Cancer Res Treat.
2006 Feb;38(1):35-39.
Serum HER2 as a Response Indicator to Various Chemotherapeutic Agents in Tissue HER2 Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Center for Clinical Services, Research Institute & Hospital National Cancer Center, Goyang-si, Korea.
- 2Center for Breast Cancer, Research Institute & Hospital National Cancer Center, Goyang- si, Korea. jungsro@ncc.re.kr
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The aim of study was to evaluate the usefulness of serum HER2 as a therapeutic response indicator in patients with HER2 positive metastatic breast cancer (MBC).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The levels of serum HER2 and CA15.3 were assayed in 148 serial serum samples from 50 HER2 positive MBC patients at both the baseline and follow-ups. The changes in the levels of serum HER2 and CA15.3 in relation to the tumor responses to the various chemotherapy regimens were monitored.
RESULTS
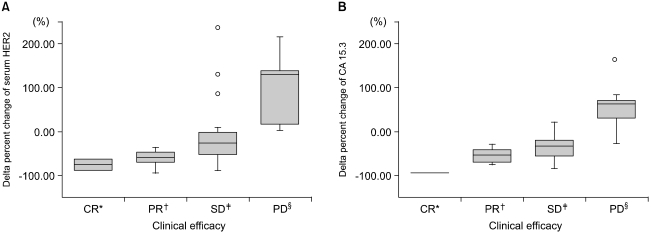
The levels of serum HER2 and CA15.3 were elevated in 82% and 62% of tissue HER2 positive patients, respectively, prior to therapies, with the changes in both tumor markers showing statistical significance in relation to the tumor responses (p<0.01) in patients with elevated baseline serum markers.
CONCLUSION
The level of serum HER2 could be a valuable response indicator, not only for trastuzumab containing therapy, but also for other common MBC chemotherapeutic agents. Also, as it is more frequently elevated, the serum level of HER2 may also be a more useful tumor marker than CA15.3 in HER2 positive MBC.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cobleigh MA, Vogel CL, Tripathy D, Robert NJ, Scholl S, Fehrenbacher L, et al. Multinational study of the efficacy and safety of humanized anti-HER2 monoclonal antibody in women who have HER2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer that has progressed after chemotherapy for metastatic disease. J Clin Oncol. 1999; 17:2639–2648. PMID: 10561337.
Article2. Slamon DJ, Leyland-Jones B, Shak S, Fuchs H, Paton V, Bajamonde A, et al. Use of chemotherapy plus a monoclonal antibody against HER2 for metastatic breast cancer that overexpresses HER2. N Engl J Med. 2001; 344:783–792. PMID: 11248153.
Article3. Maguire HC Jr, Greene MI. The neu (c-erbB-2) oncogene. Semin Oncol. 1989; 16:148–155. PMID: 2565604.4. Lin YZ, Clinton GM. A soluble protein related to the HER-2 proto-oncogene product is released from human breast carcinoma cells. Oncogene. 1991; 6:639–643. PMID: 1674366.5. Zabrecky JR, Lam T, McKenzie SJ, Carney W. The extracellular domain of p185/neu is released from the surface of human breast carcinoma cells, SK-BR-3. J Biol Chem. 1991; 266:1716–1720. PMID: 1671042.
Article6. Leitzel K, Teramoto Y, Sampson E, Mauceri J, Langton BC, Demers L, et al. Elevated soluble c-erbB-2 antigen levels in the serum and effusions of a proportion of breast cancer patients. J Clin Oncol. 1992; 10:1436–1443. PMID: 1355522.
Article7. Fehm T, Maimonis P, Weitz S, Teramoto Y, Katalinic A, Jager W. Influence of circulating c-erbB-2 serum protein on response to adjuvant chemotherapy in node-positive breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1997; 43:87–95. PMID: 9065602.
Article8. Mehta RR, McDermott JH, Hieken TJ, Marler KC, Patel MK, Wild LD, et al. Plasma c-erbB-2 levels in breast cancer patients: prognostic significance in predicting response to chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 1998; 16:2409–2416. PMID: 9667258.
Article9. Colomer R, Montero S, Lluch A, Ojeda B, Barnadas A, Casado A, et al. Circulating HER2 extracellular domain and resistance to chemotherapy in advanced breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2000; 6:2356–2362. PMID: 10873087.10. Hayes DF, Yamauchi H, Broadwater G, Cirrincione CT, Rodrigue SP, Berry DA, et al. Circulating HER-2/erbB-2/c-neu (HER-2) extracellular domain as a prognostic factor in patients with metastatic breast cancer: Cancer and Leukemia Group B Study 8662. Clin Cancer Res. 2001; 7:2703–2711. PMID: 11555582.11. Lipton A, Ali SM, Leitzel K, Demers L, Chinchilli V, Engle L, et al. Elevated serum Her-2/neu level predicts decreased response to hormone therapy in metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2002; 20:1467–1472. PMID: 11896093.
