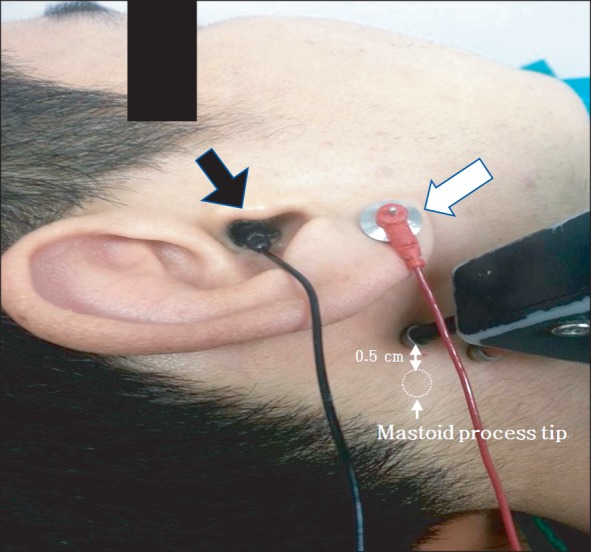
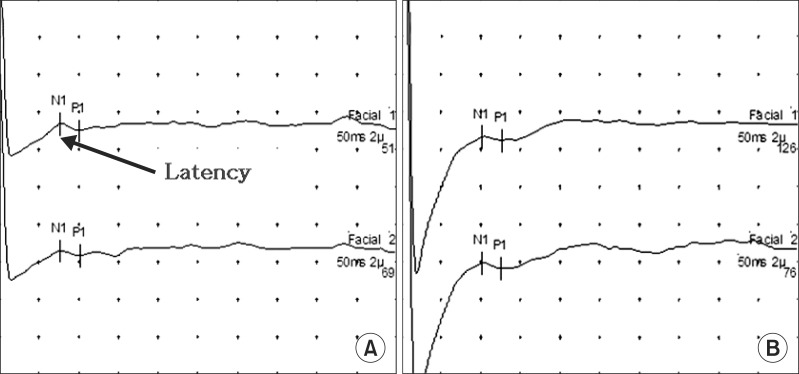
Ann Rehabil Med.
2014 Jun;38(3):381-387. 10.5535/arm.2014.38.3.381.
Diagnostic Value of Facial Nerve Antidromic Evoked Potential in Patients With Bell's Palsy: A Preliminary Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine and Rehabilitation Institute of Neuromuscular Disease, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. drtlc@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2165757
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2014.38.3.381
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To assess the practical diagnostic value of facial nerve antidromic evoked potential (FNAEP), we compared it with the diagnostic value of the electroneurography (ENoG) test in Bell's palsy.
METHODS
In total, 20 patients with unilateral Bell's palsy were recruited. Between the 1st and 17th days after the onset of facial palsy, FNAEP and ENoG tests were conducted. The degeneration ratio and FNAEP latency difference between the affected and unaffected sides were calculated in all subjects.
RESULTS
In all patients, FNAEP showed prolonged latencies on the affected side versus the unaffected side. The difference was statistically significant. In contrast, there was no significant difference between sides in the normal control group. In 8 of 20 patients, ENoG revealed a degeneration ratio less than 50%, but FNAEP show a difference of more than 0.295+/-0.599 ms, the average value of normal control group. This shows FNAEP could be a more sensitive test for Bell's palsy diagnosis than ENoG. In particular, in 10 patients tested within 7 days after onset, an abnormal ENoG finding was noted in only four of them, but FNAEP showed a significant latency difference in all patients at this early stage. Thus, FANEP was more sensitive in detecting facial nerve injury than the ENoG test (p=0.031).
CONCLUSION
FNAEP has some clinical value in the diagnosis of facial nerve degeneration. It is important that FNAEP be considered in patients with facial palsy at an early stage and integrated with other relevant tests.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. de Araujo MR, Azenha MR, Capelari MM, Marzola C. Management of Bell's palsy: a report of 2 cases. J Can Dent Assoc. 2008; 74:823–827. PMID: 19000467.2. Sittel C, Stennert E. Prognostic value of electromyography in acute peripheral facial nerve palsy. Otol Neurotol. 2001; 22:100–104. PMID: 11314702.
