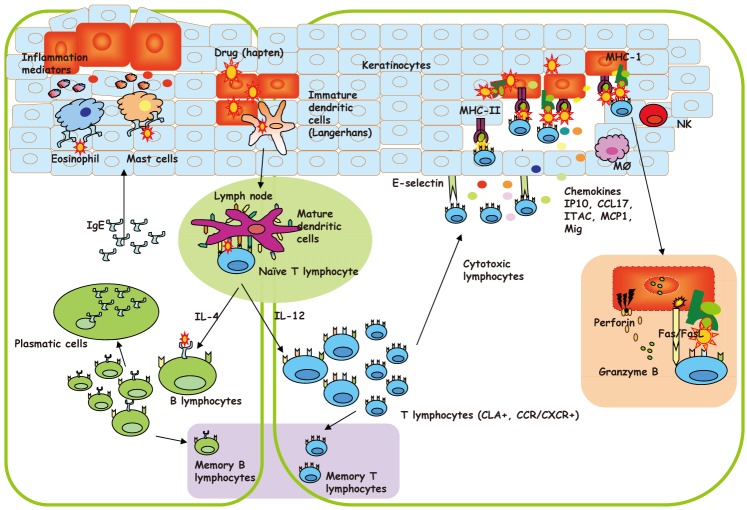
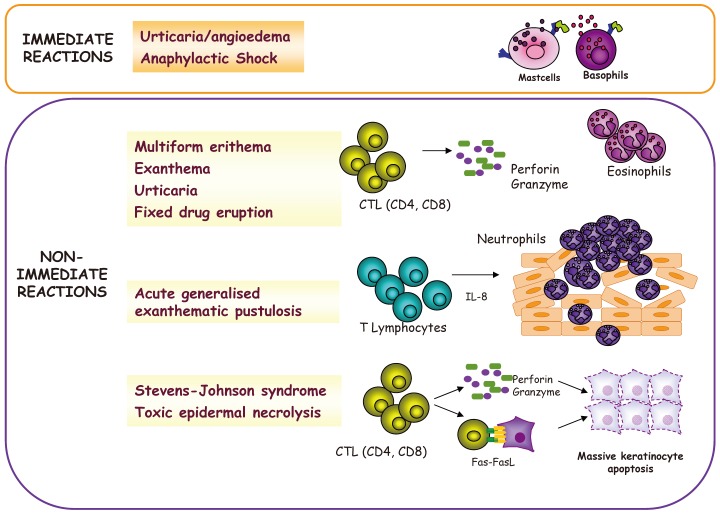
Immunologic Evaluation of Drug Allergy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Research Laboratory, Carlos Haya Hospital, Malaga, Spain.
- 2Allergy Service, Carlos Haya Hospital, Malaga, Spain. mblancag@gmail.com
- KMID: 2167043
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2012.4.5.251
Abstract
- Hypersensitivity drug reactions (HDR) consist of an individual abnormal response with the involvement of the immunological system. In addition to specific immunological mechanisms where specific antibodies or sensitised T cells participate, release of inflammatory mediators by non-specific immunological recognition may also occur. Within this category are one of the most common groups of drugs, the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. In addition to chemical drugs new emerging ones with an increasing protagonism are biological agents like humanised antibodies and others. For IgE dependent reactions both in vivo and in vitro tests can be used for the immunological evaluation. Sensitivity of these is not optimal and very often a drug provocation test must be considered for knowing the mechanism involved and/or establishing the diagnosis. For non-immediate reactions also both in vivo and in vitro tests can be used. Sensitivity for in vivo tests is generally low and in vitro tests may be needed for the immunological evaluation. Immunohistochemical studies of the affected tissue enable a more precise classification of non-immediate reactions. The monitorization of the acute response of the reactions has given clues for understanding these reactions and has promising results for the future of the immunological evaluation of HDR.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 5 articles
-
Immunologic Evaluation of Immediate Hypersensitivity to Cefaclor
Hye-Soo Yoo, Seung-Hyun Kim, Hyouk-Soo Kwon, Tae-Bum Kim, Young-Hee Nam, Young-Min Ye, Hae-Sim Park
Yonsei Med J. 2014;55(6):1473-1483. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2014.55.6.1473.Lamotrigine-induced toxic epidermal necrolysis confirmed by in vitro granulysin and cytokine assays
Ha-Kyeong Won, Ji-Won Lee, Woo-Jung Song, Jettanong Klaewsongkram, Min-Gyu Kang, Han-Ki Park, Hyun-Seung Lee, Min-Hye Kim, Yoon-Seok Chang, Sang-Heon Cho, Kyung-Up Min
Asia Pac Allergy. 2014;4(4):253-256. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2014.4.4.253.An unusual dual hypersensitivity reaction to moxifloxacin in a patient
Semra Demir, Derya Unal, Muge Olgac, Nilgun Akdeniz, Esin Aktas-Cetin, Asli Gelincik, Bahauddin Colakoglu, Suna Buyukozturk
Asia Pac Allergy. 2018;8(3):. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2018.8.e26.Usefulness of
In Vivo andIn Vitro Diagnostic Tests in the Diagnosis of Hypersensitivity Reactions to Quinolones and in the Evaluation of Cross-Reactivity: A Comprehensive Study Including the Latest Quinolone Gemifloxacin
Semra Demir, Asli Gelincik, Nilgun Akdeniz, Esin Aktas-Cetin, Muge Olgac, Derya Unal, Belkis Ertek, Raif Coskun, Bahattin Colakoğlu, Gunnur Deniz, Suna Buyukozturk
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2017;9(4):347-359. doi: 10.4168/aair.2017.9.4.347.An Ofloxacin-Induced Anaphylaxis through an IgG4-Mediated but Not IgE-Mediated Basophil Activation Mechanism
Ji Hye Kim, Dae-Hong Seo, Ga-Young Ban, Eun-Mi Yang, Yoo Seob Shin, Young-Min Ye, Hae-Sim Park
Korean J Crit Care Med. 2017;32(3):302-305. doi: 10.4266/kjccm.2017.00108.
