Infect Chemother.
2010 Jun;42(3):203-207. 10.3947/ic.2010.42.3.203.
Pylephlebitis: Report of a Case Secondary to Appendicitis and Review of Cases Reported in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kimbn@paik.ac.kr
- KMID: 2170312
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2010.42.3.203
Abstract
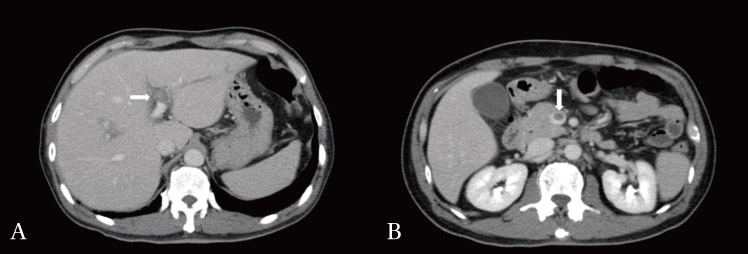
- Pylephlebitis occurs secondary to infection in the region drained by the portal venous system. We described a case of pylephlebitis which developed as a complication of appendicitis and reviewed 22 cases of pylephlebitis, including the current case, reported in Korea. Appendicitis, followed by diverticulitis, was the most common infection associated with pylephlebitis. Fever and abdominal pain were the most common presenting symptoms. Bacteremia was present in 60% of cases. Streptococci, enteric gram-negative bacilli, and Bacteroides fragilis were common organisms isolated from the blood. Liver abscess was identified in 3 cases. All patients survived regardless of anticoagulation therapy. Although pylephlebitis is a rare disease, it should be included in the differential diagnosis in patients with fever of unknown origin who present with nonspecific abdominal symptoms or abnormal liver function test.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Acute Appendicitis Presenting with Escherichia coli Bacteremia without Perforation in a Healthy Male
Seung Jin Lim, Kwon-Oh Park, Jin-Gu Kang, Jin-Seo Lee, Joong-Sik Eom
Infect Chemother. 2011;43(2):210-212. doi: 10.3947/ic.2011.43.2.210.A Case of Pylephlebitis with Pseudomonas aeruginosa Sepsis and Liver Abscess Secondary to Diverticulitis
Yoon Gwon Mun, Seong Wan Son, Minah Kim, Insoo Kim, Yong Hee Kim, Il Soon Jung, Byeong Seong Ko
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2016;67(6):327-331. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2016.67.6.327.
Reference
-
1. Plemmons RM, Dooley DP, Longfield RN. Septic thrombophlebitis of the portal vein (pylephlebitis): diagnosis and management in the modern era. Clin Infect Dis. 1995. 21:1114–1120.
Article2. Kasper DL, Sahani D, Misdraji J. Case 25-2005 - A 40-year-old man with prolonged fever and weight loss. N Engl J Med. 2005. 353:713–722.3. Balthazar EJ, Gollapudi P. Septic thrombophlebitis of the mesenteric and portal veins: CT imaging. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2000. 24:755–760.
Article4. Witte CL, Brewer ML, Witte MH, Pond GB. Protean manifestations of pylethrombosis. A review of thirty-four patients. Ann Surg. 1985. 202:191–202.5. Baril N, Wren S, Radin R, Ralls P, Stain S. The role of anticoagulation in pylephlebitis. Am J Surg. 1996. 172:449–452.
Article6. Lim HE, Cheong HJ, Woo HJ, Kim WJ, Kim MJ, Lee CH, Park SC. Pylephlebitis associated with appendicitis. Korean J Intern Med. 1999. 14:73–76.
Article7. Lee JS, Hong CK, Kim KC, Hong SP, Hwang SG, Park PW, Rim KS, Kim JW, Kim HJ. A case of portal and mesenteric venous gas and thrombosis in sigmoid diverticulitis. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2000. 36:408–412.8. Kim JK, Hong SN, Yang BR, Park JH, Moung BH, Shin JH, Kim SJ, Shin DH. A case of septic portal vein thrombophlebitis: presenting with fever of unknown origin. Korean J Infect Dis. 2001. 33:346–349.9. Hur H, Sung GY, Lee DS, Kim W, Park IY, Won JM. Pylephlebitis as a complication of acute appendicitis. J Korean Surg Soc. 2003. 64:180–183.10. Shin DH, Park JH, Yoon KW, Shin JH, Kim SJ. Clostridium perfringens septicemia with thrombophlebitis of the portal vein. J Infect. 2003. 46:253–255.
