Diabetes Metab J.
2014 Feb;38(1):51-57. 10.4093/dmj.2014.38.1.51.
Higher Prevalence and Awareness, but Lower Control Rate of Hypertension in Patients with Diabetes than General Population: The Fifth Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey in 2011
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. bycha@catholic.ac.kr
- 2Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- 3Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Anyang, Korea.
- 6Department of Internal Medicine, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 7Department of Internal Medicine, Mitochondrial Research Group, Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 8Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea.
- 9Department of Biostatistics, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 10Department of Preventive Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. markYMpark@gmail.com
- 11Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Arnold School of Public Health, University of South Carolina, Columbia, SC, USA.
- KMID: 2174185
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2014.38.1.51
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
We investigated the prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control rate of hypertension in Korean adults with diabetes using nationally representative data.
METHODS
Using data of 5,105 adults from the fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey in 2011 (4,389 nondiabetes mellitus [non-DM]), 242 newly diagnosed with DM (new-DM), and 474 previously diagnosed with DM (known-DM), we analyzed the prevalence of hypertension (mean systolic blood pressure > or =140 mm Hg, diastolic blood pressure > or =90 mm Hg, or use of antihypertensive medication) and control rate of hypertension (blood pressure [BP] <130/80 mm Hg).
RESULTS
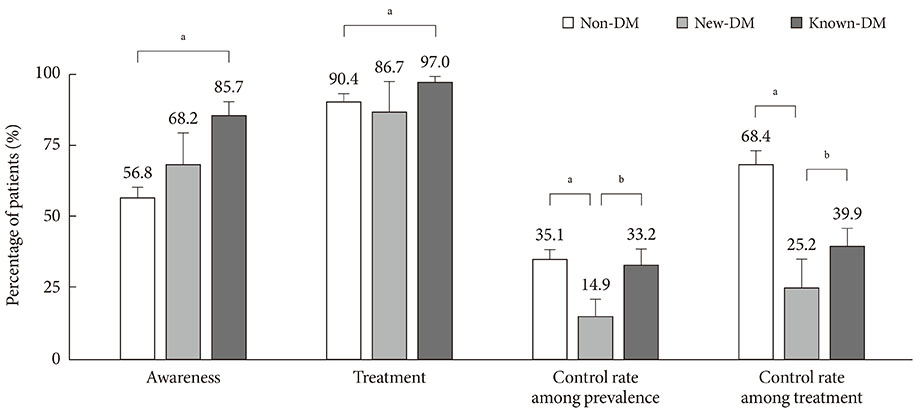
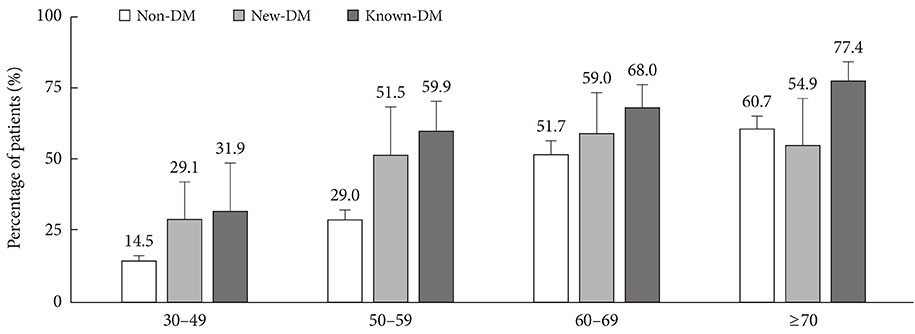
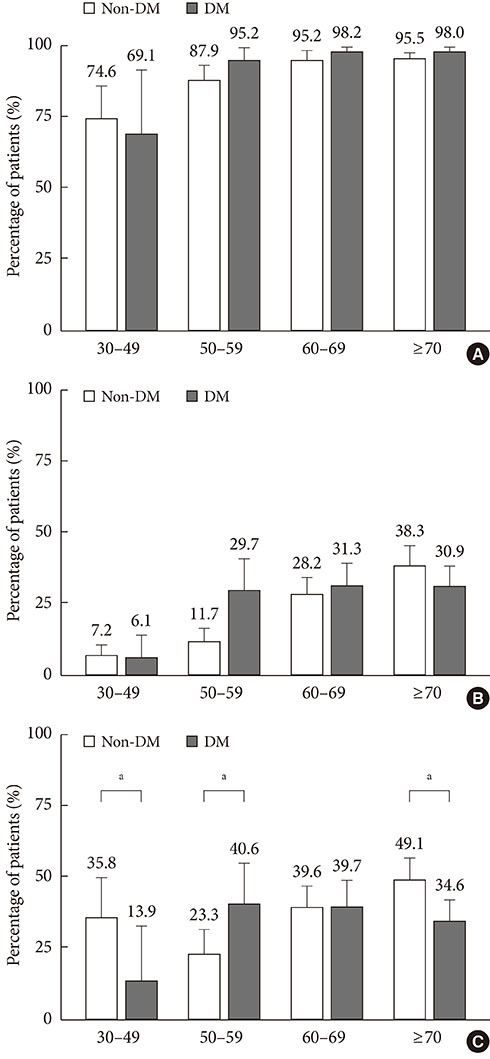
The prevalence of hypertension in diabetic adults was 54.6% (44.4% in new-DM and 62.6% in known-DM, P<0.0001 and P<0.0001, respectively) compared with non-DM adults (26.2%). Compared to non-DM, awareness (85.7%, P<0.001) and treatment (97.0%, P=0.020) rates were higher in known-DM, whereas no differences were found between new-DM and non-DM. Control rate among all hypertensive subjects was lower in new-DM (14.9%), compared to non-DM (35.1%, P<0.001) and known-DM (33.3%, P=0.004). Control rate among treated subjects was also lower in new-DM (25.2%), compared to non-DM (68.4%, P<0.0001) and known-DM (39.9%, P<0.0001).