Reference
-
1. Rawlins MD, Thompson JW. Davies DM, editor. Mechanisms of adverse drug reactions. Textbook of adverse drug reactions. 1977. Oxford: Oxford University Press.2. Demoly P, Hillaire-Buys D. Classification and epidemiology of hypersensitivity drug reactions. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2004; 24:345–356. vPMID: 15242715.
Article3. Gomes ER, Demoly P. Epidemiology of hypersensitivity drug reactions. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2005; 5:309–316. PMID: 15985812.
Article4. Thong BY, Tan TC. Epidemiology and risk factors for drug allergy. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2011; 71:684–700. PMID: 21480948.
Article5. Romano A, Pichler WJ, Blanca M. Highlights of the 4th Drug Hypersensitivity Meeting--Rome, April 22-25, 2010. Preface. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 127:S59. PMID: 21354500.6. Pichler WJ. Adverse side-effects to biological agents. Allergy. 2006; 61:912–920. PMID: 16867042.
Article7. Gell PGH, Coombs RRA. Clinical aspects of immunology. 1968. 2nd ed. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications.8. Weiss ME, Adkinson NF. Immediate hypersensitivity reactions to penicillin and related antibiotics. Clin Allergy. 1988; 18:515–540. PMID: 2977302.
Article9. Dewdney JM. Sela M, editor. Immunolgy of antibiotics. The antigens. 1977. New York: Academic Press.10. Pichler WJ. Delayed drug hypersensitivity reactions. Ann Intern Med. 2003; 139:683–693. PMID: 14568857.
Article11. Kowalski ML, Makowska JS, Blanca M, Bavbek S, Bochenek G, Bousquet J, Bousquet P, Celik G, Demoly P, Gomes ER, Niżankowska-Mogilnicka E, Romano A, Sanchez-Borges M, Sanz M, Torres MJ, De Weck A, Szczeklik A, Brockow K. Hypersensitivity to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) - classification, diagnosis and management: review of the EAACI/ENDA(#) and GA2LEN/HANNA*. Allergy. 2011; 66:818–829. PMID: 21631520.
Article12. Doña I, Blanca-López N, Cornejo-García JA, Torres MJ, Laguna JJ, Fernández J, Rosado A, Rondón C, Campo P, Agúndez JA, Blanca M, Canto G. Characteristics of subjects experiencing hypersensitivity to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: patterns of response. Clin Exp Allergy. 2011; 41:86–95. PMID: 21155908.
Article13. Johansson SG, Bieber T, Dahl R, Friedmann PS, Lanier BQ, Lockey RF, Motala C, Ortega Martell JA, Platts-Mills TA, Ring J, Thien F, Van Cauwenberge P, Williams HC. Revised nomenclature for allergy for global use: Report of the Nomenclature Review Committee of the World Allergy Organization, October 2003. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004; 113:832–836. PMID: 15131563.
Article14. Levine BB. Immunochemical mechanisms of drug allergy. Annu Rev Med. 1966; 17:23–38. PMID: 5327159.
Article15. Torres MJ, Mayorga C, Blanca M. Nonimmediate allergic reactions induced by drugs: pathogenesis and diagnostic tests. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2009; 19:80–90.16. Blanca M, Vega JM, Garcia J, Miranda A, Carmona MJ, Juarez C, Terrados S, Fernandez J. New aspects of allergic reactions to beta-lactams: crossreactions and unique specificities. Clin Exp Allergy. 1994; 24:407–415. PMID: 8087651.
Article17. Blanca M. Allergic reactions to penicillins. A changing world? Allergy. 1995; 50:777–782. PMID: 8607557.
Article18. Canto MG, Andreu I, Fernandez J, Blanca M. Selective immediate hypersensitivity reactions to NSAIDs. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 9:293–297. PMID: 19561490.19. Blanca-López N, Andreu I, Torres Jaén MJ. Hypersensitivity reactions to quinolones. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 11:285–291. PMID: 21659860.
Article20. Torres MJ, Blanca M, Fernandez J, Romano A, Weck A, Aberer W, Brockow K, Pichler WJ, Demoly P. Diagnosis of immediate allergic reactions to beta-lactam antibiotics. Allergy. 2003; 58:961–972. PMID: 14510712.21. Blanca M, Romano A, Torres MJ, Demoly P, DeWeck A. Continued need of appropriate betalactam-derived skin test reagents for the management of allergy to betalactams. Clin Exp Allergy. 2007; 37:166–173. PMID: 17250688.
Article22. Torres MJ, Ariza A, Mayorga C, Doña I, Blanca-Lopez N, Rondon C, Blanca M. Clavulanic acid can be the component in amoxicillin-clavulanic acid responsible for immediate hypersensitivity reactions. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 125:502–505. PMID: 20159266.
Article23. Torres MJ, Ariza A, Fernández J, Moreno E, Laguna JJ, Montañez MI, Ruiz-Sanchez AJ, Blanca M. Role of minor determinants of amoxicillin in the diagnosis of immediate allergic reactions to amoxicillin. Allergy. 2010; 65:590–596. PMID: 19968633.
Article24. Sánchez-Morillas L, Pérez-Ezquerra PR, Reaño-Martos M, Laguna-Martínez JJ, Sanz ML, Martínez LM. Selective allergic reactions to clavulanic acid: a report of 9 cases. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2010; 126:177–179. PMID: 20434202.25. Antunez C, Blanca-Lopez N, Torres MJ, Mayorga C, Perez-Inestrosa E, Montañez MI, Fernandez T, Blanca M. Immediate allergic reactions to cephalosporins: evaluation of cross-reactivity with a panel of penicillins and cephalosporins. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006; 117:404–410. PMID: 16461141.
