J Breast Cancer.
2008 Mar;11(1):30-35. 10.4048/jbc.2008.11.1.30.
Is US-guided 14-gauge Core Needle Biopsy Valid for Papillary Neoplasm of the Breast?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of 1Radiology, The Catholic University of Korea, College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jheerad@gmail.com
- 2Human Medical Imaging and Intervention Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, The Catholic University of Korea, College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Surgery, The Catholic University of Korea, College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2175045
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2008.11.1.30
Abstract
-
PURPOSE: We wanted to determine the underestimation rate of ultrasound (US)-guided 14-gauge core needle biopsy for papillary neoplasms that were treated with subsequent surgical excision or vacuum-assisted biopsy (VAB) and we also wanted to evaluate the sonographic findings of papillary neoplasms.
METHODS
A retrospective review of the US-guided core needle biopsies of 984 consecutive lesions from January 2004 to April 2006 revealed 29 (3%) papillary neoplasms. Twenty five lesions were further excised by surgery (n=16) or VAB (n=9). The remaining 4 lesions were not further excised and they were excluded from this study. We evaluated the concordance between results of core needle biopsy and the final pathologic results. We reevaluate the sonographic findings of the papillary neoplasms included in our study.
RESULTS
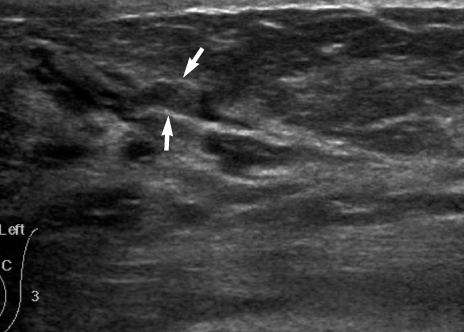
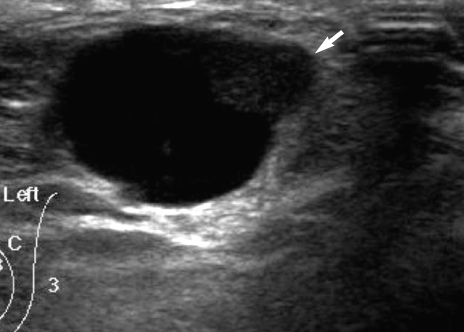
The pathologic results of core needle biopsy were benign in 21 and atypical in four. Of the 21 benign papillomas, none were revealed as carcinoma after further excision. Just one lesion showed focal atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH) after VAB. Three intraductal papillomas with ADH underwent surgical excision (n=3) or VAB (n=1), and they were proved to be the same pathologic entities with (n=1) or without (n=3) lobular neoplasia. The sonographic findings were as follows: four intraductal masses, four intracystic masses, four solid masses with peripheral anechoic rims, five extraductal masses adjacent to dilated ducts, six pure solid masses, and two mixed masses.
CONCLUSION
US-guide 14-gauge core needle biopsy for papillary neoplasm showed no underestimation after surgical excision or VAB in our study, and the procedure proved to be reliable for the assessment of papillary neoplasm if the imaging and pathologic findings were concordant. Papillary neoplasms showed variable sonographic findings.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Tavassoli FA. Tavassoli FA, editor. Papillary lesions. Pathology of the breast. 1992. Norwalk Conn: Appleton & Lange;193–227.2. Jacobs TW, Connolly JL, Schnitt SJ. Nonmalignant lesions in breast core needle biopsies: to excise or not to excise? Am J Surg Pathol. 2002. 26:1095–1110.3. Ivan D, Selinko V, Sahin AA, Sneige N, Middleton LP. Accuracy of core needle biopsy diagnosis in assessing papillary breast lesions: histologic predictors of malignancy. Mod Pathol. 2004. 17:165–171.
Article4. Page DL, Salhany KE, Jensen RA, Dupont WD. Subsequent breast carcinoma risk after biopsy with atypia in a breast papilloma. Cancer. 1996. 78:258–266.
