Clin Endosc.
2013 Sep;46(5):445-449.
Confocal Microscopy in the Esophagus and Stomach
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, University of Washington, School of Medicine, Seattle, WA, USA. jooha@u.washington.edu
Abstract
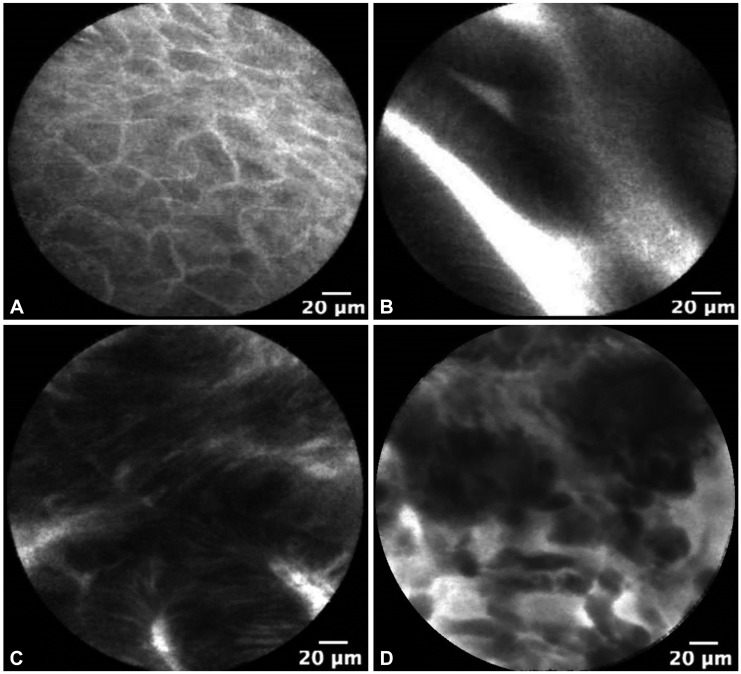
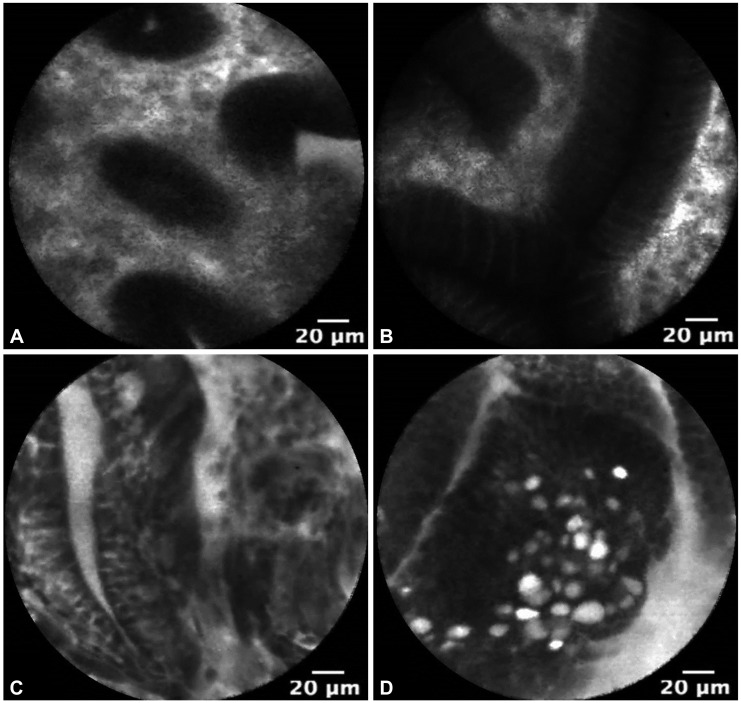
- Probe-based confocal microscopy (pCLE) is actively being investigated for applications in the esophagus and stomach. The use of pCLE allows real-time in vivo microscopy to evaluate the microarchitecture of the mucosal epithelium. pCLE appears to be particularly useful in identifying mucosal dysplasia and early malignancies that cannot be clearly distinguished using high-definition white light endoscopy, chromoendoscopy, or magnification endoscopy. In addition, the ability to detect dysplastic tissue in real-time may shift the current screening practice from random biopsy to targeted biopsy of esophageal and gastric cancers and their precursor lesions. We will review the use of pCLE for detection and surveillance of upper gastrointestinal early luminal malignancy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kiesslich R, Burg J, Vieth M, et al. Confocal laser endoscopy for diagnosing intraepithelial neoplasias and colorectal cancer in vivo. Gastroenterology. 2004; 127:706–713. PMID: 15362025.
Article2. Wallace MB, Fockens P. Probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy. Gastroenterology. 2009; 136:1509–1513. PMID: 19328799.
