Allergy Asthma Respir Dis.
2014 Mar;2(1):38-47. 10.4168/aard.2014.2.1.38.
The correlation between allergy sensitization rate in pediatric and aerobiological study for airborne pollen in Busan for 15 years
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Busan St. Mary's Hospital, Busan, Korea. sbdph1@daum.net
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Hanyang University Guri Hospital, Guri, Korea.
- KMID: 2168570
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aard.2014.2.1.38
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Airborne pollen is the most common causative agents of allergic disease. Since 2000, there isn't no more report about airborne pollen in Busan. This study is that pollen in one area of Busan was collected to investigate species, particle counts, seasonal distribution, and of its correlation with reactivity to skin prick test in children during 1998-2012.
METHODS
Rotorod sampler was installed on the rooftop of St. Mary Hospital in Busan. A 24-hour sampling of airborne allergens over a fifteen-year period was conducted 6 days/wk from January 1, 1998 to December 31, 2012. After staining they were identified, counted and recorded with the weather in Busan.
RESULTS
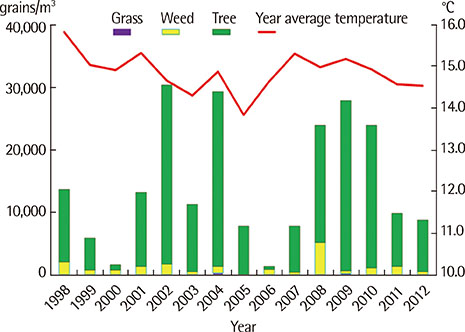
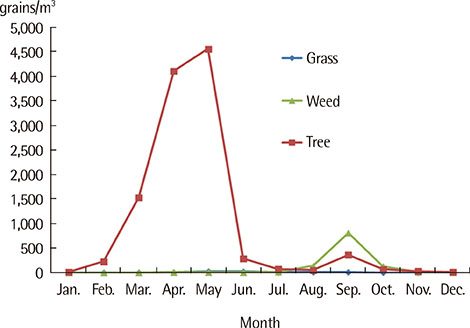
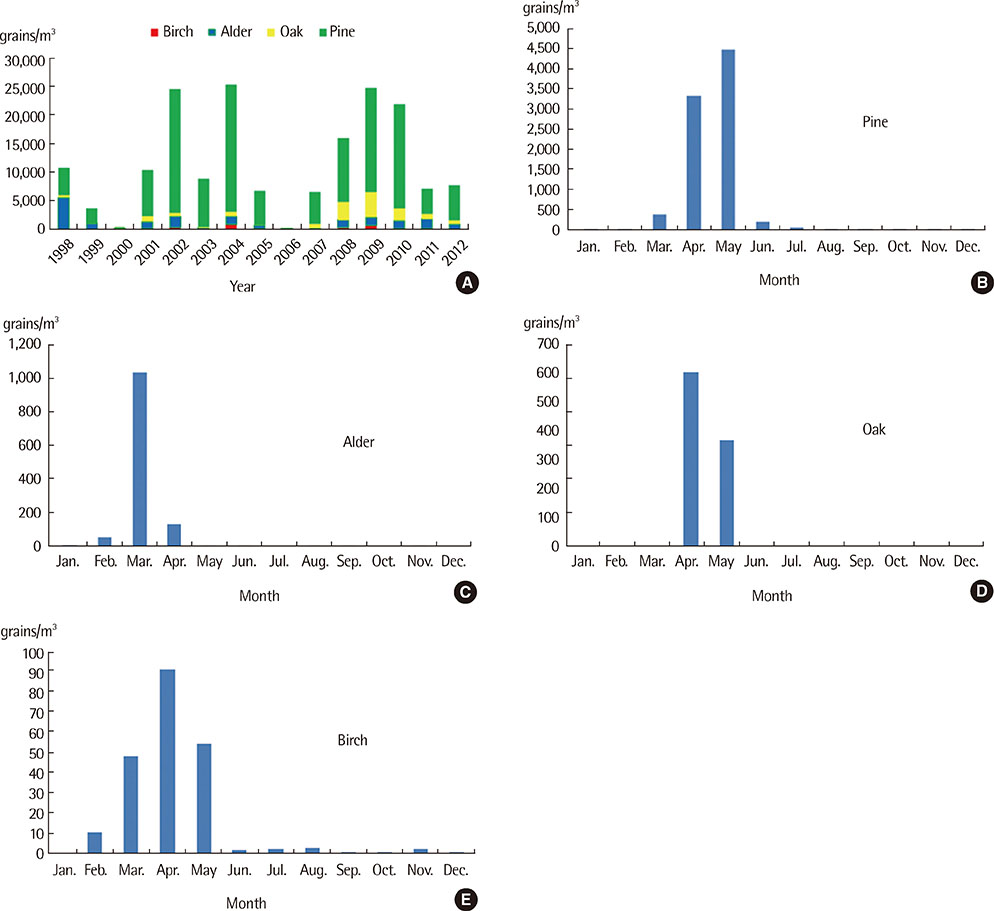
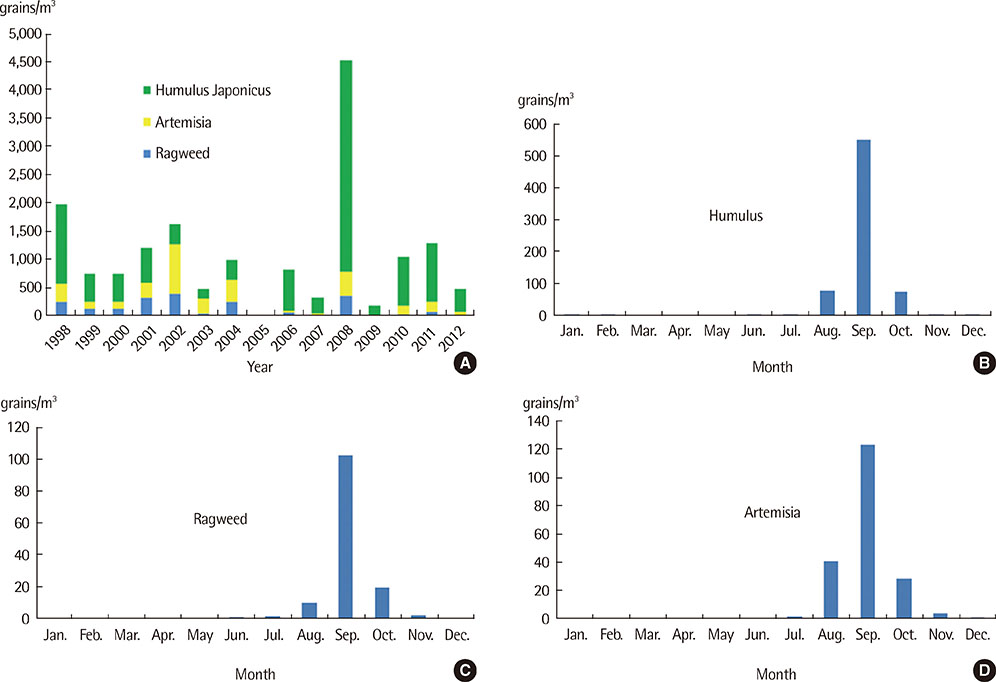
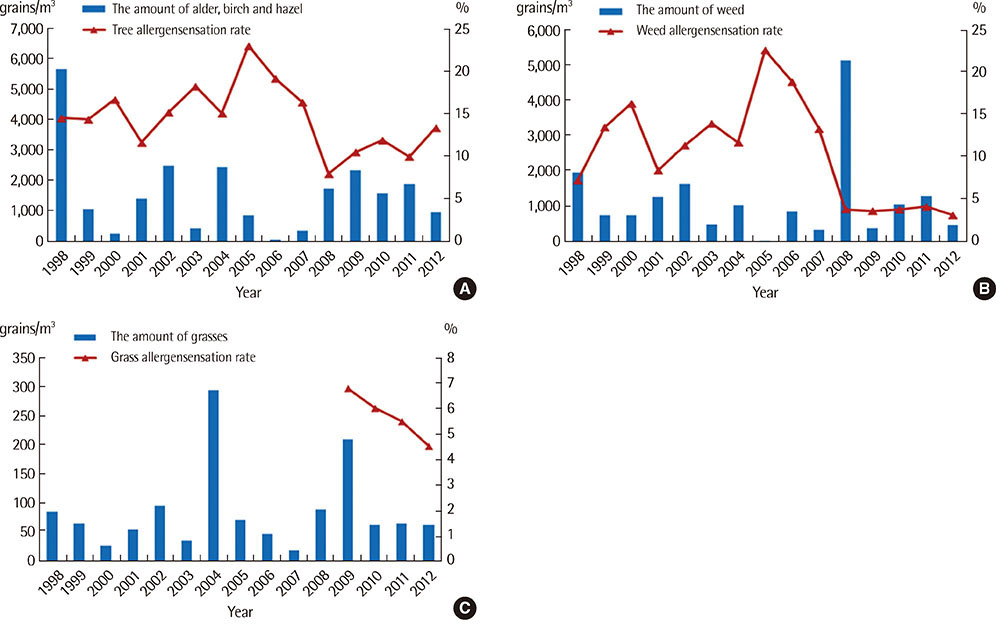
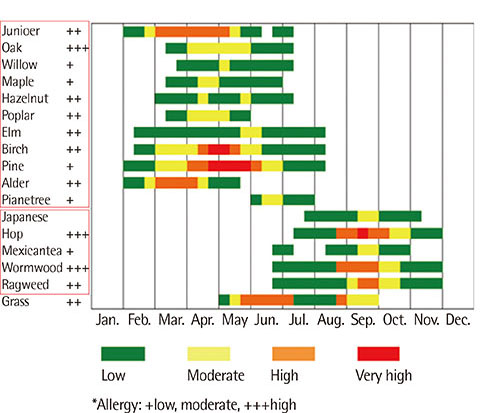