Article5. Liberman L, Bracero N, Vuolo MA, Dershaw DD, Morris EA, Abramson AF, et al. Percutaneous large-core biopsy of papillary breast lesions. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1999. 172:331–337.
Article6. Mercado CL, Hamele-Bena D, Oken SM, Singer CI, Cangiarella J. Papillary lesions of the breast at percutaneous core-needle biopsy. Radiology. 2006. 238:801–808.
Article7. Rosen EL, Bentley RC, Baker JA, Soo MS. Imaging-guided core needle biopsy of papillary lesions of the breast. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002. 179:1185–1192.
Article8. Agoff SN, Lawton TJ. Papillary lesions of the breast with and without atypical ductal hyperplasia: can we accurately predict benign behavior from core needle biopsy? Am J Clin Pathol. 2004. 122:440–443.
Article9. Ko ES, Cho N, Cha JH, Park JS, Kim SM, Moon WK. Sonographically-guided 14-gauge core needle biopsy for papillary lesions of the breast. Korean J Radiol. 2007. 8:206–211.
Article10. Liberman L, Tornos C, Huzjan R, Bartella L, Morris EA, Dershaw DD. Is surgical excision warranted after benign, concordant diagnosis of papilloma at percutaneous breast biopsy? AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006. 186:1328–1334.
Article11. Lim JY, Oh SM. Usufulness of ultrasound guided core needle biopsy of breast lesions with automated gun. J Korean Breast Cancer Soc. 1998. 1:186–191.
Article12. Lam WW, Chu WC, Tang AP, Tse G, Ma TK. Role of radiologic features in the management of papillary lesions of the breast. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006. 186:1322–1327.
Article13. Philpotts LE, Shaheen NA, Jain KS, Carter D, Lee CH. Uncommon high-risk lesions of the breast diagnosed at stereotactic core-needle biopsy: clinical importance. Radiology. 2000. 216:831–837.
Article14. Puglisi F, Zuiani C, Bazzocchi M, Valent F, Aprile G, Pertoldi B, et al. Role of mammography, ultrasound and large core biopsy in the diagnostic evaluation of papillary breast lesions. Oncology. 2003. 65:311–315.
Article15. Burbank F. Stereotactic breast biopsy of atypical ductal hyperplasia and ductal carcinoma in situ lesions: improved accuracy with directional, vacuum-assisted biopsy. Radiology. 1997. 202:843–847.
Article16. American College of Radiology. Breast imaging reporting and data system (BI-RADS). 2003. 4th ed. Reston, VA:17. Han BK, Choe YH, Ko YH, Yang JH, Nam SJ. Benign papillary lesions of the breast: sonographic-pathologic correlation. J Ultrasound Med. 1999. 18:217–223.
Article18. Ko ES, Cho N, Yang SK, Kim DY, Moon WK. Papillary lesions of the breast: Comparison of the US-guided 14-gauge automated gun method and the 11-gause directional vacuum-assisted biopsy method. J Korean Radiol Soc. 2006. 54:537–541.
Article19. Mercado CL, Hamele-Bena D, Singer C, Koenigsberg T, Pile-Spellman E, Higgins H, et al. Papillary lesions of the breast: evaluation with stereotactic directional vacuum-assisted biopsy. Radiology. 2001. 221:650–655.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Track Seeding in a Breast Cancer Patient after a 14-Gauge Core Needle Biopsy: A Case Report
- Clinicopathologic Features of the Papillary Breast Lesions Diagnosed on Ultrasonography-guided Core Needle Biopsy
- Sonographically-Guided 14-Gauge Core Needle Biopsy for Papillary Lesions of the Breast
- Pseudoaneurysm of the Breast after Core Needle Biopsy: A Case Report
- Usefulness of Ultrasound-Guided Automated Core Biopsy of Nonpalpable Breast Lesions