Article26. Chaudhry T, Hissaria P, Wiese M, Heddle R, Kette F, Smith W. Oral drug challenges in NSAID-induced urticaria, angioedema and anaphylaxis. Intern Med J. 2011; Forthcoming.27. Blanca M, Mayorga C, Torres MJ, Warrington R, Romano A, Demoly P, Silviu-Dan F, Moya M, Fernandez J, Juárez C. Side-chain-specific reactions to betalactams: 14 years later. Clin Exp Allergy. 2002; 32:192–197. PMID: 11929481.
Article28. Brockow K, Romano A, Blanca M, Ring J, Pichler W, Demoly P. General considerations for skin test procedures in the diagnosis of drug hypersensitivity. Allergy. 2002; 57:45–51. PMID: 11991289.
Article29. Blanca M, Torres MJ, García JJ, Romano A, Mayorga C, de Ramon E, Vega JM, Miranda A, Juarez C. Natural evolution of skin test sensitivity in patients allergic to beta-lactam antibiotics. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999; 103:918–924. PMID: 10329829.30. Fernandez T, Torres MJ, R-Pena R, Fuentes MS, Robles S, Mayorga C, Blanca M. Decrease of selective immunoglobulin E response to amoxicillin despite repeated administration of benzylpenicillin and penicillin V. Clin Exp Allergy. 2005; 35:1645–1650. PMID: 16393332.
Article31. Fernández TD, Torres MJ, Blanca-López N, Rodríguez-Bada JL, Gomez E, Canto G, Mayorga C, Blanca M. Negativization rates of IgE radioimmunoassay and basophil activation test in immediate reactions to penicillins. Allergy. 2009; 64:242–248. PMID: 19178404.
Article32. Torres MJ, Mayorga C, Cornejo-Garcia JA, Romano A, Blanca M. IgE antibodies to penicillin in skin test negative patients. Allergy. 2002; 57:965. PMID: 12269955.
Article33. Torres MJ, Mayorga C, Leyva L, Guzman AE, Cornejo-García JA, Juarez C, Blanca M. Controlled administration of penicillin to patients with a positive history but negative skin and specific serum IgE tests. Clin Exp Allergy. 2002; 32:270–276. PMID: 11929493.
Article34. Blanca M, Mayorga C, Perez E, Suau R, Juarez C, Vega JM, Carmona MJ, Perez-Estrada M, Garcia J. Determination of IgE antibodies to the benzyl penicilloyl determinant. A comparison between poly-L-lysine and human serum albumin as carriers. J Immunol Methods. 1992; 153:99–105. PMID: 1517607.
Article35. Garcia JJ, Blanca M, Moreno F, Vega JM, Mayorga C, Fernandez J, Juarez C, Romano A, de Ramon E. Determination of IgE antibodies to the benzylpenicilloyl determinant: a comparison of the sensitivity and specificity of three radio allergo sorbent test methods. J Clin Lab Anal. 1997; 11:251–257. PMID: 9292392.
Article36. Moreno F, Blanca M, Mayorga C, Terrados S, Moya M, Pérez E, Suau R, Vega JM, García J, Miranda A, Carmona MJ. Studies of the specificities of IgE antibodies found in sera from subjects with allergic reactions to penicillins. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1995; 108:74–81. PMID: 7544181.
Article37. Ceska M, Eriksson R, Varga JM. Radioimmunosorbent assay of allergens. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1972; 49:1–9. PMID: 4536625.
Article38. Edwards RG, Spackman DA, Dewdney JM. Development and use of three new radioallergosorbent tests in the diagnosis of penicillin allergy. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1982; 68:352–357. PMID: 6178701.
Article39. Blanca M, Mayorga C, Sanchez F, Vega JM, Fernandez J, Juarez C, Suau R, Perez E. Differences in serum IgE antibody activity to benzylpenicillin and amoxicillin measured by RAST in a group of penicillin allergic patients. Allergy. 1991; 46:632–638. PMID: 1789405.
Article40. Blanca M, Mayorga C, Torres MJ, Reche M, Moya MC, Rodriguez JL, Romano A, Juarez C. Clinical evaluation of Pharmacia CAP System RAST FEIA amoxicilloyl and benzylpenicilloyl in patients with penicillin allergy. Allergy. 2001; 56:862–870. PMID: 11551251.41. Fontaine C, Mayorga C, Bousquet PJ, Arnoux B, Torres MJ, Blanca M, Demoly P. Relevance of the determination of serum-specific IgE antibodies in the diagnosis of immediate beta-lactam allergy. Allergy. 2007; 62:47–52. PMID: 17156341.42. Kim SH, Choi JH, Park HS. Heterogeneity of the IgE response to allergenic determinants of cefaclor in serum samples from patients with cefaclor-induced anaphylaxis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2005; 94:700–704. PMID: 15984605.
Article43. Sánchez-Sancho F, Perez-Inestrosa E, Suau R, Montañez MI, Mayorga C, Torres MJ, Romano A, Blanca M. Synthesis, characterization and immunochemical evaluation of cephalosporin antigenic determinants. J Mol Recognit. 2003; 16:148–156. PMID: 12833570.
Article44. Montannez MI, Mayorga C, Torres MJ, Ariza A, Blanca M, Perez-Inestrosa E. Synthetic approach to gain insight into antigenic determinants of cephalosporins: in vitro studies of chemical structure-IgE molecular recognition relationships. Chem Res Toxicol. 2011; 24:706–717. PMID: 21425867.45. Laroche D, Chollet-Martin S, Léturgie P, Malzac L, Vergnaud MC, Neukirch C, Venemalm L, Guéant JL, Roland PN. Evaluation of a new routine diagnostic test for immunoglobulin e sensitization to neuromuscular blocking agents. Anesthesiology. 2011; 114:91–97. PMID: 21169794.
Article46. Kautz O, Schumann H, Degerbeck F, Venemalm L, Jakob T. Severe anaphylaxis to the antiseptic polyhexanide. Allergy. 2010; 65:1068–1070. PMID: 20102357.
Article47. Venemalm L, Degerbeck F, Smith W. IgE-mediated reaction to mepivacaine. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008; 121:1058–1059. PMID: 18234312.