Major pollens collected were Pine, Alder, Oak, Juniperus, Humulus. The pollen season is relatively short and the pollen dispersed mainly during the period from March to May in case of tree pollen, from April to September in case of grass pollen and from August to October in case of weed pollen. Total annual pollen count ranged from 36,412 grains/m3 (2002) to 1,342 grains/m3 (2006). The peak pollen season was seen for spring and autumn, especially in May and September during 1998-2012. In skin prick tests, birch was the highest sensitization rate (15.1%), followed by alder (14.7%), hazel (14.1%) in the tree for 15 years. And in weed, mugwort and ragweed were the highest sensitization rate (10.6%, 10.3%), followed by humulus (5.5%) for 15 years, but since 2008, was increased.
CONCLUSION
Analysis of pollens sampled in the atmosphere of Busan, Korea, for a 15-year period identified 24 species of pollens with seasonal variation of some clinically important pollen load. Analysis of data, it showed that alder and birch are main allergen in spring for 15 years, and in 1998-2008, ragweed and artemisia was main allergen in fall, since 2009, followed by humulus.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
A Six-Year Study on the Changes in Airborne Pollen Counts and Skin Positivity Rates in Korea: 2008–2013
Hye Jung Park, Jae-Hyun Lee, Kyung Hee Park, Kyu Rang Kim, Mae Ja Han, Hosoeng Choe, Jae-Won Oh, Chein-Soo Hong
Yonsei Med J. 2016;57(3):714-720. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.3.714.Tree Pollen Sensitization and Cross-Reaction of Children with Allergic Rhinitis or Asthma
Ye Jin Park, Yoon Ha Hwang
Kosin Med J. 2019;34(2):126-137. doi: 10.7180/kmj.2019.34.2.126.Characteristics of airborne pollen in Incheon and Seoul (2015–2016)