Article3. Celik M, Forta H. Electrophysiological investigations and prognosis in idiopathic facial palsy. Electromyogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1997; 37:311–315. PMID: 9298344.4. Grosheva M, Wittekindt C, Guntinas-Lichius O. Prognostic value of electroneurography and electromyography in facial palsy. Laryngoscope. 2008; 118:394–397. PMID: 18090862.
Article5. Grosheva M, Guntinas-Lichius O. Significance of electromyography to predict and evaluate facial function outcome after acute peripheral facial palsy. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2007; 264:1491–1495. PMID: 17611766.
Article6. Chow LC, Tam RC, Li MF. Use of electroneurography as a prognostic indicator of Bell's palsy in Chinese patients. Otol Neurotol. 2002; 23:598–601. PMID: 12170167.
Article7. Teudt IU, Nevel AE, Izzo AD, Walsh JT Jr, Richter CP. Optical stimulation of the facial nerve: a new monitoring technique? Laryngoscope. 2007; 117:1641–1647. PMID: 17607145.
Article8. Haginomori S, Wada S, Takamaki A, Nonaka R, Takenaka H, Takubo T. A new method for measuring compound muscle action potentials in facial palsy: a preliminary study. Muscle Nerve. 2008; 37:764–769. PMID: 18506721.
Article9. Guo L, Jasiukaitis P, Pitts LH, Cheung SW. Optimal placement of recording electrodes for quantifying facial nerve compound muscle action potential. Otol Neurotol. 2008; 29:710–713. PMID: 18434927.
Article10. Dumitru D, Amato AA, Zwarts M. Ch. 15, Electrodiagnostic medicine pitfalls. Electrodiagnostic medicine. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Hanley & Belfus;2002. p. 541–577.11. May M, Klein SR, Blumenthal F. Evoked electromyography and idiopathic facial paralysis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1983; 91:678–685. PMID: 6420750.
Article12. Aimoni C, Lombardi L, Gastaldo E, Stacchini M, Pastore A. Preoperative and postoperative electroneurographic facial nerve monitoring in patients with parotid tumors. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2003; 129:940–943. PMID: 12975265.
Article13. Nakatani H, Iwai M, Takeda T, Hamada M, Kakigi A, Nakahira M. Waveform changes in antidromic facial nerve responses in patients with Bell's palsy. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2002; 111:128–134. PMID: 11860064.
Article14. Tashima K, Takeda T, Nakatani H, Hamada M, Kakigi A. Antidromically evoked facial nerve response in guinea pigs: a long-term follow-up after nerve injury. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 2010; 71(Suppl 1):85–90. PMID: 20185955.15. Kitani S. Experimental study on antidromic evoked potential of the facial nerve for clinical application. Nihon Jibiinkoka Gakkai Kaiho. 1994; 97:645–653. PMID: 8189311.
Article16. Dumitru D, Amato AA, Zwarts M. Ch. 17, Focal cranial neuropathies. Electrodiagnostic medicine. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Hanley & Belfus;2002. p. 653–712.17. Wenhao Z, Chen MJ, Yang C, Zhang WJ. Prognostic value of facial nerve antidromic evoked potentials in bell palsy: a preliminary study. Int J Otolaryngol. 2012; 2012:960469. PMID: 22164176.
Article18. Zhang WH, Chen MJ, Zhang WJ. Antidromica evoked potentials for positioning in facial paralysis. J Oral Sci Res. 2011; 8:676–679.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Usefulness of Blink Reflex in the Evaluation of Early Stage of Bell's Palsy
- Recurrent Bilateral Bell's Palsy Who Suffered From Acute Pancreatitis
- Development of Bell's Palsy after Influenza Vaccination
- Bilateral Simultaneous Bell's Palsy-Two Case Studies
- Investigation of Facial Nerve with the Response to Magnetic & Electrical Stimulation and Clinical Application