Article48. Ebo DG, Venemalm L, Bridts CH, Degerbeck F, Hagberg H, De Clerck LS, Stevens WJ. Immunoglobulin E antibodies to rocuronium: a new diagnostic tool. Anesthesiology. 2007; 107:253–259. PMID: 17667569.49. Garvey LH, Krøigaard M, Poulsen LK, Skov PS, Mosbech H, Venemalm L, Degerbeck F, Husum B. IgE-mediated allergy to chlorhexidine. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 120:409–415. PMID: 17559915.
Article50. Florvaag E, Johansson SG, Oman H, Venemalm L, Degerbeck F, Dybendal T, Lundberg M. Prevalence of IgE antibodies to morphine. Relation to the high and low incidences of NMBA anaphylaxis in Norway and Sweden, respectively. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2005; 49:437–444. PMID: 15777289.
Article51. Burgdorff T, Venemalm L, Vogt T, Landthaler M, Stolz W. IgE-mediated anaphylactic reaction induced by succinate ester of methylprednisolone. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2002; 89:425–428. PMID: 12392389.
Article52. Magnan A, Venemalm L, Porri F, Vervloet D. Anaphylactic reaction to rifamycin SV: presence of specific IgE antibodies. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1999; 103:954–956. PMID: 10329836.
Article53. Kim JE, Kim SH, Choi GS, Ye YM, Park HS. Detection of specific IgE antibodies to cefotiam-HSA conjugate by ELISA in a nurse with occupational anaphylaxis. Allergy. 2010; 65:791–792. PMID: 19886926.
Article54. Suh YJ, Lee YM, Choi JH, Suh CH, Nahm DH, Park HS. Heterogeneity of IgE response to cefteram pivoxil was noted in 2 patients with cefteram-induced occupational asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003; 112:209–210. PMID: 12847502.
Article55. Park HS, Kim KU, Lee YM, Choi JH, Lee JH, Park SW, Jang AS, Park CS. Occupational asthma and IgE sensitization to 7-aminocephalosporanic acid. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004; 113:785–787. PMID: 15112669.
Article56. Choi GS, Sung JM, Lee JW, Ye YM, Park HS. A case of occupational asthma caused by inhalation of vancomycin powder. Allergy. 2009; 64:1391–1392. PMID: 19485984.
Article57. de Weck AL, Sanz ML, Gamboa PM, Aberer W, Bienvenu J, Blanca M, Demoly P, Ebo DG, Mayorga L, Monneret G, Sainte-Laudy J. Diagnostic tests based on human basophils: more potentials and perspectives than pitfalls. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2008; 146:177–189. PMID: 18268385.
Article58. Abuaf N, Rostane H, Rajoely B, Gaouar H, Autegarden JE, Leynadier F, Girot R. Comparison of two basophil activation markers CD63 and CD203c in the diagnosis of amoxicillin allergy. Clin Exp Allergy. 2008; 38:921–928. PMID: 18331364.
Article59. Aranda A, Mayorga C, Ariza A, Doña I, Blanca-Lopez N, Canto G, Blanca M, Torres MJ. IgE-mediated hypersensitivity reactions to methylprednisolone. Allergy. 2010; 65:1376–1380. PMID: 20486918.
Article60. Aranda A, Mayorga C, Ariza A, Doña I, Rosado A, Blanca-Lopez N, Andreu I, Torres MJ. In vitro evaluation of IgE-mediated hypersensitivity reactions to quinolones. Allergy. 2011; 66:247–254. PMID: 20722637.
Article61. Gamboa PM, Sanz ML, Caballero MR, Antépara I, Urrutia I, Jáuregui I, González G, Diéguez I, De Weck AL. Use of CD63 expression as a marker of in vitro basophil activation and leukotriene determination in metamizol allergic patients. Allergy. 2003; 58:312–317. PMID: 12708979.
Article62. Gómez E, Blanca-Lopez N, Torres MJ, Requena G, Rondon C, Canto G, Blanca M, Mayorga C. Immunoglobulin E-mediated immediate allergic reactions to dipyrone: value of basophil activation test in the identification of patients. Clin Exp Allergy. 2009; 39:1217–1224. PMID: 19400910.63. Ebo DG, Bridts CH, Hagendorens MM, Mertens CH, De Clerck LS, Stevens WJ. Flow-assisted diagnostic management of anaphylaxis from rocuronium bromide. Allergy. 2006; 61:935–939. PMID: 16867045.
Article64. Mertes PM, Aimone-Gastin I, Guéant-Rodriguez RM, Mouton-Faivre C, Audibert G, O'Brien J, Frendt D, Brezeanu M, Bouaziz H, Guéant JL. Hypersensitivity reactions to neuromuscular blocking agents. Curr Pharm Des. 2008; 14:2809–2825. PMID: 18991700.
Article65. Gamboa PM, Sanz ML, Urrutia I, Jáuregui I, Antépara I, Diéguez I, De Weck AL. CD63 expression by flow cytometry in the in vitro diagnosis of allergy to omeprazole. Allergy. 2003; 58:538–539. PMID: 12757465.
Article66. Ebo DG, Bridts CH, Stevens WJ. IgE-mediated anaphylaxis from chlorhexidine: diagnostic possibilities. Contact Dermatitis. 2006; 55:301–302. PMID: 17026697.
Article67. Sanz ML, Gamboa PM, Antépara I, Uasuf C, Vila L, Garcia-Avilés C, Chazot M, De Weck AL. Flow cytometric basophil activation test by detection of CD63 expression in patients with immediate-type reactions to betalactam antibiotics. Clin Exp Allergy. 2002; 32:277–286. PMID: 11929494.
Article68. Torres MJ, Padial A, Mayorga C, Fernández T, Sanchez-Sabate E, Cornejo-García JA, Antúnez C, Blanca M. The diagnostic interpretation of basophil activation test in immediate allergic reactions to betalactams. Clin Exp Allergy. 2004; 34:1768–1775. PMID: 15544603.
