J Bacteriol Virol.
2013 Jun;43(2):120-130. 10.4167/jbv.2013.43.2.120.
The Synergistic Effects of Antimicrobial Peptides on the Growth Inhibition of Salmonella Typhimurium through Imd Pathway in Drosophila Intestine
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Microbiology, Cancer Research Institute, College of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea. jekpark@cnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2168681
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4167/jbv.2013.43.2.120
Abstract
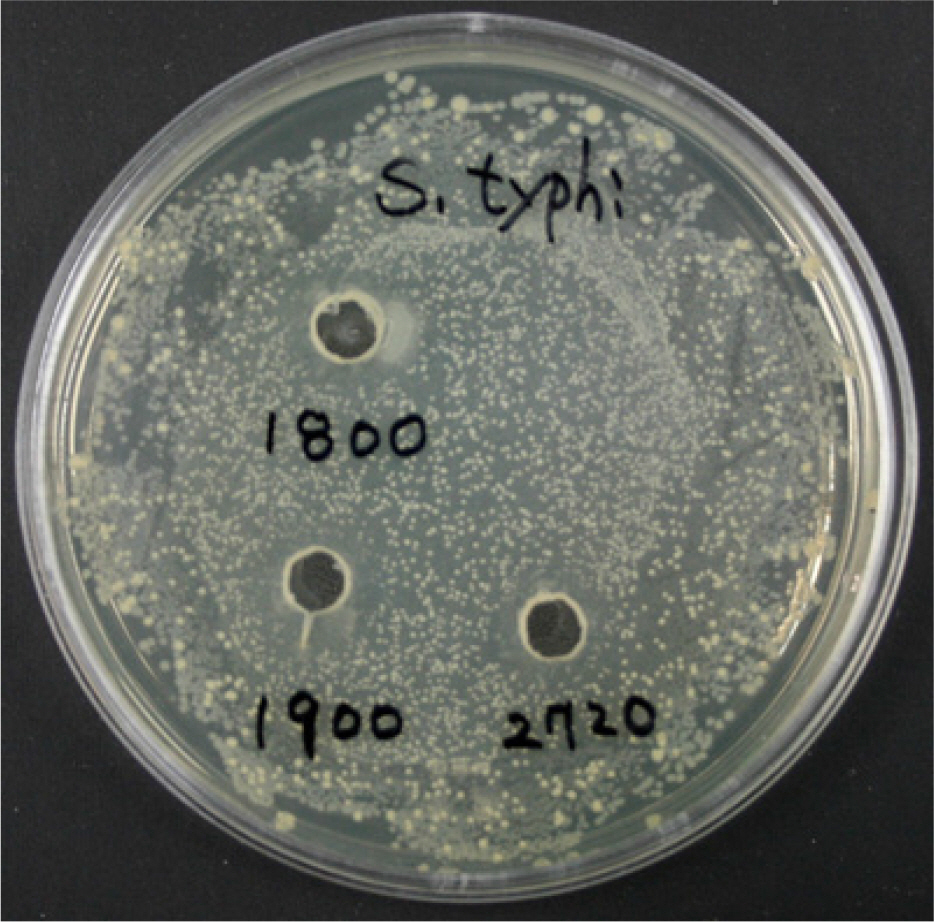
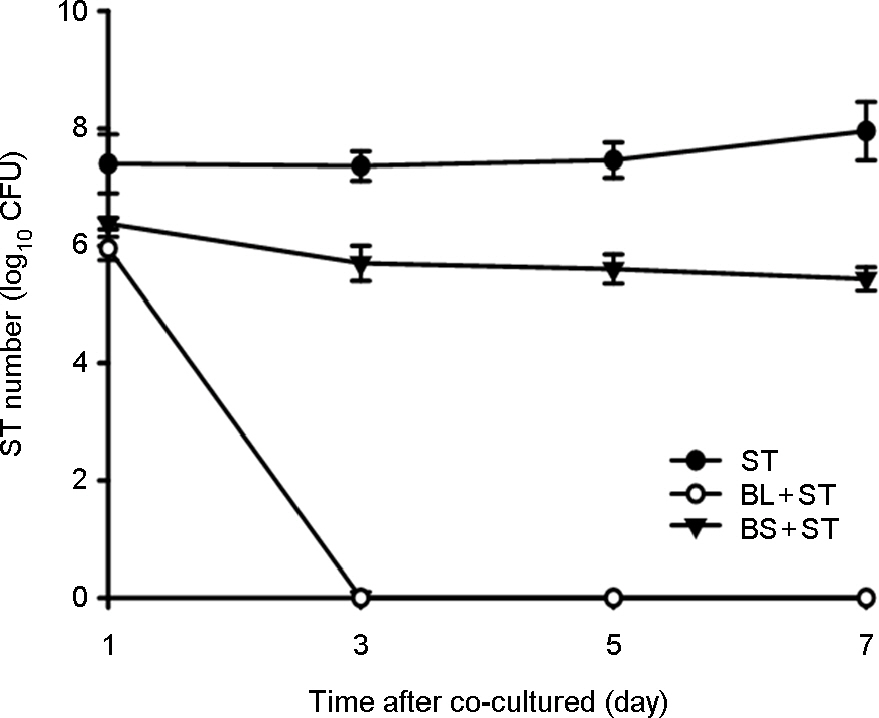
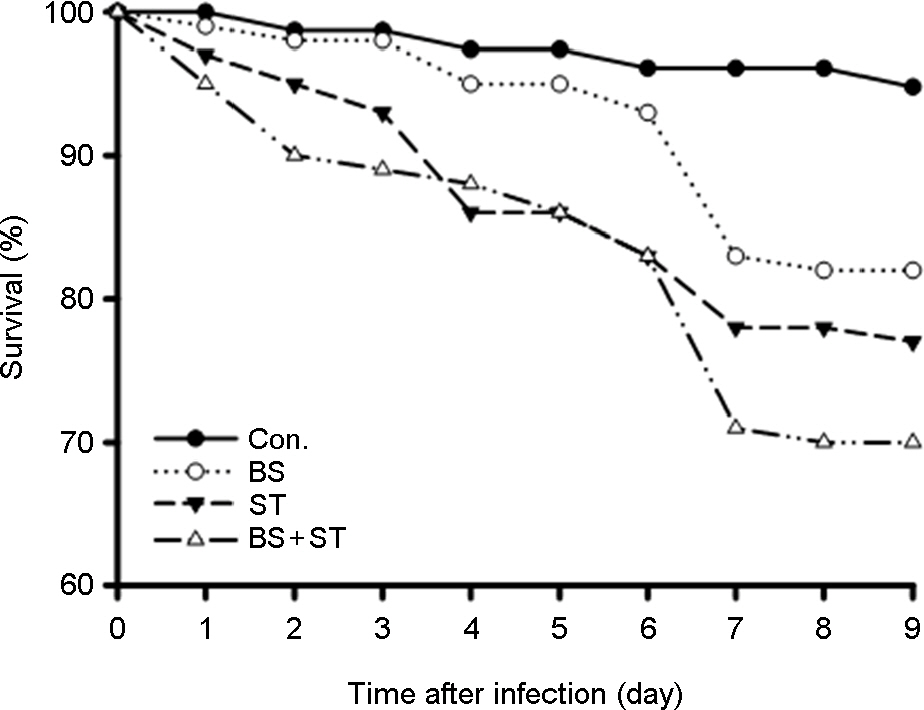
- Some Bacillus species present in fermented foods are regarded as probiotics because of their ability to modulate the prevention of some intestinal infections and the modulation of the inflammatory immune response. We isolated bacteriocin-like substances producing Bacillus subtilis and B. lentus from Cheonggukjang, a traditional Korean fermented soybean paste having an inhibitory effect against Salmonella Typhimurium using a well diffusion inhibition assay and a broth co-culturing method. B. subtilis or B. letus was fed to Drosophila melanogaster alone as well as in combination with Salmonella Typhimurium and survival was monitored daily. The survival rates by oral feeding B. subtilis, B. lentus and Salmonella Typhimurium separately resulted in 85, 90 and 75%, respectively. In contrast, survival rates of co-feeding of B. lentus with Salmonella Typhimurium were increased from 75 to 90% during 7 days post-feeding as compared to Salmonella Typhimurium alone. However, B. subtilis in co-feeding with Salmonella Typhimurium significantly reduced D. melanogaster survival rate (85 to 70%). We found that the immune response to B. lentus and Salmonella Typhimurium is characterized synergistic activation of antimicrobial peptide gene expression by Imd pathway. In conclusion, the in vitro and natural-route infection of the D. melanogaster digestive system can result in the use of the probiotic B. lentus for effective treatment of Salmonella Typhimurium infection. We therefore propose the strain B. lentus as a suitable candidate probiotics for use in the prevention and treatment of the intestinal infections caused by Salmonella Typhimurium.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Antimicrobial Proteins in Intestine and Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
Jung Mogg Kim
Intest Res. 2014;12(1):20-33. doi: 10.5217/ir.2014.12.1.20.
