Hanyang Med Rev.
2014 Nov;34(4):173-180. 10.7599/hmr.2014.34.4.173.
Recent Progress in Clinical Islet Transplantation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kmhyj111@gmail.com
- KMID: 2168349
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7599/hmr.2014.34.4.173
Abstract
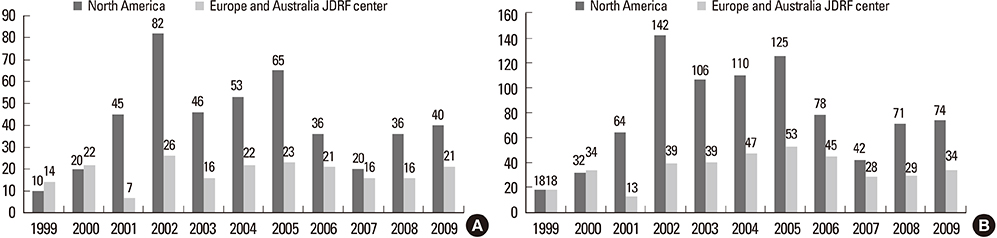
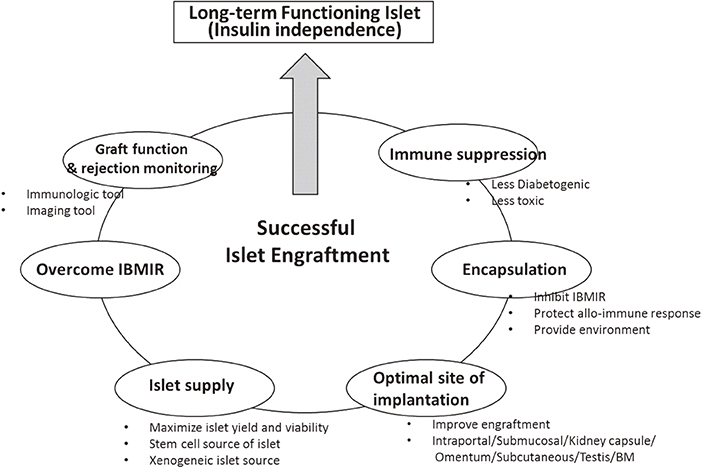
- Allo-islet transplantation is believed to be a promising treatment for normalizing blood glucose levels without hypoglycemic episodes in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). In 2000, a pioneering study by the Edmonton group showed that allo-islet transplantation could achieve insulin independence for at least 1 year post-transplantation in all seven consecutive patients. This breakthrough study excited numerous researchers, clinicians, and patients. Although longer follow-up studies did not have the same success as the first study, substantial efforts to establish successful islet transplantation have been made in the last decade. Several leading centers of islet transplantation have reported success rates of nearly 50% insulin independence at 5 years post-transplantation. However, recent advancements in transplant outcomes are limited to only a few centers and select patients; thus, we are still confronted with numerous hurdles against long-term successful islet transplantation. Herein, we review the recent advances and challenges for allo-islet transplantation to be accepted as a standard therapy for patients with T1DM.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Cutting Edge Technologies in Organ Transplantation
Dongho Choi
Hanyang Med Rev. 2014;34(4):143-144. doi: 10.7599/hmr.2014.34.4.143.
Reference
-
1. The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993; 329:977–986.2. Gruessner RW, Gruessner AC. The current state of pancreas transplantation. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2013; 9:555–562.
Article3. Reckard CR, Ziegler MM, Barker CF. Physiological and immunological consequences of transplanting isolated pancreatic islets. Surgery. 1973; 74:91–99.4. Ballinger WF, Lacy PE. Transplantation of intact pancreatic islets in rats. Surgery. 1972; 72:175–186.5. Lacy PE, Kostianovsky M. Method for the isolation of intact islets of Langerhans from the rat pancreas. Diabetes. 1967; 16:35–39.
Article6. Kemp CB, Knight MJ, Scharp DW, Lacy PE, Ballinger WF. Transplantation of isolated pancreatic islets into the portal vein of diabetic rats. Nature. 1973; 244:447.
Article7. Ricordi C, Lacy PE, Finke EH, Olack BJ, Scharp DW. Automated method for isolation of human pancreatic islets. Diabetes. 1988; 37:413–420.
Article8. Tzakis AG, Ricordi C, Alejandro R, Zeng Y, Fung JJ, Todo S, et al. Pancreatic islet transplantation after upper abdominal exenteration and liver replacement. Lancet. 1990; 336:402–405.
Article9. Bretzel RG, Hering BJ, Schultz AO, Geier C, Federlin K. International islet transplant registry report. Yearbook of Cell and Tissue Transplantation 1996-1997. Springer;1996. p. 153–160.10. Shapiro AM, Lakey JR, Ryan EA, Korbutt GS, Toth E, Warnock GL, et al. Islet transplantation in seven patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus using a glucocorticoid-free immunosuppressive regimen. N Engl J Med. 2000; 343:230–238.
