Investig Magn Reson Imaging.
2015 Jun;19(2):67-75. 10.13104/imri.2015.19.2.67.
Evaluation of Hippocampal Volume Based on Various Inversion Time in Normal Adults by Manual Tracing and Automated Segmentation Methods
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Convergence Medical Science, Gyeongsang National University Graduate School, Jinju, Korea.
- 2Department of Radiology, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea. choids@gshp.gsnu.ac.kr
- 3Department of Radiology, Gyeongsang National University Hospital, Jinju, Korea.
- 4Department of Neurology, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea.
- 5Neuroscience Research Institute, Kangwon National University School of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 6Department of Radiology, Kangwon National University School of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 7Gyeongsang Institute of Health Science, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea.
- KMID: 2175586
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2015.19.2.67
Abstract
- PURPOSE
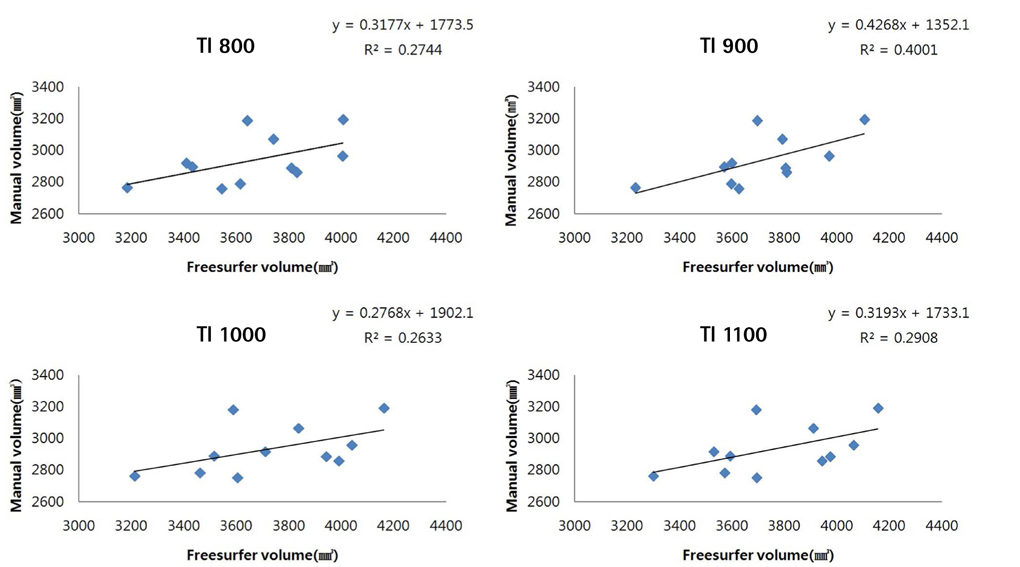
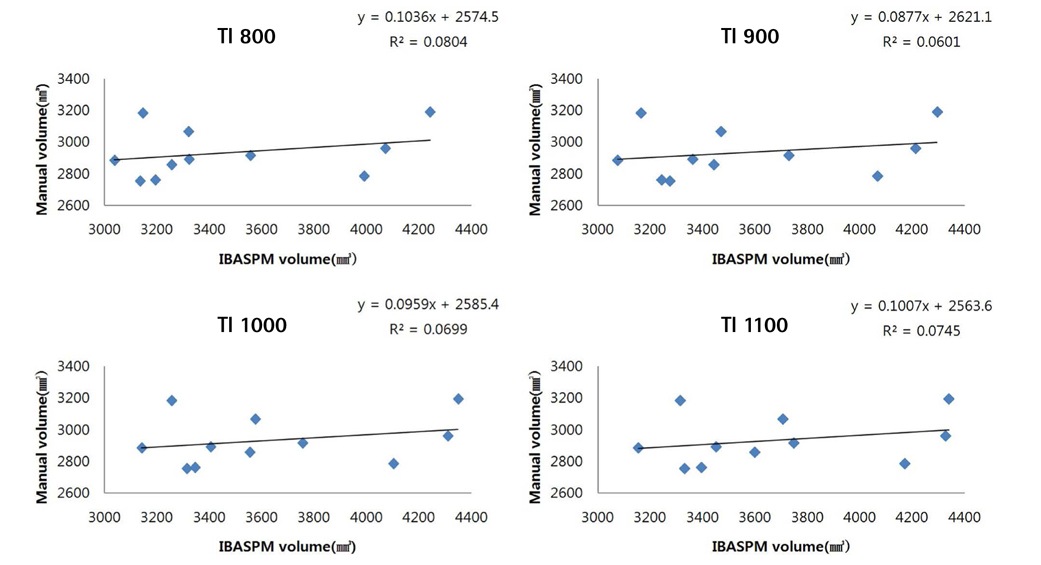
To investigate the value of image post-processing software (FreeSurfer, IBASPM [individual brain atlases using statistical parametric mapping software]) and inversion time (TI) in volumetric analyses of the hippocampus and to identify differences in comparison with manual tracing.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
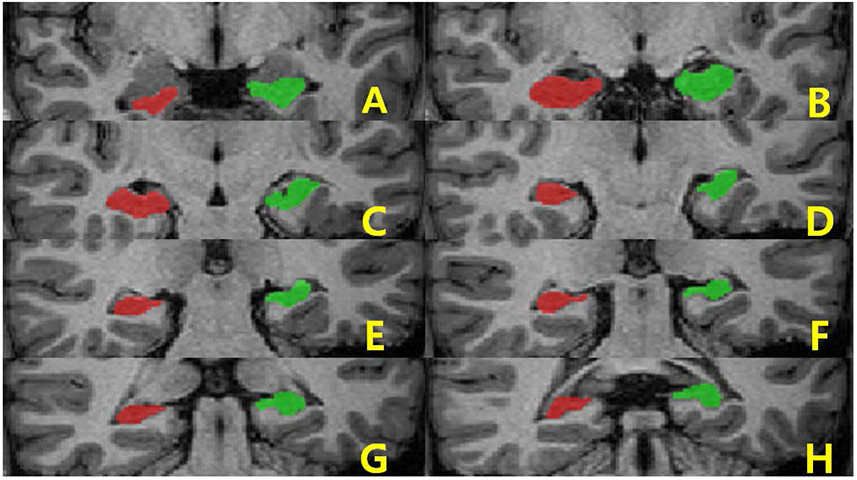
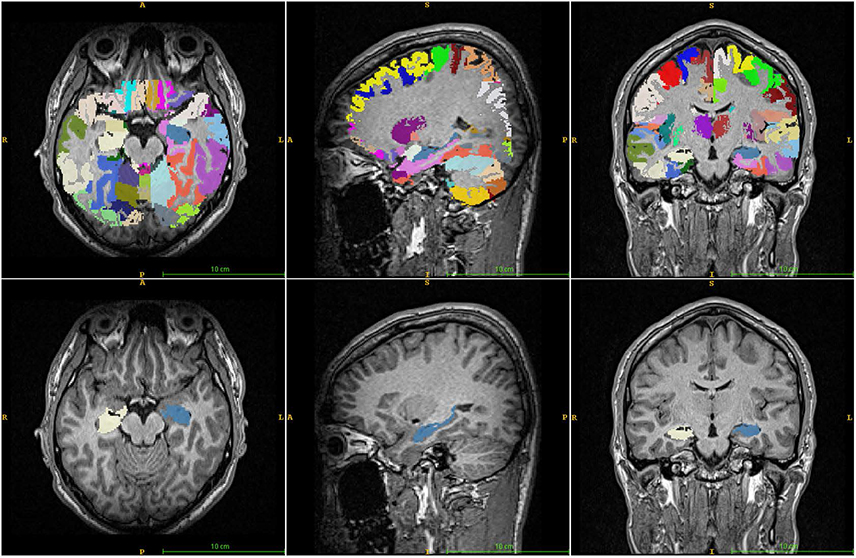
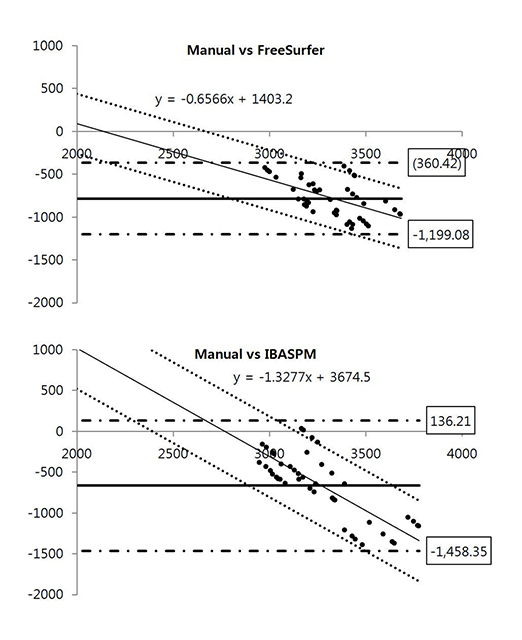
Brain images from 12 normal adults were acquired using magnetization prepared rapid acquisition gradient echo (MPRAGE) with a slice thickness of 1.3 mm and TI of 800, 900, 1000, and 1100 ms. Hippocampal volumes were measured using FreeSurfer, IBASPM and manual tracing. Statistical differences were examined using correlation analyses accounting for spatial interpretations percent volume overlap and percent volume difference.