Reference
-
1). Kim S. Salmonella serovars from foodborne and waterborne diseases in Korea, 1998–2007: total isolates decreasing versus rare serovars emerging. J Korean Med Sci. 2010; 25:1693–9.2). Atassi F, Servin AL. Individual and co-operative roles of lactic acid and hydrogen peroxide in the killing activity of enteric strain Lactobacillus johnsonii NCC933 and vaginal strain Lactobacillus gasseri KS120.1 against enteric, uropathogenic and vaginosis-associated pathogens. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2010; 304:29–38.3). Chenoll E, Casinos B, Bataller E, Astals P, Echevarría J, Iglesias JR, et al. Novel probiotic Bifidobacterium bifidum CECT 7366 strain active against the pathogenic bacterium Helicobacter pylori. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011; 77:1335–43.4). Pineiro M, Stanton C. Probiotic bacteria: legislative framework– requirements to evidence basis. J Nutr. 2007; 137:850S–3S.
Article5). Jung JY, Lee SH, Kim JM, Park MS, Bae JW, Hahn Y, et al. Metagenomic analysis of kimchi, a traditional Korean fermented food. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011; 77:2264–74.
Article6). Song YR, Song NE, Kim JH, Nho YC, Baik SH. Exopolysaccharide produced by Bacillus licheniformis strains isolated from Kimchi. J Gen Appl Microbiol. 2011; 57:169–75.7). Kim TW, Lee JH, Park MH, Kim HY. Analysis of bacterial and fungal communities in Japanese- and Chinese-fermented soybean pastes using nested PCR-DGGE. Curr Microbiol. 2010; 60:315–20.
Article8). Kwon GH, Lee HA, Park JY, Kim JS, Lim J, Park CS, et al. Development of a RAPD-PCR method for identification of Bacillus species isolated from Cheonggukjang. Int J Food Microbiol. 2009; 129:282–7.
Article9). Logan NA. Bacillus and relatives in foodborne illness. J Appl Microbiol. 2012; 112:417–29.
Article10). Reva ON, Smirnov VV, Pettersson B, Priest FG. Bacillus endophyticus sp. nov., isolated from the inner tissues of cotton plants (Gossypium sp.). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2002; 52:101–7.11). Hong HA, To E, Fakhry S, Baccigalupi L, Ricca E, Cutting SM. Defining the natural habitat of Bacillus spore-formers. Res Microbiol. 2009; 160:375–9.
Article12). Jones SE, Knight KL. Bacillus subtilis-mediated protection from Citrobacter rodentium-associated enteric disease requires espH and functional flagella. Infect Immun. 2012; 80:710–9.13). Deng W, Dong XF, Tong JM, Zhang Q. The probiotic Bacillus licheniformis ameliorates heat stress-induced impairment of egg production, gut morphology, and intestinal mucosal immunity in laying hens. Poult Sci. 2012; 91:575–82.14). Wolfenden RE, Pumford NR, Morgan MJ, Shivaramaiah S, Wolfenden AD, Pixley CM, et al. Evaluation of selected direct-fed microbial candidates on live performance and Salmonella reduction in commercial turkey brooding houses. Poult Sci. 2011; 90:2627–31.