Article69. De Week AL, Sanz ML, Gamboa PM, Aberer W, Sturm G, Bilo MB, Montroni M, Blanca M, Torres MJ, Mayorga L, Campi P, Manfredi M, Drouet M, Sainte-Laudy J, Romano A, Merk H, Weber JM, Jermann TM. ENDA (European Network for Drug Allergy). European Network for Drug Allergy). Diagnosis of immediate-type beta-lactam allergy in vitro by flow-cytometric basophil activation test and sulfidoleukotriene production: a multicenter study. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2009; 19:91–109.70. Sanz ML, Gamboa PM, Mayorga C. Basophil activation tests in the evaluation of immediate drug hypersensitivity. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 9:298–304. PMID: 19483617.
Article71. Bobadilla-González P, Pérez-Rangel I, García-Menaya JM, Sánchez-Vega S, Cordobés-Durán C, Zambonino-Carreiras MA. Type IV reaction due to phenylephrine administered nasally with cross-reactivity with ethylephrine. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2011; 21:69–72.72. Roujeau JC. Clinical heterogeneity of drug hypersensitivity. Toxicology. 2005; 209:123–129. PMID: 15767024.
Article73. Mayorga C, Torres MJ, Fernandez J, Canto G, Blanca M. Cutaneous symptoms in drug allergy: what have we learnt? Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 9:431–436. PMID: 19697448.
Article74. Auquier-Dunant A, Mockenhaupt M, Naldi L, Correia O, Schröder W, Roujeau JC. SCAR Study Group. Correlations between clinical patterns and causes of erythema multiforme majus, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necrolysis: results of an international prospective study. Arch Dermatol. 2002; 138:1019–1024. PMID: 12164739.
Article75. Rzany B, Mockenhaupt M, Baur S, Schröder W, Stocker U, Mueller J, Holländer N, Bruppacher R, Schöpf E. Epidemiology of erythema exsudativum multiforme majus, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necrolysis in Germany (1990-1992): structure and results of a population-based registry. J Clin Epidemiol. 1996; 49:769–773. PMID: 8691227.
Article76. Mayorga C, Pena RR, Blanca-López N, López S, Martin E, Torres MJ. Monitoring the acute phase response in non-immediate allergic drug reactions. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006; 6:249–257. PMID: 16825864.
Article77. Tsuge I, Okumura A, Kondo Y, Itomi S, Kakami M, Kawamura M, Nakajima Y, Komatsubara R, Urisu A. Allergen-specific T-cell response in patients with phenytoin hypersensitivity; simultaneous analysis of proliferation and cytokine production by carboxyfluorescein succinimidyl ester (CFSE) dilution assay. Allergol Int. 2007; 56:149–155. PMID: 17460442.
Article78. Torres MJ, Mayorga C, Fernández TD, Cornejo-García JA, Antúnez C, Valenzuela M, Del Prado MF, Rodriguez-Pena R, Blanca M. T cell assessment in allergic drug reactions during the acute phase according to the time of occurrence. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2006; 19:119–130. PMID: 16569350.
Article79. Torres MJ, Mayorga C, Cornejo-Garcia JA, Lopez S, Chaves P, Rondon C, Fernandez T, Blanca M. Monitoring non-immediate allergic reactions to iodine contrast media. Clin Exp Immunol. 2008; 152:233–238. PMID: 18341616.
Article80. Pichler WJ, Yawalkar N, Britschgi M, Depta J, Strasser I, Schmid S, Kuechler P, Naisbitt D. Cellular and molecular pathophysiology of cutaneous drug reactions. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2002; 3:229–238. PMID: 12010068.
Article81. Barbaud AM, Béné MC, Reichert-Penetrat S, Jacquin-Petit MA, Schmutz JL, Faure GC. Immunocompetent cells and adhesion molecules in 14 cases of cutaneous drug reactions induced with the use of antibiotics. Arch Dermatol. 1998; 134:1040–1041. PMID: 9722745.
Article82. Yawalkar N, Shrikhande M, Hari Y, Nievergelt H, Braathen LR, Pichler WJ. Evidence for a role for IL-5 and eotaxin in activating and recruiting eosinophils in drug-induced cutaneous eruptions. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000; 106:1171–1176. PMID: 11112902.
Article83. Hertl M, Bohlen H, Jugert F, Boecker C, Knaup R, Merk HF. Predominance of epidermal CD8+ T lymphocytes in bullous cutaneous reactions caused by beta-lactam antibiotics. J Invest Dermatol. 1993; 101:794–799. PMID: 8245507.84. Rozieres A, Vocanson M, Saïd BB, Nosbaum A, Nicolas JF. Role of T cells in nonimmediate allergic drug reactions. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 9:305–310. PMID: 19474707.
Article85. Rozieres A, Hennino A, Rodet K, Gutowski MC, Gunera-Saad N, Berard F, Cozon G, Bienvenu J, Nicolas JF. Detection and quantification of drug-specific T cells in penicillin allergy. Allergy. 2009; 64:534–542. PMID: 19154548.
Article86. Hertl M, Jugert F, Merk HF. CD8+ dermal T cells from a sulphamethoxazole-induced bullous exanthem proliferate in response to drug-modified liver microsomes. Br J Dermatol. 1995; 132:215–220. PMID: 7534104.
Article87. Padial A, Antunez C, Blanca-Lopez N, Fernandez TD, Cornejo-Garcia JA, Mayorga C, Torres MJ, Blanca M. Non-immediate reactions to beta-lactams: diagnostic value of skin testing and drug provocation test. Clin Exp Allergy. 2008; 38:822–828. PMID: 18331363.88. Schaerli P, Britschgi M, Keller M, Steiner UC, Steinmann LS, Moser B, Pichler WJ. Characterization of human T cells that regulate neutrophilic skin inflammation. J Immunol. 2004; 173:2151–2158. PMID: 15265952.
Article89. Sidoroff A, Halevy S, Bavinck JN, Vaillant L, Roujeau JC. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP)--a clinical reaction pattern. J Cutan Pathol. 2001; 28:113–119. PMID: 11168761.90. Britschgi M, Pichler WJ. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis, a clue to neutrophil-mediated inflammatory processes orchestrated by T cells. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2002; 2:325–331. PMID: 12130947.