Article11. Lee IK, Kim SA, Lee YS, Oh ST, Jeon HM, Kim EK, Chang SK, Jung SE. Thrombophlebitis of the inferior mesenteric vein. J Korean Soc Coloproctol. 2005. 21:329–332.12. Kim TD, Kim TN, Oh HJ, Kim JH, Lee HJ, Park WK, Jang JC. Clinical characteristics and radiologic findings of pylephlebitis. Korean J Med. 2005. 69:Suppl3. S798–S806.13. Park MS, Choi JY, Lee SM, Hong SW. Portal pyelophlebitis associated with acute appendicitis. J Korean Surg Soc. 2006. 71:304–307.14. Kim BK, Lee SK. A case of thrombophlebitis in superior mesenteric vein due to appendicitis. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2007. 49:267–269.15. Chang YS, Min SY, Joo SH, Lee SH. Septic thrombophlebitis of the porto-mesenteric veins as a complication of acute appendicitis. World J Gastroenterol. 2008. 14:4580–4582.
Article16. Kim SH, Hong ES, Kim WY, Ahn R, Hong JS. Acute appendicitis with superior mesenteric vein thrombosis and portal vein thrombosis. J Korean Soc Emerg Med. 2008. 19:142–146.17. Ku BH, Kim YS, Kim JH, Choi YK, Yeon JW, Lee SG, Kim SY. A case of pylephlebitis with Streptococcus viridans and Bacteroides fragilis bacteremia secondary to diverticulitis. Korean J Med. 2009. 76:622–626.18. Lee BK, Ryu HH. A case of pylephlebitis secondary to cecal diverticulitis. J Emerg Med. 2009. [Epub ahead of print].
Article19. Jung HS, Shim KN, Jung JM, Kang MJ, Na YJ, Jung SA, Yoo K. A case of pylephlebitis of the inferior mesenteric vein and portal vein. Intest Res. 2009. 7:105–109.20. Aguas M, Bastida G, Nos P, Beltran B, Grueso JL, Grueso J. Septic thrombophlebitis of the superior mesenteric vein and multiple liver abscesses in a patient with Crohn's disease at onset. BMC Gastroenterol. 2007. 7:22.
Article21. Nouira K, Bedioui H, Azaiez O, Belhiba H, Messaoud MB, Ksantini R, Jouini M, Menif E. Percutaneous drainage of suppurative pylephlebitis complicating acute pancreatitis. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2007. 30:1242–1244.
Article22. Peters TG, Locke JR, Weight GR. Suppurative pylephlebitis caused by toothpick perforation. South Med J. 1988. 81:414–415.
Article23. Uzun GV, Gusarenko VD, Piskunova NV, Gerasimenko AI, Kurennaia SS. Suppurative pylephlebitis in suppurative cholecystitis and cholangitis. Klin Khir. 1990. 25–27.24. Gelber AC, Schachna L, Mitchell L, Schwartzman G, Hartnell G, Geschwind JF. Behcet's disease complicated by pylephlebitis and hepatic abscesses. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2001. 19:Suppl 24. S59–S61.25. Drabick JJ, Landry FJ. Suppurative pylephlebitis. South Med J. 1991. 84:1396–1398.
Article26. Chau NG, Bhatia S, Raman M. Pylephlebitis and pyogenic liver abscesses: a complication of hemorrhoidal banding. Can J Gastroenterol. 2007. 21:601–603.
Article27. Slovis TL, Haller JO, Cohen HL, Berdon WE, Watts FB Jr. Complicated appendiceal inflammatory disease in children: pylephlebitis and liver abscess. Radiology. 1989. 171:823–825.
Article28. Chirinos JA, Garcia J, Alcaide ML, Toledo G, Baracco GJ, Lichtstein DM. Septic thrombophlebitis: diagnosis and management. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2006. 6:9–14.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pylephlebitis as a Complication of Acute Appendicitis
- Pylephlebitis associated with appendicitis
- A case of pylephlebitis with Streptococcus viridans and Bacteroides fragilis bacteremia secondary to diverticulitis
- A Case of Pylephlebitis with Pseudomonas aeruginosa Sepsis and Liver Abscess Secondary to Diverticulitis
- A Case of Pylephlebitis of the Inferior Mesenteric Vein and Portal Vein