Article15). Nithya V, Muthukumar SP, Halami PM. Safety assessment of Bacillus licheniformis Me1 isolated from milk for probiotic application. Int J Toxicol. 2012; 31:228–37.16). Sorokulova IB, Pinchuk IV, Denayrolles M, Osipova IG, Huang JM, Cutting SM, et al. The safety of two Bacillus probiotic strains for human use. Dig Dis Sci. 2008; 53:954–63.
Article17). Nagpal R, Kumar A, Kumar M, Behare PV, Jain S, Yadav H. Probiotics, their health benefits and applications for developing healthier foods: a review. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2012; 334:1–15.
Article18). Apidianakis Y, Rahme LG. Drosophila melanogaster as a model for human intestinal infection and pathology. Dis Model Mech. 2011; 4:21–30.19). Charroux B, Royet J. Gut-microbiota interactions in nonmammals: what can we learn from Drosophila? Semin Immunol. 2012; 24:17–24.
Article20). Choi YH, Chung J, Na HS. Molecular methods for studying the human microbiota. J Bacteriol Virol. 2013; 43:67–72.
Article21). Lavermicocca P, Valerio F, Lonigro SL, Di Leo A, Visconti A. Antagonistic activity of potential probiotic Lactobacilli against the ureolytic pathogen Yersinia enterocolitica. Curr Microbiol. 2008; 56:175–81.22). Abriouel H, Franz CM, Ben Omar N, Gálvez A. Diversity and applications of Bacillus bacteriocins. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2011; 35:201–32.23). Kamada N, Kim YG, Sham HP, Vallance BA, Puente JL, Martens EC, et al. Regulated virulence controls the ability of a pathogen to compete with the gut microbiota. Science. 2012; 336:1325–9.
Article24). Bernet-Camard MF, Liévin V, Brassart D, Neeser JR, Servin AL, Hudault S. The human Lactobacillus acidophilus strain LA1 secretes a nonbacteriocin antibacterial substance(s) active in vitro and in vivo. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1997; 63:2747–53.25). van de Guchte M, Ehrlich SD, Maguin E. Production of growth-inhibiting factors by Lactobacillus delbrueckii. J Appl Microbiol. 2001; 91:147–53.26). Cutting SM. Bacillus probiotics. Food Microbiol. 2011; 28:214–20.
Article27). Kreuzer S, Machnowska P, Aßmus J, Sieber M, Pieper R, Schmidt MF, et al. Feeding of the probiotic bacterium Enterococcus faecium NCIMB 10415 differentially affects shedding of enteric viruses in pigs. Vet Res. 2012; 43:58.28). Apidianakis Y, Rahme LG. Drosophila melanogaster as a model for human intestinal infection and pathology. Dis Model Mech. 2011; 4:21–30.29). Frandsen JL, Gunn B, Muratoglu S, Fossett N, Newfeld SJ. Salmonella pathogenesis reveals that BMP signaling regulates blood cell homeostasis and immune responses in Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008; 105:14952–7.
Article30). Liehl P, Blight M, Vodovar N, Boccard F, Lemaitre B. Prevalence of local immune response against oral infection in a Drosophila/Pseudomonas infection model. PLoS Pathog. 2006; 2:e56.
Article31). Nehme NT, Liégeois S, Kele B, Giammarinaro P, Pradel E, Hoffmann JA, et al. A model of bacterial intestinal infections in Drosophila melanogaster. PLoS Pathog. 2007; 3:e173.32). Yuk JM, Jo EK. Toll-like receptors and innate immunity. J Bacteriol Virol. 2011; 41:225–35.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of Artemisia Capillaris Extract on the Growth of Food-Borne Pathogens
- Ultrastructural Study of Crypt Cells in the Ileum of Mouse after Salmonella typhimurium Infection
- Multidrug-resistant Salmonella typhimurium and Salmonella enteritidis Identified by Multiplex PCR in Korea
- Evaluation of antibacterial and therapeutic effects of egg-white lysozyme against Salmonella Typhimurium in ICR mice infected with Salmonella Typhimurium
- Electron microscopic study on the response of the intestinal mucosa and macrophage to invasion of salmonella typhimurium