Healthc Inform Res.
2013 Mar;19(1):25-32. 10.4258/hir.2013.19.1.25.
Association Rules to Identify Complications of Cerebral Infarction in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Medical Informatics, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 2Biomedical Informatics Technology Center, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. ynkim@dsmc.or.kr
- 3Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- KMID: 2166658
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2013.19.1.25
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
The purpose of this study was to find risk factors that are associated with complications of cerebral infarction in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF) and to discover useful association rules among these factors.
METHODS
The risk factors with respect to cerebral infarction were selected using logistic regression analysis with the Wald's forward selection approach. The rules to identify the complications of cerebral infarction were obtained by using the association rule mining (ARM) approach.
RESULTS
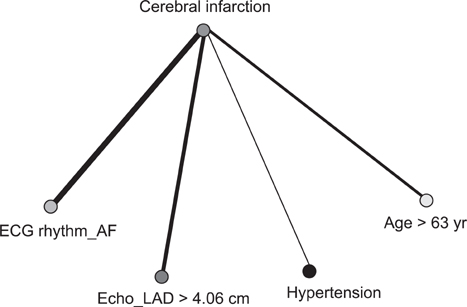
We observed that 4 independent factors, namely, age, hypertension, initial electrocardiographic rhythm, and initial echocardiographic left atrial dimension (LAD), were strong predictors of cerebral infarction in patients with AF. After the application of ARM, we obtained 4 useful rules to identify complications of cerebral infarction: age (>63 years) and hypertension (Yes) and initial ECG rhythm (AF) and initial Echo LAD (>4.06 cm); age (>63 years) and hypertension (Yes) and initial Echo LAD (>4.06 cm); hypertension (Yes) and initial ECG rhythm (AF) and initial Echo LAD (>4.06 cm); age (>63 years) and hypertension (Yes) and initial ECG rhythm (AF).
CONCLUSIONS
Among the induced rules, 3 factors (the initial ECG rhythm [i.e., AF], initial Echo LAD, and age) were strongly associated with each other.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Marini C, De Santis F, Sacco S, Russo T, Olivieri L, Totaro R, et al. Contribution of atrial fibrillation to incidence and outcome of ischemic stroke: results from a population-based study. Stroke. 2005. 36(6):1115–1119.
Article2. Sherman DG, Goldman L, Whiting RB, Jurgensen K, Kaste M, Easton JD. Thromboembolism in patients with atrial fibrillation. Arch Neurol. 1984. 41(7):708–710.
Article3. The Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation Investigators. Predictors of thromboembolism in atrial fibrillation: I. clinical features of patients at risk. Ann Intern Med. 1992. 116(1):1–5.4. Lee SM, Park RW. Basic concepts and principles of data mining in clinical practice. J Korean Soc Med Inform. 2009. 15(2):175–189.
Article5. Son CS, Jang BK, Seo ST, Kim MS, Kim YN. A hybrid decision support model to discover informative knowledge in diagnosing acute appendicitis. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2012. 12:17.
Article6. Prather JC, Lobach DF, Goodwin LK, Hales JW, Hage ML, Hammond WE. Medical data mining: knowledge discovery in a clinical data warehouse. Proc AMIA Annu Fall Symp. 1997. 101–105.7. Richards G, Rayward-Smith VJ, Sonksen PH, Carey S, Weng C. Data mining for indicators of early mortality in a database of clinical records. Artif Intell Med. 2001. 22(3):215–231.
Article8. Doddi S, Marathe A, Ravi SS, Torney DC. Discovery of association rules in medical data. Med Inform Internet Med. 2001. 26(1):25–33.
Article9. Mullins IM, Siadaty MS, Lyman J, Scully K, Garrett CT, Miller WG, et al. Data mining and clinical data repositories: insights from a 667,000 patient data set. Comput Biol Med. 2006. 36(12):1351–1377.
Article10. Son CS, Kim YN, Kim HS, Park HS, Kim MS. Decision-making model for early diagnosis of congestive heart failure using rough set and decision tree approaches. J Biomed Inform. 2012. 45(5):999–1008.
Article11. Agrawal R, Srikant R. Bocca J, Jarke M, Zaniolo C, editors. Fast algorithms for mining association rules in large databases. Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Very Large Data Bases. 1994. 1994 Sep 12-15; Santiago de Chile, Chile. San Francisco, CA: Morgan Kaufmann;487–499.12. Shin AM. System design and implementation of disease association rule mining using large electronic medical record data. 2011. Daegu, Korea: Keimyung University.13. Go AS, Hylek EM, Phillips KA, Chang Y, Henault LE, Selby JV, et al. Prevalence of diagnosed atrial fibrillation in adults: national implications for rhythm management and stroke prevention: the AnTicoagulation and Risk Factors in Atrial Fibrillation (ATRIA) Study. JAMA. 2001. 285(18):2370–2375.
Article14. Olsson SB, Halperin JL. Prevention of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation. Semin Vasc Med. 2005. 5(3):285–292.
Article15. Fuster V, Ryden LE, Cannom DS, Crijns HJ, Curtis AB, Ellenbogen KA, et al. ACC/AHA/ESC 2006 Guidelines for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the European Society of Cardiology Committee for Practice Guidelines (writing committee to revise the 2001 guidelines for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation): developed in collaboration with the European Heart Rhythm Association and the Heart Rhythm Society. Circulation. 2006. 114(7):e257–e354.16. Lip GY, Nieuwlaat R, Pisters R, Lane DA, Crijns HJ. Refining clinical risk stratification for predicting stroke and thromboembolism in atrial fibrillation using a novel risk factor-based approach: the Euro Heart Survey on atrial fibrillation. Chest. 2010. 137(2):263–272.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cerebral Infarction After Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation in Patients With Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation
- Non-medication Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation
- Spontaneous Conversion of Atrial Fibrillation to Normal Sinus Rhythm Following Recurrent Cerebral Infarctions
- Simultaneously Presented Acute Ischemic Stroke and Non-ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction in a Patient with Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation
- Brachioaxillary Artery Thromboembolism and Multiple Cerebral Infarction Manifested as Left Hand Clumsiness and Paresthesia