Article91. Britschgi M, Steiner UC, Schmid S, Depta JP, Senti G, Bircher A, Burkhart C, Yawalkar N, Pichler WJ. T-cell involvement in drug-induced acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis. J Clin Invest. 2001; 107:1433–1441. PMID: 11390425.
Article92. Padial MA, Alvarez-Ferreira J, Tapia B, Blanco R, Mañas C, Blanca M, Bellón T. Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis associated with pseudoephedrine. Br J Dermatol. 2004; 150:139–142. PMID: 14746629.
Article93. Shiohara T, Mizukawa Y. Fixed drug eruption: a disease mediated by self-inflicted responses of intraepidermal T cells. Eur J Dermatol. 2007; 17:201–208. PMID: 17478380.94. Mizukawa Y, Yamazaki Y, Shiohara T. In vivo dynamics of intraepidermal CD8+ T cells and CD4+ T cells during the evolution of fixed drug eruption. Br J Dermatol. 2008; 158:1230–1238. PMID: 18363767.95. Wu Y, Farrell J, Pirmohamed M, Park BK, Naisbitt DJ. Generation and characterization of antigen-specific CD4+, CD8+, and CD4+ CD8+ T-cell clones from patients with carbamazepine hypersensitivity. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 119:973–981. PMID: 17320939.96. Chung WH, Hung SI, Yang JY, Su SC, Huang SP, Wei CY, Chin SW, Chiou CC, Chu SC, Ho HC, Yang CH, Lu CF, Wu JY, Liao YD, Chen YT. Granulysin is a key mediator for disseminated keratinocyte death in Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Nat Med. 2008; 14:1343–1350. PMID: 19029983.
Article97. Barbaud A. Drug patch testing in systemic cutaneous drug allergy. Toxicology. 2005; 209:209–216. PMID: 15767038.
Article98. Barbaud A. Skin testing in delayed reactions to drugs. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 2009; 29:517–535. PMID: 19563995.
Article99. Lammintausta K, Kortekangas-Savolainen O. The usefulness of skin tests to prove drug hypersensitivity. Br J Dermatol. 2005; 152:968–974. PMID: 15888154.
Article100. Romano A, Di Fonso M, Papa G, Pietrantonio F, Federico F, Fabrizi G, Venuti A. Evaluation of adverse cutaneous reactions to aminopenicillins with emphasis on those manifested by maculopapular rashes. Allergy. 1995; 50:113–118. PMID: 7604932.
Article101. Blanca-López N, Zapatero L, Alonso E, Torres MJ, Fuentes V, Martínez-Molero MI, Blanca M. Skin testing and drug provocation in the diagnosis of nonimmediate reactions to aminopenicillins in children. Allergy. 2009; 64:229–233. PMID: 19178402.
Article102. Padial A, Posadas S, Alvarez J, Torres MJ, Alvarez JA, Mayorga C, Blanca M. Nonimmediate reactions to systemic corticosteroids suggest an immunological mechanism. Allergy. 2005; 60:665–670. PMID: 15813813.
Article103. Nyfeler B, Pichler WJ. The lymphocyte transformation test for the diagnosis of drug allergy: sensitivity and specificity. Clin Exp Allergy. 1997; 27:175–181. PMID: 9061217.
Article104. Luque I, Leyva L, José Torres M, Rosal M, Mayorga C, Segura JM, Blanca M, Juárez C. In vitro T-cell responses to beta-lactam drugs in immediate and nonimmediate allergic reactions. Allergy. 2001; 56:611–618. PMID: 11421918.
Article105. Jurado-Palomo J, Cabañas R, Prior N, Bobolea ID, Fiandor-Román AM, López-Serrano MC, Quirce S, Bellón T. Use of the lymphocyte transformation test in the diagnosis of DRESS syndrome induced by ceftriaxone and piperacillin-tazobactam: two case reports. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2010; 20:433–436.106. Trcka J, Seitz CS, Bröcker EB, Gross GE, Trautmann A. Aminopenicillin-induced exanthema allows treatment with certain cephalosporins or phenoxymethyl penicillin. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2007; 60:107–111. PMID: 17510067.
Article107. Schnyder B, Pichler WJ. Skin and laboratory tests in amoxicillin- and penicillin-induced morbilliform skin eruption. Clin Exp Allergy. 2000; 30:590–595. PMID: 10718859.
Article108. Rodriguez-Pena R, Lopez S, Mayorga C, Antunez C, Fernandez TD, Torres MJ, Blanca M. Potential involvement of dendritic cells in delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions to beta-lactams. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006; 118:949–956. PMID: 17030251.109. Lopez S, Torres MJ, Rodríguez-Pena R, Blanca-Lopez N, Fernandez TD, Antunez C, Canto G, de Luque V, Mayorga C. Lymphocyte proliferation response in patients with delayed hypersensitivity reactions to heparins. Br J Dermatol. 2009; 160:259–265. PMID: 18945304.
Article110. Antunez C, Barbaud A, Gomez E, Audonnet S, Lopez S, Guéant-Rodriguez RM, Aimone-Gastin I, Gomez F, Blanca M, Guéant JL. Recognition of iodixanol by dendritic cells increases the cellular response in delayed allergic reactions to contrast media. Clin Exp Allergy. 2011; 41:657–664. PMID: 21375605.
Article111. Aberer W, Bircher A, Romano A, Blanca M, Campi P, Fernandez J, Brockow K, Pichler WJ, Demoly P. European Network for Drug Allergy (ENDA). EAACI interest group on drug hypersensitivity. Drug provocation testing in the diagnosis of drug hypersensitivity reactions: general considerations. Allergy. 2003; 58:854–863. PMID: 12911412.
