Ann Dermatol.
2011 Dec;23(Suppl 3):S371-S374. 10.5021/ad.2011.23.S3.S371.
Aquagenic Urticaria: A Report of Two Cases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea. ph7163@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Dermatology, College of Medicine, Hallym University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2171875
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2011.23.S3.S371
Abstract
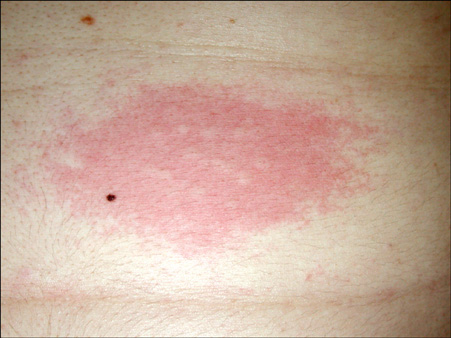
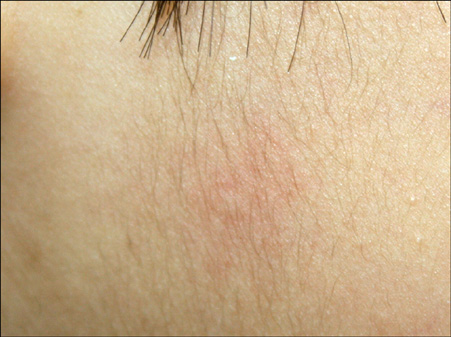
- Aquagenic urticaria is a rare form of physical urticaria, in which contact with water evokes wheals. A 19-year-old man and a 4-year-old boy complained of recurrent episodes of urticaria. Urticaria appeared while taking a bath or a shower, in the rain, or in a swimming pool. Well-defined pin head to small pea-sized wheals surrounded by variable sized erythema were provoked by contact with water on the face, neck, and trunk, regardless of its temperature or source. Results from a physical examination and a baseline laboratory evaluation were within normal limits. Treatment of the 19-year-old man with 180 mg fexofenadine daily was successful to prevent the wheals and erythema. Treatment with 5 ml ketotifen syrup bid per day resulted in improvement of symptoms in the 4-year-old boy.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Aquagenic Urticaria Diagnosed by the Water Provocation Test and the Results of Histopathologic Examination
Jung Eun Seol, Do Hyeong Kim, So Hee Park, Jeong Nan Kang, Ho Suk Sung, Hyojin Kim
Ann Dermatol. 2017;29(3):341-345. doi: 10.5021/ad.2017.29.3.341.
Reference
-
1. Shelley WB, Rawnsley HM. Aquagenic urticaria. Contact sensitivity reaction to water. JAMA. 1964. 189:895–898.2. Dice JP. Physical urticaria. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2004. 24:225–246.
Article3. Treudler R, Tebbe B, Steinhoff M, Orfanos CE. Familial aquagenic urticaria associated with familial lactose intolerance. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002. 47:611–613.
Article4. Fearfield LA, Gazzard B, Bunker CB. Aquagenic urticaria and human immunodeficiency virus infection: treatment with stanozolol. Br J Dermatol. 1997. 137:620–622.
Article5. Pitarch G, Torrijos A, Martínez-Menchón T, Sánchez-Carazo JL, Fortea JM. Familial aquagenic urticaria and bernard-soulier syndrome. Dermatology. 2006. 212:96–97.
Article6. Czarnetzki BM, Breetholt KH, Traupe H. Evidence that water acts as a carrier for an epidermal antigen in aquagenic urticaria. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1986. 15:623–627.
Article7. Baptist AP, Baldwin JL. Aquagenic urticaria with extracutaneous manifestations. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2005. 26:217–220.8. Luong KV, Nguyen LT. Aquagenic urticaria: report of a case and review of the literature. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1998. 80:483–485.
Article9. Panconesi E, Lotti T. Aquagenic urticaria. Clin Dermatol. 1987. 5:49–51.10. Lee HG, Lee AY, Lee YS. A case of aquagenic urticaria. Korean J Dermatol. 1990. 28:456–458.11. Sibbald RG, Black AK, Eady RA, James M, Greaves MW. Aquagenic urticaria: evidence of cholinergic and histaminergic basis. Br J Dermatol. 1981. 105:297–302.
Article12. Tkach JR. Aquagenic urticaria. Cutis. 1981. 28:454. 463.13. Hide M, Yamamura Y, Sanada S, Yamamoto S. Aquagenic urticaria: a case report. Acta Derm Venereol. 2000. 80:148–149.14. Gallo R, Cacciapuoti M, Cozzani E, Guarrera M. Localized aquagenic urticaria dependent on saline concentration. Contact Dermatitis. 2001. 44:110–111.
Article15. Medeiros M Jr. Aquagenic urticaria. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 1996. 6:63–64.16. Martínez-Escribano JA, Quecedo E, De la Cuadra J, Frías J, Sánchez-Pedreño P, Aliaga A. Treatment of aquagenic urticaria with PUVA and astemizole. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997. 36:118–119.
Article17. Bayle P, Gadroy A, Messer L, Bazex J. Localized aquagenic urticaria: efficacy of a barrier cream. Contact Dermatitis. 2003. 49:160–161.
Article