Article11. Ryan EA, Paty BW, Senior PA, Bigam D, Alfadhli E, Kneteman NM, et al. Five-year follow-up after clinical islet transplantation. Diabetes. 2005; 54:2060–2069.
Article12. Shapiro AM, Ricordi C, Hering BJ, Auchincloss H, Lindblad R, Robertson RP, et al. International trial of the Edmonton protocol for islet transplantation. N Engl J Med. 2006; 355:1318–1330.
Article13. Ryan EA, Shandro T, Green K, Paty BW, Senior PA, Bigam D, et al. Assessment of the severity of hypoglycemia and glycemic lability in type 1 diabetic subjects undergoing islet transplantation. Diabetes. 2004; 53:955–962.
Article14. Hering BJ, Kandaswamy R, Ansite JD, Eckman PM, Nakano M, Sawada T, et al. Single-donor, marginal-dose islet transplantation in patients with type 1 diabetes. JAMA. 2005; 293:830–835.
Article15. Froud T, Ricordi C, Baidal DA, Hafiz MM, Ponte G, Cure P, et al. Islet transplantation in type 1 diabetes mellitus using cultured islets and steroid-free immunosuppression: MIAMI experience. Am J Transplant. 2005; 5:2037–2046.
Article16. Moberg L, Johansson H, Lukinius A, Berne C, Foss A, Kallen R, et al. Production of tissue factor by pancreatic islet cells as a trigger of detrimental thrombotic reactions in clinical islet transplantation. Lancet. 2002; 360:2039–2045.
Article17. Johansson H, Lukinius A, Moberg L, Lundgren T, Berne C, Foss A, et al. Tissue factor produced by the endocrine cells of the islets of Langerhans is associated with a negative outcome of clinical islet transplantation. Diabetes. 2005; 54:1755–1762.
Article18. Johansson H, Goto M, Dufrane D, Siegbahn A, Elgue G, Gianello P, et al. Low molecular weight dextran sulfate: a strong candidate drug to block IBMIR in clinical islet transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2006; 6:305–312.
Article19. Moberg L, Olsson A, Berne C, Felldin M, Foss A, Kallen R, et al. Nicotinamide inhibits tissue factor expression in isolated human pancreatic islets: implications for clinical islet transplantation. Transplantation. 2003; 76:1285–1288.
Article20. Cabric S, Sanchez J, Lundgren T, Foss A, Felldin M, Kallen R, et al. Islet surface heparinization prevents the instant blood-mediated inflammatory reaction in islet transplantation. Diabetes. 2007; 56:2008–2015.
Article21. Barton FB, Rickels MR, Alejandro R, Hering BJ, Wease S, Naziruddin B, et al. Improvement in outcomes of clinical islet transplantation: 1999-2010. Diabetes Care. 2012; 35:1436–1445.
Article22. Senior PA, Kin T, Shapiro J, Koh A. Islet Transplantation at the University of Alberta: status update and review of progress over the last decade. Can J Diabetes. 2012; 36:32–37.
Article23. O'Connell PJ, Holmes-Walker DJ, Goodman D, Hawthorne WJ, Loudovaris T, Gunton JE, et al. Multicenter Australian trial of islet transplantation: improving accessibility and outcomes. Am J Transplant. 2013; 13:1850–1858.24. Vantyghem MC, Kerr-Conte J, Arnalsteen L, Sergent G, Defrance F, Gmyr V, et al. Primary graft function, metabolic control, and graft survival after islet transplantation. Diabetes Care. 2009; 32:1473–1478.
Article25. Bellin MD, Kandaswamy R, Parkey J, Zhang HJ, Liu B, Ihm SH, et al. Prolonged insulin independence after islet allotransplants in recipients with type 1 diabetes. Am J Transplant. 2008; 8:2463–2470.
Article26. Posselt AM, Szot GL, Frassetto LA, Masharani U, Tavakol M, Amin R, et al. Islet transplantation in type 1 diabetic patients using calcineurin inhibitor-free immunosuppressive protocols based on T-cell adhesion or costimulation blockade. Transplantation. 2010; 90:1595–1601.
Article27. Posselt AM, Bellin MD, Tavakol M, Szot GL, Frassetto LA, Masharani U, et al. Islet transplantation in type 1 diabetics using an immunosuppressive protocol based on the anti-LFA-1 antibody efalizumab. Am J Transplant. 2010; 10:1870–1880.
Article28. Zhang N, Su D, Qu S, Tse T, Bottino R, Balamurugan AN, et al. Sirolimus is associated with reduced islet engraftment and impaired beta-cell function. Diabetes. 2006; 55:2429–2436.
Article29. Lowe MC, Badell IR, Turner AP, Thompson PW, Leopardi FV, Strobert EA, et al. Belatacept and sirolimus prolong nonhuman primate islet allograft survival: adverse consequences of concomitant alefacept therapy. Am J Transplant. 2013; 13:312–319.