Article112. Terrados S, Blanca M, Garcia J, Vega J, Torres MJ, Carmona MJ, Miranda A, Moya M, Juarez C, Fernandez J. Nonimmediate reactions to betalactams: prevalence and role of the different penicillins. Allergy. 1995; 50:563–567. PMID: 8588688.
Article113. Romano A, Blanca M, Torres MJ, Bircher A, Aberer W, Brockow K, Pichler WJ, Demoly P. ENDA. EAACI. Diagnosis of nonimmediate reactions to beta-lactam antibiotics. Allergy. 2004; 59:1153–1160. PMID: 15461594.
Article114. Gamboa PM. The epidemiology of drug allergy-related consultations in Spanish Allergology services: Alergologica-2005. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2009; 19(Suppl 2):45–50.115. Szczeklik A, Nizankowska-Mogilnicka E, Sanak M. Adkinson NF, Bochner BS, Busse WW, Holgate ST, Lemanske RF, Simons FER, editors. Hypersensitivity to aspirin and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Middleton's allergy: principles & practice. 2009. 7th ed. New York: Mosby Elsevier;p. 1227–1243.
Article116. Gray PA, Warner TD, Vojnovic I, Del Soldato P, Parikh A, Scadding GK, Mitchell JA. Effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on cyclo-oxygenase and lipoxygenase activity in whole blood from aspirin-sensitive asthmatics vs healthy donors. Br J Pharmacol. 2002; 137:1031–1038. PMID: 12429575.
Article117. Doña I, Torres MJ, García-Nuñez I, Gómez F, Salas M, Rondón C, Canto MG, Blanca M. Hypersensitivity reactions to drugs: patterns of responses, drug involved and temporal variation in a large serie of patients evaluated. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2012; Forthcoming.118. Stevenson DD, Sanchez-Borges M, Szczeklik A. Classification of allergic and pseudoallergic reactions to drugs that inhibit cyclooxygenase enzymes. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2001; 87:177–180. PMID: 11570612.
Article119. Makowska JS, Grzegorczyk J, Bienkiewicz B, Wozniak M, Kowalski ML. Systemic responses after bronchial aspirin challenge in sensitive patients with asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2008; 121:348–354. PMID: 18086495.
Article120. Pérez-Calderón R, Gonzalo-Garijo MA, Pérez-Rangel I, Sánchez-Vega S, Zambonino MA. Fixed drug eruption due to nabumetone in a patient with previous fixed drug eruptions due to naproxen. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2011; 21:153–154.121. Celik G, Bavbek S, Misirligil Z, Melli M. Release of cysteinyl leukotrienes with aspirin stimulation and the effect of prostaglandin E(2) on this release from peripheral blood leucocytes in aspirin-induced asthmatic patients. Clin Exp Allergy. 2001; 31:1615–1622. PMID: 11678863.122. Sanz ML, Gamboa P, de Weck AL. A new combined test with flow-cytometric basophil activation and determination of sulfidoleukotrienes is useful for in vitro diagnosis of hypersensitivity to aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2005; 136:58–72. PMID: 15608437.
Article123. Gamboa P, Sanz ML, Caballero MR, Urrutia I, Antépara I, Esparza R, de Weck AL. The flow-cytometric determination of basophil activation induced by aspirin and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) is useful for in vitro diagnosis of the NSAID hypersensitivity syndrome. Clin Exp Allergy. 2004; 34:1448–1457. PMID: 15347380.
Article124. Kowalski ML. Pawankar R, Holgate ST, Rosenwasser LJ, editors. Diagnosis of aspirin sensitivity in aspirin exacerbated respiratory disease. Allergy frontiers: diagnosis and health economics. 2009. Tokyo, New York: Springer;p. 349–372.
Article125. Mewes T, Riechelmann H, Klimek L. Increased in vitro cysteinyl leukotriene release from blood leukocytes in patients with asthma, nasal polyps, and aspirin intolerance. Allergy. 1996; 51:506–510. PMID: 8863928.
Article126. May A, Weber A, Gall H, Kaufmann R, Zollner TM. Means of increasing sensitivity of an in vitro diagnostic test for aspirin intolerance. Clin Exp Allergy. 1999; 29:1402–1411. PMID: 10520062.
Article127. Pierzchalska M, Mastalerz L, Sanak M, Zazula M, Szczeklik A. A moderate and unspecific release of cysteinyl leukotrienes by aspirin from peripheral blood leucocytes precludes its value for aspirin sensitivity testing in asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 2000; 30:1785–1791. PMID: 11122218.
Article128. Szczeklik A, Stevenson DD. Aspirin-induced asthma: advances in pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003; 111:913–921. quiz 22. PMID: 12743549.
Article129. Liccardi G, Cazzola M, De Giglio C, Manfredi D, Piscitelli E, D'Amato M, D'Amato G. Safety of celecoxib in patients with adverse skin reactions to acetaminophen (paracetamol) and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2005; 15:249–253.130. Quiralte J, Blanco C, Delgado J, Ortega N, Alcntára M, Castillo R, Anguita JL, Sáenz de San Pedro B, Carrillo T. Challenge-based clinical patterns of 223 Spanish patients with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory-drug-induced-reactions. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2007; 17:182–188.131. Gonzalo-Garijo MA, Cordobés-Duran C, Lamilla-Yerga AM, Moreno-Gastón I. Severe immediate reaction to nabumetone. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol. 2007; 17:274–276.132. Nizankowska-Mogilnicka E, Bochenek G, Mastalerz L, Swierczyńska M, Picado C, Scadding G, Kowalski ML, Setkowicz M, Ring J, Brockow K, Bachert C, Wöhrl S, Dahlén B, Szczeklik A. EAACI/GA2LEN guideline: aspirin provocation tests for diagnosis of aspirin hypersensitivity. Allergy. 2007; 62:1111–1118. PMID: 17521312.
Article133. Schubert B, Grosse Perdekamp MT, Pfeuffer P, Raith P, Bröcker EB, Trautmann A. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug hypersensitivity: fable or reality? Eur J Dermatol. 2005; 15:164–167. PMID: 15908299.134. Hausmann OV, Seitz M, Villiger PM, Pichler WJ. The complex clinical picture of side effects to biologicals. Med Clin North Am. 2010; 94:791–804. xi–ii. PMID: 20609863.
