Allergy Asthma Respir Dis.
2016 May;4(3):221-224. 10.4168/aard.2016.4.3.221.
Toxic epidermal necrolysis induced by deflazacort
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yjcho@ewha.ac.kr
- KMID: 2165086
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aard.2016.4.3.221
Abstract
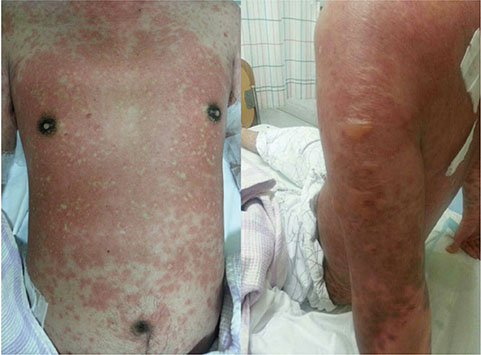
- Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) are severe cutaneous adverse reactions to drugs, which carry significant morbidities and mortalities. Although SJS and TEN can be treated by corticosteroids or intravenous immunoglobulin, they may be induced by steroids. We experienced a 36-year-old man who developed whole body erythromatous maculopapular rashes and multiple bullae after ingestion of deflazacort. After avoidance of deflazacort and use of dexamethasone, skin lesions resorbed. We reported a case of TEN diagnosed by characteristic clinical findings with a brief review of the literature.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Letko E, Papaliodis DN, Papaliodis GN, Daoud YJ, Ahmed AR, Foster CS. Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: a review of the literature. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2005; 94:419–436.
Article2. Yang MS, Jung JW, Kang HR. Severe cutaneous adverse reaction. Korean J Med. 2014; 87:665–674.
Article3. Schwartz RA, McDonough PH, Lee BW. Toxic epidermal necrolysis: part II. Prognosis, sequelae, diagnosis, differential diagnosis, prevention, and treatment. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013; 69:187.e1–187.e6.4. Roujeau JC, Kelly JP, Naldi L, Rzany B, Stern RS, Anderson T, et al. Medication use and the risk of Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis. N Engl J Med. 1995; 333:1600–1607.
Article5. Khalili B, Bahna SL. Pathogenesis and recent therapeutic trends in Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2006; 97:272–280.
Article6. Navarro Llanos A, Elizalde Eguinoa J, Boto de los Bueys B, Pujol de la Llave E. Toxic epidermal necrolysis in a patient treated with high doses of deflazacort. Med Clin (Barc). 1996; 106:599.7. Kim DW, Jung DE, Koo JW. Steroid and enalapril therapy: possible cause of toxic epidermal necrolysis. Korean J Pediatr. 2006; 49:332–336.
Article8. Lee EC, Kim GA, Koo JW. Toxic epidermal necrolysis associated with deflazacort therapy with nephrotic syndrome. Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2014; 33:222–225.
Article9. Edwards IR, Aronson JK. Adverse drug reactions: definitions, diagnosis, and management. Lancet. 2000; 356:1255–1259.
Article10. Borchers AT, Lee JL, Naguwa SM, Cheema GS, Gershwin ME. Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Autoimmun Rev. 2008; 7:598–605.
Article11. Schwartz RA, McDonough PH, Lee BW. Toxic epidermal necrolysis: part I. Introduction, history, classification, clinical features, systemic manifestations, etiology, and immunopathogenesis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013; 69:173.e1–173.e13.12. Faye O, Roujeau JC. Treatment of epidermal necrolysis with high-dose intravenous immunoglobulins (IV Ig): clinical experience to date. Drugs. 2005; 65:2085–2090.
Article13. Jat KR, Khairwa A. Deflazacort in comparison to other steroids for nephrotic syndrome. Indian J Nephrol. 2012; 22:239–245.
Article14. Browne F, Wilkinson SM. Effective prescribing in steroid allergy: controversies and cross-reactions. Clin Dermatol. 2011; 29:287–294.
Article15. Buttoni U, Pulsoni A, Innocenzi D, Pranteda G, Latini A, Bonaccorsi P, et al. Toxic epidermal necrolyis (TEN) in a patient with non-Hodgkin lymphoma: successful treatment with dexamethasone at high dosage. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2000; 14:140–142.16. van der Meer JB, Schuttelaar ML, Toth GG, Kardaun SH, Beerthuizen G, de Jong MC, et al. Successful dexamethasone pulse therapy in a toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) patient featuring recurrent TEN to oxazepam. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2001; 26:654–656.
Article17. Barman KD, Verma KK, Agrawal S, Agarwalla A, Rijal A. Stevens-Johnson syndrome with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura treated with dexamethasone pulse therapy. J Dermatol. 2003; 30:54–58.18. Kardaun SH, Jonkman MF. Dexamethasone pulse therapy for Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis. Acta Derm Venereol. 2007; 87:144–148.
Article19. Lauerma AI, Reitamo S, Maibach HI. Systemic hydrocortisone/cortisol induces allergic skin reactions in presensitized subjects. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1991; 24(2 Pt 1):182–185.
Article20. Koh WL, Tay YK, Koh MJ. Danazol-induced Stevens-Johnson syndrome in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus. Dermatol Online J. 2015; 21(1):pii: 13030/qt24v513b9.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Carbamazepine- Induced- Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis
- A Case of Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Due to Contact of Paraquat(Gramoxone(R))
- Toxic epidermal necrolysis associated with deflazacort therapy with nephrotic syndrome
- A Case of Complete Vaginal Ostruction Following Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis
- A Case of Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis and Review of Literatures