RESULTS
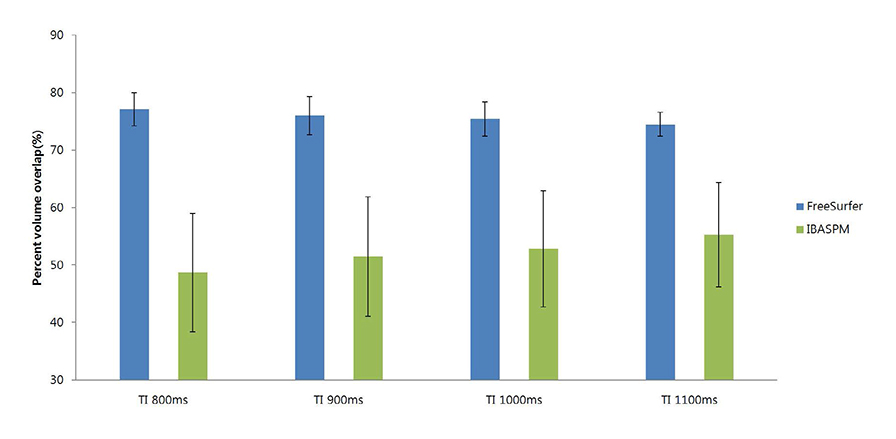
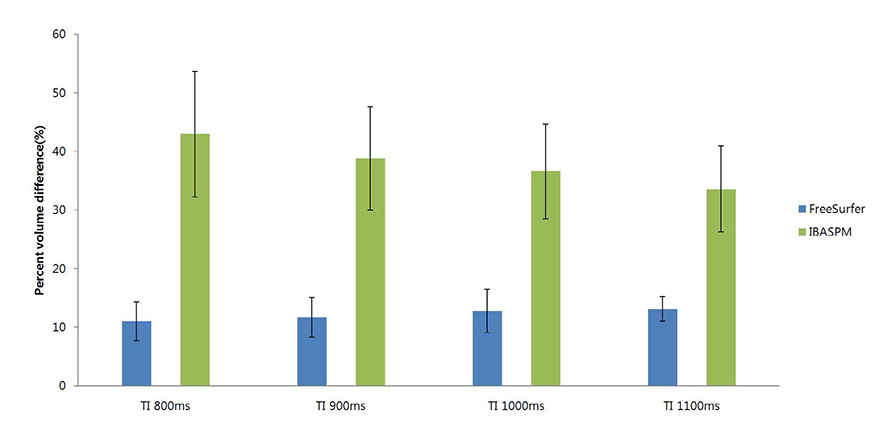
FreeSurfer revealed a maximum percent volume overlap and maximum percent volume difference at TI = 800 ms (77.1 +/- 2.9%) and TI = 1100 ms (13.1 +/- 2.1%), respectively. The respective values for IBASPM were TI = 1100 ms (55.3 +/- 9.1%) and TI = 800 ms (43.1 +/- 10.7%). FreeSurfer presented a higher correlation than IBASPM but it was not statistically significant.
CONCLUSIONS
FreeSurfer performed better in volumetric determination than IBASPM. Given the subjective nature of manual tracing, automated image acquisition and analysis image is accurate and preferable.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sanchez-Benavides G, Gomez-Anson B, Sainz A, Vives Y, Delfino M, Pena-Casanova J. Manual validation of FreeSurfer's automated hippocampal segmentation in normal aging, mild cognitive impairment, and Alzheimer Disease subjects. Psychiatry Res. 2010; 181:219–225.2. Takao H, Abe O, Ohtomo K. Computational analysis of cerebral cortex. Neuroradiology. 2010; 52:691–698.3. Geuze E, Vermetten E, Bremner JD. MR-based in vivo hippocampal volumetrics: 2. Findings in neuropsychiatric disorders. Mol Psychiatry. 2005; 10:160–184.4. Giedd JN, Vaituzis AC, Hamburger SD, et al. Quantitative MRI of the temporal lobe, amygdala, and hippocampus in normal human development: ages 4-18 years. J Comp Neurol. 1996; 366:223–230.5. Tae WS, Kim SS, Lee KU, Nam EC, Kim KW. Validation of hippocampal volumes measured using a manual method and two automated methods (FreeSurfer and IBASPM) in chronic major depressive disorder. Neuroradiology. 2008; 50:569–581.6. Petersen RC, Doody R, Kurz A, et al. Current concepts in mild cognitive impairment. Arch Neurol. 2001; 58:1985–1992.7. Chupin M, Chetelat G, Lemieux L, et al. Fully automatic hippocampus segmentation discriminates between early alzheimer's disease and normal aging. In : Biomedical imaging from nano to macro: 5th IEEE International Symposium; 2008. p. 97–100.8. Dickerson BC, Goncharova I, Sullivan MP, et al. MRI-derived entorhinal and hippocampal atrophy in incipient and very mild Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2001; 22:747–775.9. Pedraza O, Bowers D, Gilmore R. Asymmetry of the hippocampus and amygdala in MRI volumetric measurements of normal adults. J Int Neuropsychol Soc. 2004; 10:664–678.10. Hammers A, Heckemann R, Koepp MJ, et al. Automatic detection and quantification of hippocampal atrophy on MRI in temporal lobe epilepsy: a proof-of-principle study. Neuroimage. 2007; 36:38–47.11. Brewer JB. Fully-automated volumetric MRI with normative ranges: translation to clinical practice. Behav Neurol. 2009; 21:21–28.12. Jung WB, Kang MJ, Son DB, et al. Reproducibility analysis of brain volumetry measured from inter MR scanner of multi-Institute. J Korean Soc Magn Reson Med. 2012; 16:243–252.13. Nelson F, Poonawalla A, Hou P, Wolinsky JS, Narayana PA. 3D MPRAGE improves classification of cortical lesions in multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler. 2008; 14:1214–1219.14. van der Kouwe AJ, Benner T, Salat DH, Fischl B. Brain morphometry with multiecho MPRAGE. Neuroimage. 