Article135. Baudouin V, Crusiaux A, Haddad E, Schandene L, Goldman M, Loirat C, Abramowicz D. Anaphylactic shock caused by immunoglobulin E sensitization after retreatment with the chimeric anti-interleukin-2 receptor monoclonal antibody basiliximab. Transplantation. 2003; 76:459–463. PMID: 12923429.
Article136. Vultaggio A, Matucci A, Nencini F, Pratesi S, Parronchi P, Rossi O, Romagnani S, Maggi E. Anti-infliximab IgE and non-IgE antibodies and induction of infusion-related severe anaphylactic reactions. Allergy. 2010; 65:657–661. PMID: 19951375.
Article137. Chung CH, Mirakhur B, Chan E, Le QT, Berlin J, Morse M, Murphy BA, Satinover SM, Hosen J, Mauro D, Slebos RJ, Zhou Q, Gold D, Hatley T, Hicklin DJ, Platts-Mills TA. Cetuximab-induced anaphylaxis and IgE specific for galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose. N Engl J Med. 2008; 358:1109–1117. PMID: 18337601.138. Kwan JM, Reese AM, Trafeli JP. Delayed autoimmune hemolytic anemia in efalizumab-treated psoriasis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008; 58:1053–1055. PMID: 18328597.
Article139. Bishara AI, Hagmeyer KO. Acute profound thrombocytopenia following abciximab therapy. Ann Pharmacother. 2000; 34:924–930. PMID: 10928405.
Article140. Curtis BR, Swyers J, Divgi A, McFarland JG, Aster RH. Thrombocytopenia after second exposure to abciximab is caused by antibodies that recognize abciximab-coated platelets. Blood. 2002; 99:2054–2059. PMID: 11877279.
Article141. Ashraf-Benson S, Wall GC, Veach LA. Serum sickness-like reaction associated with efalizumab. Ann Pharmacother. 2009; 43:383–386. PMID: 19193578.
Article142. Gamarra RM, McGraw SD, Drelichman VS, Maas LC. Serum sickness-like reactions in patients receiving intravenous infliximab. J Emerg Med. 2006; 30:41–44. PMID: 16434333.
Article143. Pilette C, Coppens N, Houssiau FA, Rodenstein DO. Severe serum sickness-like syndrome after omalizumab therapy for asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 120:972–973. PMID: 17716723.
Article144. Torres MJ, Chaves P, Doña I, Blanca-López N, Canto G, Mayorga C, Blanca M. T-cell involvement in delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions to infliximab. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 128:1365–1367.e1. PMID: 21839501.
Article145. Salama M, Lawrance IC. Stevens-Johnson syndrome complicating adalimumab therapy in Crohn's disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2009; 15:4449–4452. PMID: 19764100.
Article146. Moneret-Vautrin DA, Morisset M, Vignaud JM, Kanny G. T cell mediated allergy to abciximab. Allergy. 2002; 57:269–270. PMID: 11906353.
Article147. Jacquenet S, Moneret-Vautrin DA, Bihain BE. Mammalian meat-induced anaphylaxis: clinical relevance of anti-galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose IgE confirmed by means of skin tests to cetuximab. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 124:603–605. PMID: 19733301.148. Commins SP, James HR, Kelly LA, Pochan SL, Workman LJ, Perzanowski MS, Kocan KM, Fahy JV, Nganga LW, Ronmark E, Cooper PJ, Platts-Mills TA. The relevance of tick bites to the production of IgE antibodies to the mammalian oligosaccharide galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 127:1286–1293.e6. PMID: 21453959.149. Commins SP, Satinover SM, Hosen J, Mozena J, Borish L, Lewis BD, Woodfolk JA, Platts-Mills TA. Delayed anaphylaxis, angioedema, or urticaria after consumption of red meat in patients with IgE antibodies specific for galactose-alpha-1,3-galactose. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009; 123:426–433. PMID: 19070355.150. Moreno F, Blanca M, Fernandez J, Ferrer A, Mayorga C, del Caño A, Aguilar F, Juarez C, Garcia J. Determination of inflammatory markers in allergic reactions to drugs. Allergy Proc. 1995; 16:119–122. PMID: 7557369.
Article151. Fernandez J, Blanca M, Moreno F, Garcia J, Segurado E, del Cano A, Aguilar F. Role of tryptase, eosinophil cationic protein and histamine in immediate allergic reactions to drugs. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 1995; 107:160–162. PMID: 7542066.
Article152. Blanca M, Campo P, Rondon C, Cornejo J, Doña I, Haggeman L, Torres M, Melendez L, Rodriguez-Bada J, Canto G. Response to nasal challenge with lysine-aspirin in subjects with hypersensitivity reactions to NSAIDs with respiratory versus cutaneous involvement [abstract]. J Allergy Clin immunol. 2011; 127(Suppl):AB192. Abstract no. 737.153. Posadas SJ, Leyva L, Torres MJ, Rodriguez JL, Bravo I, Rosal M, Fernandez J, Juarez C, Blanca M. Subjects with allergic reactions to drugs show in vivo polarized patterns of cytokine expression depending on the chronology of the clinical reaction. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000; 106:769–776. PMID: 11031349.
Article154. Cornejo-Garcia JA, Fernandez TD, Torres MJ, Carballo M, Hernan I, Antunez C, Blanca M, Mayorga C. Differential cytokine and transcription factor expression in patients with allergic reactions to drugs. Allergy. 2007; 62:1429–1438. PMID: 17983377.
Article155. Fernandez TD, Mayorga C, Torres MJ, Cornejo-Garcia JA, López S, Chaves P, Rondon C, Blanca M. Cytokine and chemokine expression in the skin from patients with maculopapular exanthema to drugs. Allergy. 2008; 63:712–719. PMID: 18384452.
Article