Article3. Wallace M, Lauwers GY, Chen Y, et al. Miami classification for probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy. Endoscopy. 2011; 43:882–891. PMID: 21818734.
Article4. Wang TD, Friedland S, Sahbaie P, et al. Functional imaging of colonic mucosa with a fibered confocal microscope for real-time in vivo pathology. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007; 5:1300–1305. PMID: 17936692.
Article5. Polglase AL, McLaren WJ, Skinner SA, Kiesslich R, Neurath MF, Delaney PM. A fluorescence confocal endomicroscope for in vivo microscopy of the upper- and the lower-GI tract. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005; 62:686–695. PMID: 16246680.
Article6. Wallace MB, Meining A, Canto MI, et al. The safety of intravenous fluorescein for confocal laser endomicroscopy in the gastrointestinal tract. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2010; 31:548–552. PMID: 20002025.
Article7. American Gastroenterological Association. Spechler SJ, Sharma P, Souza RF, Inadomi JM, Shaheen NJ. American Gastroenterological Association medical position statement on the management of Barrett's esophagus. Gastroenterology. 2011; 140:1084–1091. PMID: 21376940.
Article8. ASGE Standards of Practice Committee. Evans JA, Early DS, et al. The role of endoscopy in Barrett's esophagus and other premalignant conditions of the esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 76:1087–1094. PMID: 23164510.
Article9. Abrams JA, Kapel RC, Lindberg GM, et al. Adherence to biopsy guidelines for Barrett's esophagus surveillance in the community setting in the United States. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009; 7:736–742. PMID: 19268726.
Article10. Gaddam S, Mathur SC, Singh M, et al. Novel probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy criteria and interobserver agreement for the detection of dysplasia in Barrett's esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011; 106:1961–1969. PMID: 21946283.
Article11. Bajbouj M, Vieth M, Rösch T, et al. Probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy compared with standard four-quadrant biopsy for evaluation of neoplasia in Barrett's esophagus. Endoscopy. 2010; 42:435–440. PMID: 20506064.
Article12. Sharma P, Meining AR, Coron E, et al. Real-time increased detection of neoplastic tissue in Barrett's esophagus with probe-based confocal laser endomicroscopy: final results of an international multicenter, prospective, randomized, controlled trial. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 74:465–472. PMID: 21741642.
Article13. Shaheen NJ, Overholt BF, Sampliner RE, et al. Durability of radiofrequency ablation in Barrett's esophagus with dysplasia. Gastroenterology. 2011; 141:460–468. PMID: 21679712.14. Gupta M, Iyer PG, Lutzke L, et al. Recurrence of esophageal intestinal metaplasia after endoscopic mucosal resection and radiofrequency ablation of Barrett's esophagus: results from a US Multicenter Consortium. Gastroenterology. 2013; 145:79–86. PMID: 23499759.
Article15. Wallace MB, Crook JE, Saunders M, et al. Multicenter, randomized, controlled trial of confocal laser endomicroscopy assessment of residual metaplasia after mucosal ablation or resection of GI neoplasia in Barrett's esophagus. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 76:539–547. PMID: 22749368.
Article16. Uedo N, Iishi H, Tatsuta M, et al. Longterm outcomes after endoscopic mucosal resection for early gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 2006; 9:88–92. PMID: 16767363.
Article17. Capelle LG, Haringsma J, de Vries AC, et al. Narrow band imaging for the detection of gastric intestinal metaplasia and dysplasia during surveillance endoscopy. Dig Dis Sci. 2010; 55:3442–3448. PMID: 20393882.
Article18. Kato M, Kaise M, Yonezawa J, et al. Magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging achieves superior accuracy in the differential diagnosis of superficial gastric lesions identified with white-light endoscopy: a prospective study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 72:523–529. PMID: 20598685.
Article19. Guo YT, Li YQ, Yu T, et al. Diagnosis of gastric intestinal metaplasia with confocal laser endomicroscopy in vivo: a prospective study. Endoscopy. 2008; 40:547–553. PMID: 18618938.
Article20. Bok GH, Jeon SR, Cho JY, et al. The accuracy of probe-based confocal endomicroscopy versus conventional endoscopic biopsies for the diagnosis of superficial gastric neoplasia (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 77:899–908. PMID: 23473002.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy and Molecular Imaging in Barrett Esophagus and Stomach
- Inflammatory Vitiligo Confirmed Diagnosis and Treatment Outcome Using a Reflectance Confocal Microscopy
- Usefulness and Future Prospects of Confocal Laser Endomicroscopy for Gastric Premalignant and Malignant Lesions
- Comparision of Specular Microscopy and Confocal Microscopy for Evaluation of Corneal Endothelium
- In vivo tandem scanning confocal microscopy in acanthamoeba keratitis