2008; 40:559–569.15. Kim HD, Chang KH, Han MH, Kim HJ, Lee SG, Lee MC. The significance and limitation of MR volumetry: comparison between normal adults and the patients with epilepsy and hippocampal sclerosis. J Korean Soc Magn Reson Med. 2002; 6:47–54.16. Choi N, Nam Y, Kim DH. Cortical thickness estimation using DIR imaging with GRAPPA factor 2. J Korean Soc Magn Reson Med. 2010; 14:56–63.17. Kim JH, Kim SH, Choi DS. A study of changes of inversion time effect on brain volume of normal volunteers. J Korean Soc Magn Reson Med. 2013; 17:286–293.18. Morey RA, Petty CM, Xu Y, et al. A comparison of automated segmentation and manual tracing for quantifying hippocampal and amygdala volumes. Neuroimage. 2009; 45:855–866.19. Khan AR, Wang L, Beg MF. FreeSurfer-initiated fully-automated subcortical brain segmentation in MRI using Large Deformation Diffeomorphic Metric Mapping. Neuroimage. 2008; 41:735–746.20. Fischl B. FreeSurfer. Neuroimage. 2012; 62:774–781.21. Jenkinson M, Beckmann CF, Behrens TE, Woolrich MW, Smith SM. Fsl. Neuroimage. 2012; 62:782–790.22. Alemán-Gómez Y, Melie-García L, Valdés-Hernandez P. IBASPM: toolbox for automatic parcellation of brain structures. In : Presented at the 12th Annual Meeting of the organization for human brain mapping; June 2006; Florence, Italy. Available on CD-Rom in neuroImage, vol.27, no. 1.23. Watson C, Andermann F, Gloor P, et al. Anatomic basis of amygdaloid and hippocampal volume measurement by magnetic resonance imaging. Neurology. 1992; 42:1743–1750.24. Hasboun D, Chantome M, Zouaoui A, et al. MR determination of hippocampal volume: comparison of three methods. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1996; 17:1091–1098.25. Jack CR Jr, Theodore WH, Cook M, McCarthy G. MRI-based hippocampal volumetrics: data acquisition, normal ranges, and optimal protocol. Magn Reson Imaging. 1995; 13:1057–1064.26. Yushkevich PA, Piven J, Hazlett HC, et al. User-guided 3D active contour segmentation of anatomical structures: significantly improved efficiency and reliability. Neuroimage. 2006; 31:1116–1128.27. Fischl B, Salat DH, Busa E, et al. Whole brain segmentation: automated labeling of neuroanatomical structures in the human brain. Neuron. 2002; 33:341–355.28. Tzourio-Mazoyer N, Landeau B, Papathanassiou D, et al. Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. Neuroimage. 2002; 15:273–289.29. Jung WB, Son DB, Kim YJ, Kim YH, Eun CK, Mun CW. A comparison study on human brain volume of white matter, gray matter and hippocampus depending on magnetic resonance imaging conditions and applied brain template. J Korean Soc Magn Reson Med. 2011; 15:242–250.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Inter-observer and intra-observer reliability between manual segmentation and semi-automated segmentation for carotid vessel wall volume measurements on three-dimensional ultrasonography
- Feasibility of Commercially Available, Fully Automated Hepatic CT Volumetry for Assessing Both Total and Territorial Liver Volumes in Liver Transplantation
- Comparative accuracy of artificial intelligence-based AudaxCeph software, Dolphin software, and the manual technique for orthodontic landmark identification and tracing of lateral cephalograms
- Effects of Various Intracranial Volume Measurements on Hippocampal Volumetry and Modulated Voxel-based Morphometry
- Automated Segmentation of Left Ventricular Myocardium on Cardiac Computed Tomography Using Deep Learning