Hye Ju So, Soon Jeong Moon, Seon Yeong Hwang, Jeong Hee Kim, Hae Ji Jang, Jung Heum Jo, Tae Jung Sung, Dae Hyun Lim
Asia Pac Allergy. 2017;7(3):138-147. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2017.7.3.138.
Reference
-
1. Lewis WH, Vinay P, Zenger VE. Airborne and allergenic pollen of North America. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins Univerity Press;1983.2. Nilsson S, Praglowski J, Nisson N. Atlas of airborne pollen grains and spores in nothern Europe. Stockholm: Almqust & Wiksell International;1977.3. Nilsson ST, Spieksm FM. Traveller's allergy service guide. Stockholm: Palynological Laboratory, Swedish Museum of Natural History;1992.4. Min YG. The pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment of allergic rhinitis. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2010; 2:65–76.
Article5. Jung JW, Choi JC, Shin JW, Kim JY, Park IW, Choi BW. Clinical characteristics according to sensitized allergens in adult Korean patients with bronchial asthma. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2010; 2:102–107.
Article6. Taylor G, Walker J, Backley CH. 1820-1900: A detailed description of the astonishing achievement of Backley in describing the causes of hay fever. Clin Allergy. 1973; 3:103–108.7. Anderson JH. Allergenic airborne pollen and spores in Anchorage, Alaska. Ann Allergy. 1985; 54:390–399.8. Buck P, Levetin E. Airborne pollen and mold spores in a subalpine environment. Ann Allergy. 1985; 55:794–801.9. Yasueda H, Yui Y, Shimizu T, Shida T. Isolation and partial characterization of the major allergen from Japanese cedar (Cryptomeria japonica) pollen. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1983; 71(1 Pt 1):77–86.
