Korean J Gastroenterol.
2014 Aug;64(2):115-118. 10.4166/kjg.2014.64.2.115.
A Case of Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis Following Argon Plasma Coagulation for Angiodysplasias in the Colon
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. rshdrryu@medimail.co.kr
- KMID: 2164423
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2014.64.2.115
Abstract
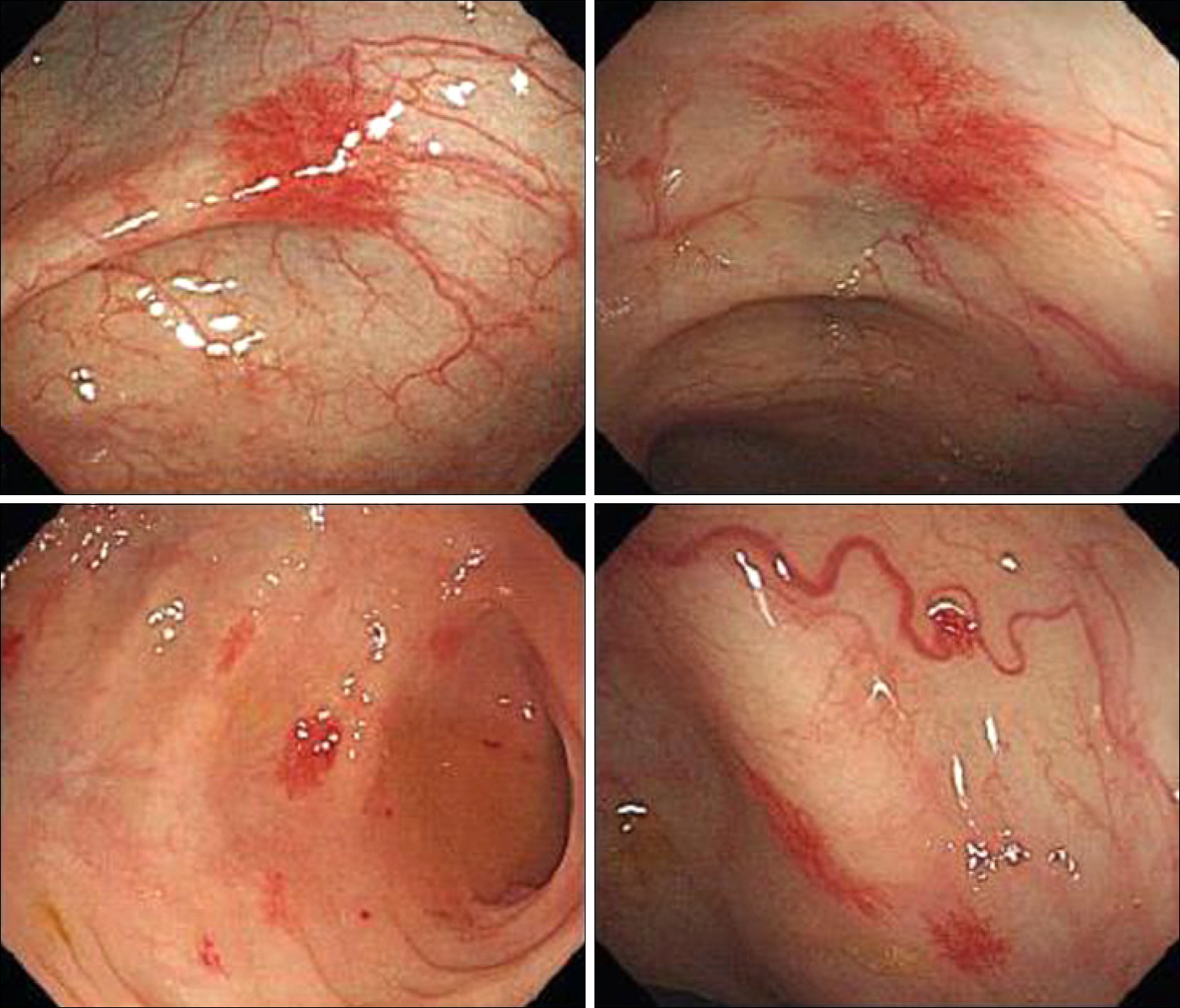
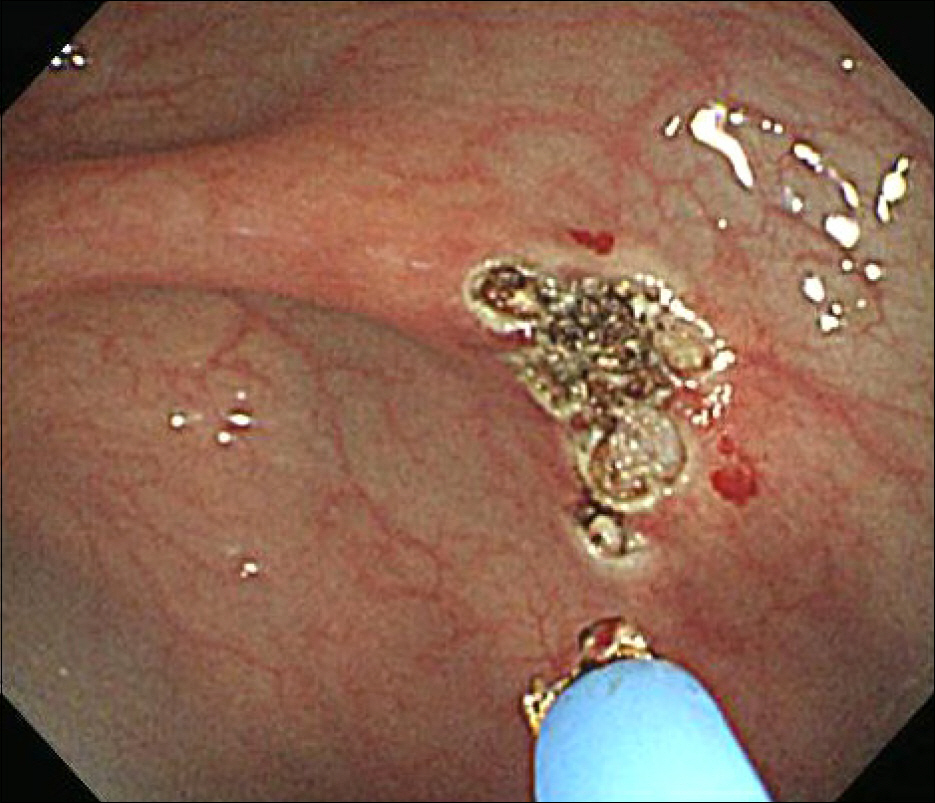
- Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP) is the most common infection in liver cirrhosis patients, and is not a result of surgery or intra abdominal infection. Argon plasma coagulation (APC) is an endoscopic procedure used with a high-frequency electrical current for control of bleeding from gastrointestinal vascular ectasias including angiodysplasia and gastric antral vascular ectasia. This procedure is known to be safe because it uses a noncontact method. Therefore, tissue injury is minimal and up to two to three millimeters. However, we experienced a case of SBP occurring immediately after performance of APC for control of severe bleeding from angiodysplasia in the colon in a patient with liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
MeSH Terms
-
Aged
Angiodysplasia/complications/*diagnosis
Anti-Bacterial Agents/therapeutic use
*Argon Plasma Coagulation
Bacterial Infections/*diagnosis/drug therapy/microbiology
Carcinoma, Hepatocellular/complications/diagnosis
Colonic Diseases/complications/*diagnosis
Colonoscopy
Female
Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage/therapy
Gram-Negative Bacteria/isolation & purification
Humans
Liver Cirrhosis/complications/diagnosis
Liver Neoplasms/complications/diagnosis
Peritonitis/*diagnosis/drug therapy/microbiology
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Ginés P, Rimola A, Planas R, et al. Norfloxacin prevents spontaneous bacterial peritonitis recurrence in cirrhosis: results of a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Hepatology. 1990; 12:716–724.
