). For this study, 48 sound permanent teeth with no signs of demineralization, cracks, or dental restorations were used. The specimens were immersed in lactic acid demineralization solution for 2 days in order to produce artificial dental caries that consist of surface and subsurface lesions. Each of 9 or 10 specimens was immersed in pH 5.5 lactic acid buffering remineralization solution of four different degrees of saturation (0.507, 0.394, 0.301, and 0.251) for 12 days. After the demineralization and remineralization, images were taken by a polarizing microscope (x100). The results were obtained by observing images of the specimens, and using computer programs, the density of caries lesions were estimated. While the group with the lowest degree of saturation (0.251) showed total remineralization feature from the surface to the subsurface of the lesion, the group with the highest degree of saturation (0.507) showed demineralization mainly on the surface of the lesion at the constant organic acid concentration 0.01 M and pH 5.5.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Effect of fluoride concentration in pH 4.3 and pH 7.0 supersaturated solutions on the crystal growth of hydroxyapatite
Haneol Shin, Sung-Ho Park, Jeong-Won Park, Chan-Young Lee
Restor Dent Endod. 2012;37(1):16-23. doi: 10.5395/rde.2012.37.1.16.
Reference
-
1. Ingram GS, Silverstone LM. A chemical and histological study of artificial caries in human dental enamel in vitro. Caries Res. 1981. 15:393–398.
Article2. Shellis RP. Relationship between human enamel structure and the formation of caries-like lesions. Arch Oral Biol. 1984. 29:975–981.
Article3. Silverstone LM. Observations on the dark zone in early enamel caries and artificial caries-like lesions. Caries Res. 1967. 1:260–274.
Article4. Ten Cate JM, Arends J. Remineralization of artificial enamel lesions in vitro. Caries Res. 1981. 15:60–69.5. Brudevold F, McCann HG. Enamel solubility tests and their significance in regard to dental caries. Ann N.Y. Acad Sci. 1968. 153:20–51.
Article6. Christoffersen J, Arends J. Progress of artificial lesion progression in enamel. J Dent Res. 1984. 63:13–18.7. Moreno EC, Zahradnik RT. Chemistry of enamel subsurface demineralization in vitro. J Dent Res. 1974. 53:226–235.
Article8. Featherstone JDB, Duncan JF, Cutress TW. Surface layer phenomenon in vitro early caries-like lesions in human tooth enamel. Arch Oral Biol. 1978. 23:397–404.
Article9. Ten Cate JM. In vitro studies on the effects of F on de- and remineralization. J Dent Res. 1990. 69:614–619.10. Varughese K, Moreno E.C. Crystal growth of calcium apatites in dilute solutions containing fluorides. Calcif Tissue Int. 1981. 33(4):431–439.
Article11. Ten Cate JM. In vitro studies on the effects of F on deand remineralization. J Dent Res. 1990. 69:614–619.12. Park JH, Roh BD, Lee SJ. The accuracy of the frequency dependent type apex locator. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 1996. 21:161–173.13. Lammers PC, Borggreven JM, Driessens FC. Influence of fluoride and pH on in vitro remneralization of bovine enamel. Caries Res. 1992. 26:8–13.
Article14. Amjad Z, Nancollas G.H. Effect of fluoride on the growth of hydroxyapatite and human dental enamel. Caries Res. 1979. 13:250–258.
Article15. Park SH, Lee CY, Lee CS. The effect of acid concentration and ph of lactate buffer solution on the progress of artificial caries lesion in human tooth enamel. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 1993. 18:277–290.16. Kwak YJ, Kim ES, Park SH, Gong HK, Lee Y, Lee CY. The remineralizing features of ph 5.5 solutions of different decree of saturations on artificially demineralized enamel. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2008. 33(5):481–492.
Article17. Head JA. A study of saliva and its action on tooth enamel in reference to its hardening and softing. J Am Med Assoc. 1912. 59:2118–2122.18. Arends J, Jongebloed W, Ogaard B, Rolla G. SEM and microradiographic investigation of initial enamel caries. Scand J Dent Res. 1987. 95:193–201.
Article19. Featherstone JDB, Rodger BF. Effect of acetic, lactic and other organic acids on the formation of artificial caries lesion. Caries Res. 1981. 15:377–385.
Article20. Featherstone JDB. Comparison of artificial caries like lesions by quantitative microradiography and microhardness profile. Caries Res. 1983. 17:385–391.
Article21. Silverstone LM, Wefer JS, Zimmerman BF, Clark BH, Featherstone MJ. Remineralization phenomena. Caries Res. 1977. 11:59–84.
Article22. Ten Cate JM, Duijsters PPE. Alternating demineralization and remineralization of artificial enamel lesions. Caries Res. 1982. 16:201–210.
Article23. Darling AI. Studies of the early lesion of enamel caries with transmitted light, polarized light and radiography. Brit Dent J. 1956. 6:289–341.24. Silverstone LM. Observations on the dark zone in early enamel caries and artificial caries-like lesions. Caries Res. 1967. 1:260–274.
Article25. Silverstone LM, Wefer JS, Zimmerman BF, Clark BH, Featherstone MJ. Remineralization phenomena. Caries Res. 1977. 11:59–84.
Article26. Ten Cate JM, Duijsters PPE. Alternating demineralization and remineralization of artificial enamel lesions. Caries Res. 1982. 16:201–210.
Article27. Rooij J.F., Nancollas G.H. The formation and remineralization of artificial white spot lesions: A Constant composition approach. J Dent Res. 1984. 63(6):864–867.
Article28. Exterkate RAM, Damen JJM, ten Cate JM. A single-section model for enamel de- and remineralization studies. 1. The effects of different Ca/P ratios in remineralization solutions. J Dent Res. 1993. 72:1599–1603.
Article29. Park JW, Hur B, Lee CY. The effects of the degree of saturation of acidulated buffer solutions in enamel and dentin remineralization and afm observation of hydroxyapatite crystals. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2000. 25:459–473.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The dynamic change of arttificially demineralized enamel by degree of saturation of remineralization at pH 4.3
- The remineralizing features of pH 5.5 solutions of different degree of saturations on artificially demineralized enamel
- The change of the configuration of hydroxyapatite crystals in enamel by changes of pH and degree of saturation of lactic acid buffer solution
- The effect of lactic acid concentration and ph of lactic acid buffer solutions on enamel remineralization
- The effect of the pH of remineralized buffer solutions on dentin remineralization