CONCLUSION
Higher prevalence and low control rate of hypertension in adults with diabetes suggest that stringent efforts are needed to control BP in patients with diabetes, particularly in newly diagnosed diabetic patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Diabetes Fact Sheets in Korea, 2020: An Appraisal of Current Status
Chan-Hee Jung, Jang Won Son, Shinae Kang, Won Jun Kim, Hun-Sung Kim, Hae Soon Kim, Mihae Seo, Hye-Jung Shin, Seong-Su Lee, Su Jin Jeong, Yongin Cho, Seung Jin Han, Hyang Mi Jang, Mira Rho, Shinbi Lee, Mihyun Koo, Been Yoo, Jung-Wha Moon, Hye Young Lee, Jae-Seung Yun, Sun Young Kim, Sung Rae Kim, In-Kyung Jeong, Ji-Oh Mok, Kun Ho Yoon
Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(1):1-10. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2020.0254.Diabetes Fact Sheet in Korea, 2016: An Appraisal of Current Status
Jong Chul Won, Jae Hyuk Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim, Eun Seok Kang, Kyu Chang Won, Dae Jung Kim, Moon-Kyu Lee
Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(5):415-424. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2018.0017.
Reference
-
1. Adler AI, Stratton IM, Neil HA, Yudkin JS, Matthews DR, Cull CA, Wright AD, Turner RC, Holman RR. Association of systolic blood pressure with macrovascular and microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 36): prospective observational study. BMJ. 2000; 321:412–419.2. Stamler J, Vaccaro O, Neaton JD, Wentworth D. Diabetes, other risk factors, and 12-yr cardiovascular mortality for men screened in the Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial. Diabetes Care. 1993; 16:434–444.3. Geiss LS, Rolka DB, Engelgau MM. Elevated blood pressure among U.S. adults with diabetes, 1988-1994. Am J Prev Med. 2002; 22:42–48.4. Hansson L, Zanchetti A, Carruthers SG, Dahlof B, Elmfeldt D, Julius S, Menard J, Rahn KH, Wedel H, Westerling S. HOT Study Group. Effects of intensive blood-pressure lowering and low-dose aspirin in patients with hypertension: principal results of the Hypertension Optimal Treatment (HOT) randomised trial. Lancet. 1998; 351:1755–1762.5. Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation Study Investigators. Effects of ramipril on cardiovascular and microvascular outcomes in people with diabetes mellitus: results of the HOPE study and MICRO-HOPE substudy. Lancet. 2000; 355:253–259.6. American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes: 2007. Diabetes Care. 2007; 30:Suppl 1. S4–S41.7. Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo JL Jr, Jones DW, Materson BJ, Oparil S, Wright JT Jr, Roccella EJ. Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. National High Blood Pressure Education Program Coordinating Committee. Seventh report of the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure. Hypertension. 2003; 42:1206–1252.8. Ko SH, Kim SR, Kim DJ, Oh SJ, Lee HJ, Shim KH, Woo MH, Kim JY, Kim NH, Kim JT, Kim CH, Kim HJ, Jeong IK, Hong EK, Cho JH, Mok JO, Yoon KH. Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines, Korean Diabetes Association. 2011 Clinical practice guidelines for type 2 diabetes in Korea. Diabetes Metab J. 2011; 35:431–436.9. International Diabetes Federation 2005: Global guideline for type 2 diabetes. updated 2013 Nov 21. Available from: http://www.idf.org/.10. Nilsson PM, Cederholm J. Diabetes, hypertension, and outcome studies: overview 2010. Diabetes Care. 2011; 34:Suppl 2. S109–S113.11. American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes: 2013. Diabetes Care. 2013; 36:Suppl 1. S11–S66.12. Cooper-DeHoff RM, Gong Y, Handberg EM, Bavry AA, Denardo SJ, Bakris GL, Pepine CJ. Tight blood pressure control and cardiovascular outcomes among hypertensive patients with diabetes and coronary artery disease. JAMA. 2010; 304:61–68.13. Gunarathne A, Patel JV, Gammon B, Gill PS, Hughes EA, Lip GY. Ischemic stroke in South Asians: a review of the epidemiology, pathophysiology, and ethnicity-related clinical features. Stroke. 