Article10. Kaufman HS, Ranck K. Antigen recognition in Filipinos, Japanese, Chinese, and Caucasians. Ann Allergy. 1988; 60:53–56.11. Platts-Mills TA, Solomon WR. Aerobiology and inhalant allergens. In : Middletone E, Reed CE, Ellis E, editors. Allergy principles and practice. 4th ed. St. Louis: Mosby;1992. p. 469–528.12. Solomon WR, Weber RW, Dolen WK. Common allergenic pollen and fungi. In : Bierman CW, Pearlman DS, Shapiro GG, Busse WW, editors. Allergy, asthma, and immunology from infancy to adulthood. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders;1996. p. 93–114.13. Kim JH, Oh JW, Lee HB, Kim SW, Kang IJ, Kook MH, et al. Changes in sensitization rate to weed allergens in children with increased weeds pollen counts in Seoul metropolitan area. J Korean Med Sci. 2012; 27:350–355.
Article14. Kim HS, Lee MK, Park HS, Kim HJ, Hong CS. Pollen counts in the air of Seoul during 88 Seoul Olymphics. Allergy. 1989; 9:564–570.15. Park CW, Sim SS, Jung M, Park CH, Ryu HS, Lee YM, et al. Survey of airborn pollens in Mokpo, 1992. Allergy. 1993; 13:342–350.16. Oh JW, Lee HB. Aerobiological study for airborne plooern and mold in Kuri-shi, Kyunggi-do. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 1997; 7:57–68.17. Oh JW, Lee HR, Kim JS, Lee KI, Kang YJ, Kim SW, et al. Aerobiological study of pollen and mold in the 10 states of Korea. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2000; 10:22–33.18. Kim MJ, Cheon KW, Kim SW. Aerobiological study for airborne pollen and mold in Pusan. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2000; 10:119–130.19. Chang NK. Illustrated flora and fauna of Korea Vol. 29 pollens. Seoul: Ministry of Education;1986.20. Lee YS, Lee ST. Plant taxonomy. Seoul: Woo Sung Press;1994.21. Punt W, Hoen PP, Blackmore S, Nilsson S, Le Thomas A. Glossary of pollen and spore terminology. Utrecht: LPP Foundation, Laboratory of Palaeobotany and Palynology, University of Utrecht;1994.22. Nilsson ST, Praglowski J. Erdtman's handbook of palynology. 2nd ed. Copenhagen: Munksgaard;1992.23. Climate Change Information Center [Internet]. Seoul: Korea Meteorological Administration, Climate Change Information Center;2009. 2013 Mar 30. Available from: http://www.climate.go.kr/home/02_information/04_2.html.24. Kim KR, Park KJ, Lee HR, Kim M, Choi YJ, Oh JW. Development and evaluation of the forecast models for daily pollen allergy. Korean J Agric For Meteorol. 2012; 4:265–268.
Article25. Oh JW. Characteristics of allergic pollen and the pollen amount was recently changed in Korea. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 27:1–7.26. Bassett IJ, Crompton CW, Parmelee JA. An atlas of airborne pollen grains and common fungus spores of Canada. Ottawa: Department of Agriculture, Research Branch;1978.27. Solomon WR, Burge HA, Muilenberg ML. Allergen carriage by atmospheric aerosol. I. Ragweed pollen determinants in smaller micronic fractions. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1983; 72(5 Pt 1):443–447.28. Oh JW, Kang IJ, Kim SW, Kook MH, Kim BS, Shin KS, et al. The correlation between increased sensitization rate to weeds in children and the annual increase in weed pollen in Korea. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 2006; 16:114–121.29. Brown HM, Irving KR. The size and weight of common allergenic pollens: an investigation of their number per microgram and size. Acta Allergol. 1973; 28:132–137.30. Oh JW. Characteristics and distribution of airborne pollen and mold. Pediatr Allergy Respir Dis. 1998; 8:1–15.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- An aerobiological perspective in allergy and asthma
- Characteristics and Distribution of Airborne Pollen and Mold
- Pollen Sensitization and Clinical Significance in Childhood
- The Correlation between Increased Sensitization Rate to Weeds in Children and the Annual Increase in Weed Pollen in Korea
- Characteristics of allergic pollens and the recent increase of sensitization rate to weed pollen in childhood in Korea