Article30. Takita M, Itoh T, Shimoda M, Kanak MA, Shahbazov R, Kunnathodi F, et al. Pancreatic Ductal Perfusion at Organ Procurement Enhances Islet Yield in Human Islet Isolation. Pancreas. 2014; 43:1249–1255.
Article31. Lu Y, Jin X, Chen Y, Li S, Yuan Y, Mai G, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells protect islets from hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced injury. Cell Biochem Funct. 2010; 28:637–643.
Article32. Park KS, Kim YS, Kim JH, Choi B, Kim SH, Tan AH, et al. Trophic molecules derived from human mesenchymal stem cells enhance survival, function, and angiogenesis of isolated islets after transplantation. Transplantation. 2010; 89:509–517.
Article33. Eich T, Eriksson O, Lundgren T, Nordic Network. Visualization of early engraftment in clinical islet transplantation by positron-emission tomography. N Engl J Med. 2007; 356:2754–2755.
Article34. Borot S, Crowe LA, Parnaud G, Ris F, Meier R, Giovannoni L, et al. Quantification of islet loss and graft functionality during immune rejection by 3-tesla MRI in a rat model. Transplantation. 2013; 96:438–444.
Article35. Pattou F, Kerr-Conte J, Wild D. GLP-1-receptor scanning for imaging of human beta cells transplanted in muscle. N Engl J Med. 2010; 363:1289–1290.
Article36. Ludwig B, Rotem A, Schmid J, Weir GC, Colton CK, Brendel MD, et al. Improvement of islet function in a bioartificial pancreas by enhanced oxygen supply and growth hormone releasing hormone agonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012; 109:5022–5027.
Article37. Pedraza E, Coronel MM, Fraker CA, Ricordi C, Stabler CL. Preventing hypoxia-induced cell death in beta cells and islets via hydrolytically activated, oxygen-generating biomaterials. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012; 109:4245–4250.
Article38. Im BH, Jeong JH, Haque MR, Lee DY, Ahn CH, Kim JE, et al. The effects of 8-arm-PEG-catechol/heparin shielding system and immunosuppressive drug, FK506 on the survival of intraportally allotransplanted islets. Biomaterials. 2013; 34:2098–2106.
Article39. Marek N, Krzystyniak A, Ergenc I, Cochet O, Misawa R, Wang LJ, et al. Coating human pancreatic islets with CD4(+)CD25(high)CD127(-) regulatory T cells as a novel approach for the local immunoprotection. Ann Surg. 2011; 254:512–518.
Article40. Veriter S, Gianello P, Igarashi Y, Beaurin G, Ghyselinck A, Aouassar N, et al. Improvement of Subcutaneous Bioartificial Pancreas Vascularization and Function by Co-Encapsulation of Pig Islets and Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Primates. Cell Transplant. 2014; 23:1349–1364.
Article41. Ito T, Itakura S, Todorov I, Rawson J, Asari S, Shintaku J, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell and islet co-transplantation promotes graft revascularization and function. Transplantation. 2010; 89:1438–1445.
Article42. Solari MG, Srinivasan S, Boumaza I, Unadkat J, Harb G, Garcia-Ocana A, et al. Marginal mass islet transplantation with autologous mesenchymal stem cells promotes long-term islet allograft survival and sustained normoglycemia. J Autoimmun. 2009; 32:116–124.
Article43. Echeverri GJ, McGrath K, Bottino R, Hara H, Dons EM, van der Windt DJ, et al. Endoscopic gastric submucosal transplantation of islets (ENDO-STI): technique and initial results in diabetic pigs. Am J Transplant. 2009; 9:2485–2496.
Article44. Maffi P, Balzano G, Ponzoni M, Nano R, Sordi V, Melzi R, et al. Autologous pancreatic islet transplantation in human bone marrow. Diabetes. 2013; 62:3523–3531.
Article45. Campbell PM, Salam A, Ryan EA, Senior P, Paty BW, Bigam D, et al. Pretransplant HLA antibodies are associated with reduced graft survival after clinical islet transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2007; 7:1242–1248.
Article46. Thompson P, Badell IR, Lowe M, Cano J, Song M, Leopardi F, et al. Islet xenotransplantation using gal-deficient neonatal donors improves engraftment and function. Am J Transplant. 2011; 11:2593–2602.
Article47. van der Windt DJ, Bottino R, Kumar G, Wijkstrom M, Hara H, Ezzelarab M, et al. Clinical islet xenotransplantation: how close are we? Diabetes. 2012; 61:3046–3055.
Article48. Chen Y, Stewart JM, Gunthart M, Hawthorne WJ, Salvaris EJ, O'Connell PJ, et al. Xenoantibody response to porcine islet cell transplantation using GTKO, CD55, CD59, and fucosyltransferase multiple transgenic donors. Xenotransplantation. 2014; 21:244–253.
Article49. Lowe M, Badell IR, Thompson P, Martin B, Leopardi F, Strobert E, et al. A novel monoclonal antibody to CD40 prolongs islet allograft survival. Am J Transplant. 2012; 12:2079–2087.
Article