Article2. Silva RA, Correia AJ, Dias LM, Viana HL, Viana RL. Argon plasma coagulation therapy for hemorrhagic radiation proctosigmoiditis. Gastrointest Endosc. 1999; 50:221–224.
Article3. Taïeb S, Rolachon A, Cenni JC, et al. Effective use of argon plasma coagulation in the treatment of severe radiation proctitis. Dis Colon Rectum. 2001; 44:1766–1771.
Article4. Grund KE, Storek D, Farin G. Endoscopic argon plasma coagulation (APC) first clinical experiences in flexible endoscopy. Endosc Surg Allied Technol. 1994; 2:42–46.5. Ben Soussan E, Mathieu N, Roque I, Antonietti M. Bowel explosion with colonic perforation during argon plasma coagulation for hemorrhagic radiation-induced proctitis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003; 57:412–413.6. Fernández J, Navasa M, Gómez J, et al. Bacterial infections in cirrhosis: epidemiological changes with invasive procedures and norfloxacin prophylaxis. Hepatology. 2002; 35:140–148.
Article7. Suzuki K, Takikawa Y. Marked improvement in the resolution of, and survival rates in, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. J Gastroenterol. 2002; 37:149–150.
Article8. Garcia-Tsao G. Identifying new risk factors for spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: how important is it? Gastroenterology. 1999; 117:495–499.
Article9. Song HG, Lee HC, Joo YH, et al. Clinical and microbiological characteristics of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP) in a recent five year period. Taehan Kan Hakhoe Chi. 2002; 8:61–70.10. Park MK, Lee JH, Byun YH, et al. Changes in the profiles of causative agents and antibiotic resistance rate for spontaneous bacterial peritonitis: an analysis of cultured microorganisms in recent 12 years. Korean J Hepatol. 2007; 13:370–377.
Article11. Seo YS, Um SH, Yim HJ, et al. Clinical features and outcomes of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in patients with cirrhosis. Korean J Hepatol. 2007; 13(Suppl 3):S71.12. Lee MR, Chon JY, Moon YM, Park IS, Lee KW. Efficacy of ascitic fluid culture technique using blood culture media in the diagnosis of spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Korean J Gastroenterol. 1995; 27:659–671.13. Bernard B, Grangé JD, Khac EN, Amiot X, Opolon P. Poynar Antibiotic prophylaxis for the prevention of bacterial infectio in cirrhotic patients with gastrointestinal bleeding: a me analysis. Hepatology. 1999; 29:1655–1661.14. Chiu YC, Lu LS, Wu KL, et al. Comparison of argon plasma coagulation in management of upper gastrointestinal angiodysplasia and gastric antral vascular ectasia hemorrhage. BMC Gastroenterol. 2012; 12:67.
Article15. Poole GV. Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis during bowel preparation: an example of clinical translocation. South Med J. 1991; 84:1412–1413.
Article16. Gumpenberger C, Kirchgatterer A, Wallner M, Kramar R, Prischl FC. Peritonitis following argon plasma coagulation of colonic angiodysplasia in a CAPD patient–an avoidable complication? Perit Dial Int. 2005; 25:500–502.17. Macrae FA, Tan KG, Williams CB. Towards safer colonoscopy: a report on the complications of 5000 diagnostic or therapeutic colonoscopies. Gut. 1983; 24:376–383.
Article18. Bunchorntavakul C, Chavalitdhamrong D. Bacterial infections other than spontaneous bacterial peritonitis in cirrhosis. World J Hepatol. 2012; 4:158–168.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Two Cases of Asymptomatic Pneumoperitoneum after Argon Plasma Coagulation Treatment
- A Case of Huge Gastric Angiodysplasia Treated with Argon Plasma Coagulation
- A case of gastric antral vascular ectasia treated with argon plasma coagulation
- A Case of Argon Plasma Coagulation Therapy for Hemorrhagic Radiation-induced Gastritis
- Direct cholangioscopy with argon plasma coagulation of an intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the bile duct