Article12. Cheung KL, Graves CR, Robertson JF. Tumour marker measurements in the diagnosis and monitoring of breast cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 2000; 26:91–102. PMID: 10772967.
Article13. Seregni E, Coli A, Mazzucca N. Circulating tumour markers in breast cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2004; 31(Suppl 1):S15–S22. PMID: 15127239.
Article14. Baselga J. Is circulating HER-2 more than just a tumor marker? Clin Cancer Res. 2001; 7:2605–2607. PMID: 11555569.15. Sugano K, Ushiama M, Fukutomi T, Tsuda H, Kitoh T, Ohkura H. Combined measurement of the c-erbB-2 protein in breast carcinoma tissues and sera is useful as a sensitive tumor marker for monitoring tumor relapse. Int J Cancer. 2000; 89:329–336. PMID: 10956406.
Article16. Burstein HJ, Harris LN, Marcom PK, Lambert-Falls R, Havlin K, Overmoyer B, et al. Trastuzumab and vinorelbine as first-line therapy for HER2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer: multicenter phase II trial with clinical outcomes, analysis of serum tumor markers as predictive factors, and cardiac surveillance algorithm. J Clin Oncol. 2003; 21:2889–2895. PMID: 12885806.
Article17. Cook GB, Neaman IE, Goldblatt JL, Cambetas DR, Hussain M, Luftner D, et al. Clinical utility of serum HER-2/neu testing on the Bayer Immuno 1 automated system in breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 2001; 21:1465–1470. PMID: 11396233.18. Fehm T, Gebauer G, Jager W. Clinical utility of serial serum c-erbB-2 determinations in the follow-up of breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2002; 75:97–106. PMID: 12243512.
Article19. Robertson JF, Jaeger W, Syzmendera JJ, Selby C, Coleman R, Howell A, et al. European Group for Serum Tumour Markers in Breast Cancer. The objective measurement of remission and progression in metastatic breast cancer by use of serum tumour markers. Eur J Cancer. 1999; 35:47–53. PMID: 10211087.
Article20. Ali SM, Leitzel K, Chinchilli VM, Engle L, Demers L, Harvey HA, et al. Relationship of serum HER-2/neu and serum CA 15-3 in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Clin Chem. 2002; 48:1314–1320. PMID: 12142389.
Article21. Jensen BV, Johansen JS, Price PA. High levels of serum HER-2/neu and YKL-40 independently reflect aggressiveness of metastatic breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2003; 9:4423–4434. PMID: 14555515.22. Colomer R, Llombart-Cussac A, Lluch A, Barnadas A, Ojeda B, Caranana V, et al. Biweekly paclitaxel plus gemcitabine in advanced breast cancer: phase II trial and predictive value of HER2 extracellular domain. Ann Oncol. 2004; 15:201–206. PMID: 14760109.
Article23. Pegram MD, Lipton A, Hayes DF, Weber BL, Baselga JM, Tripathy D, et al. Phase II study of receptor-enhanced chemosensitivity using recombinant humanized anti-p185HER2/neu monoclonal antibody plus cisplatin in patients with HER2/neu-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer refractory to chemotherapy treatment. J Clin Oncol. 1998; 16:2659–2671. PMID: 9704716.
Article24. Esteva FJ, Valero V, Booser D, Guerra LT, Murray JL, Pusztai L, et al. Phase II study of weekly docetaxel and trastuzumab for patients with HER-2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2002; 20:1800–1808. PMID: 11919237.
Article25. Kostler WJ, Schwab B, Singer CF, Neumann R, Rucklinger E, Brodowicz T, et al. Monitoring of serum Her-2/neu predicts response and progression-free survival to trastuzumab-based treatment in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2004; 10:1618–1624. PMID: 15014012.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Silver-Enhanced In Situ Hybridization as an Alternative to Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization for Assaying HER2 Amplification in Clinical Breast Cancer
- Prognostic Value of the Evolution of HER2-Low Expression after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
- The Predictive Value of Serum HER2/neu for Response to Anthracycline-Based and Trastuzumab-Based Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy
- HER2-Low Breast Cancer: Now and in the Future
- HER2 status in breast cancer: changes in guidelines and complicating factors for interpretation