2009; 40:e415–e423.14. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (KCDC): Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. updated 2013 Nov 21. Available from: http://knhanes.cdc.go.kr/.15. Ko SH, Kwon HS, Song KH, Ahn YB, Yoon KH, Yim HW, Lee WC, Park YM. Long-term changes of the prevalence and control rate of hypertension among Korean adults with diagnosed diabetes: 1998-2008 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2012; 97:151–157.16. Jeon JY, Ko SH, Kwon HS, Kim NH, Kim JH, Kim CS, Song KH, Won JC, Lim S, Choi SH, Jang MJ, Kim Y, Oh K, Kim DJ, Cha BY;. Prevalence of diabetes and prediabetes according to fasting plasma glucose and HbA1c. Diabetes Metab J. 2013; 37:349–357.17. McAlister FA, Wilkins K, Joffres M, Leenen FH, Fodor G, Gee M, Tremblay MS, Walker R, Johansen H, Campbell N. Changes in the rates of awareness, treatment and control of hypertension in Canada over the past two decades. CMAJ. 2011; 183:1007–1013.18. Wang J, Geiss LS, Cheng YJ, Imperatore G, Saydah SH, James C, Gregg EW. Long-term and recent progress in blood pressure levels among U.S. adults with diagnosed diabetes, 1988-2008. Diabetes Care. 2011; 34:1579–1581.19. The Statistics Korea. updated 2013 Nov 21. Available from: http://kostat.go.kr/.20. American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2010; 33:Suppl 1. S62–S69.21. Maahs DM, Kinney GL, Wadwa P, Snell-Bergeon JK, Dabelea D, Hokanson J, Ehrlich J, Garg S, Eckel RH, Rewers MJ. Hypertension prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control in an adult type 1 diabetes population and a comparable general population. Diabetes Care. 2005; 28:301–306.22. Suh DC, Kim CM, Choi IS, Plauschinat CA, Barone JA. Trends in blood pressure control and treatment among type 2 diabetes with comorbid hypertension in the United States: 1988-2004. J Hypertens. 2009; 27:1908–1916.23. Campbell NR, Gilbert RE, Leiter LA, Larochelle P, Tobe S, Chockalingam A, Ward R, Morris D, Tsuyuki RT, Harris SB. Hypertension in people with type 2 diabetes: update on pharmacologic management. Can Fam Physician. 2011; 57:997–1002.24. Brown MJ, Castaigne A, de Leeuw PW, Mancia G, Palmer CR, Rosenthal T, Ruilope LM. Influence of diabetes and type of hypertension on response to antihypertensive treatment. Hypertension. 2000; 35:1038–1042.25. Pop-Busui R. Cardiac autonomic neuropathy in diabetes: a clinical perspective. Diabetes Care. 2010; 33:434–441.26. Ozawa M, Tamura K, Iwatsubo K, Matsushita K, Sakai M, Tsurumi-Ikeya Y, Azuma K, Shigenaga A, Okano Y, Masuda S, Wakui H, Ishigami T, Umemura S. Ambulatory blood pressure variability is increased in diabetic hypertensives. Clin Exp Hypertens. 2008; 30:213–224.27. Grossman E, Messerli FH. Management of blood pressure in patients with diabetes. Am J Hypertens. 2011; 24:863–875.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Trend Analysis of the Prevalence, Awareness, Treatment, and Control of Hypertension by Age Group
- Trends in the prevalence and management of major metabolic risk factors for chronic disease over 20 years: findings from the 1998-2018 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Changes in the management of hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and hypercholesterolemia in Korean adults before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: data from the 2010-2020 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Comparison of Health Status in Primary Care Underserved Area Residents and the General Population in Korea
- The Association between the Local Safety Level Index and Cardiovascular Risk Factors: The Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2016–2018