J Korean Acad Prosthodont.
2016 Apr;54(2):152-159. 10.4047/jkap.2016.54.2.152.
Implant supported fixed prosthesis for complete edentulous maxilla with severe alveolar ridge resorption: A case report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, KEPCO Medical Center, Seoul, Republic of Korea. eeeze@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Periodontology, KEPCO Medical Center, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
- KMID: 2162392
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jkap.2016.54.2.152
Abstract
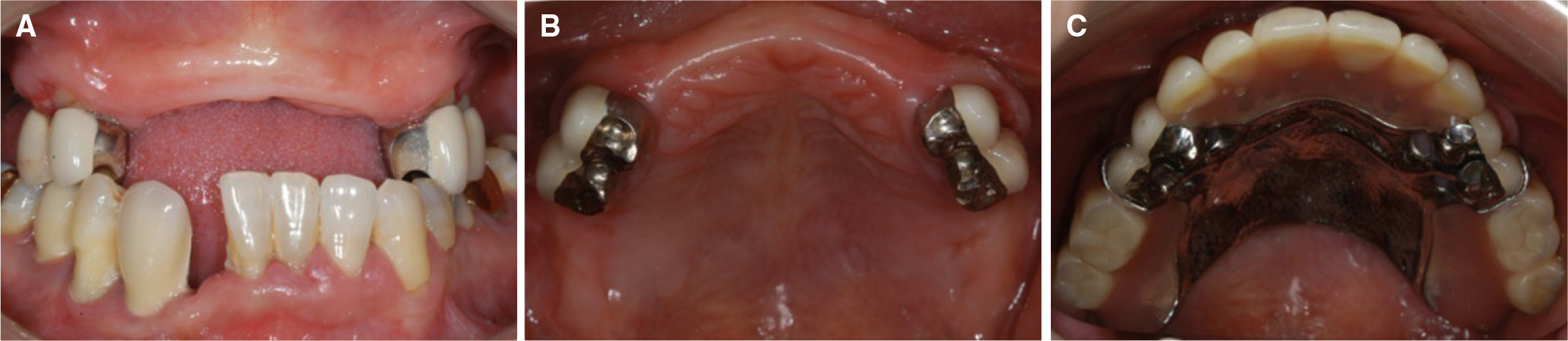
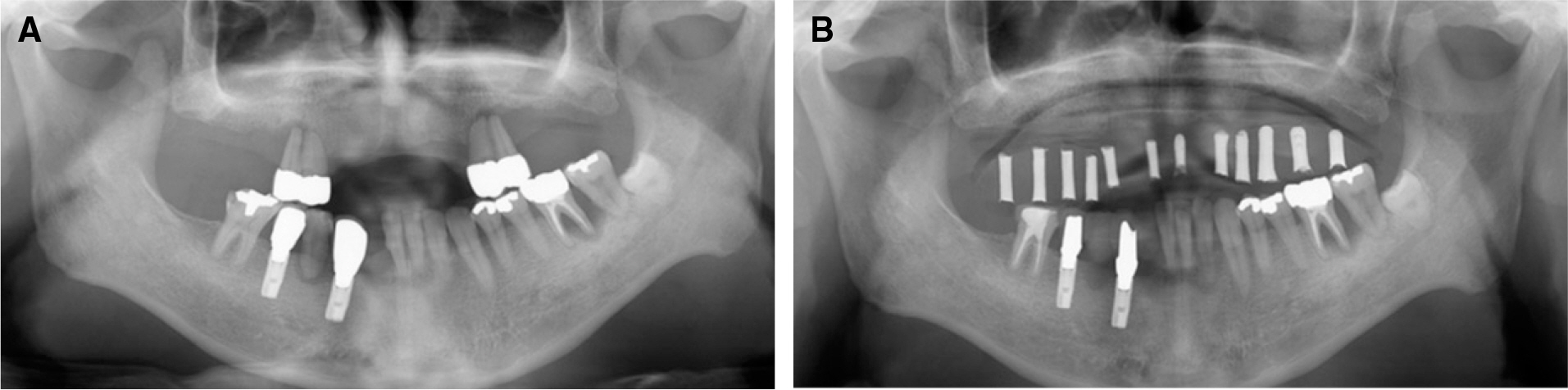
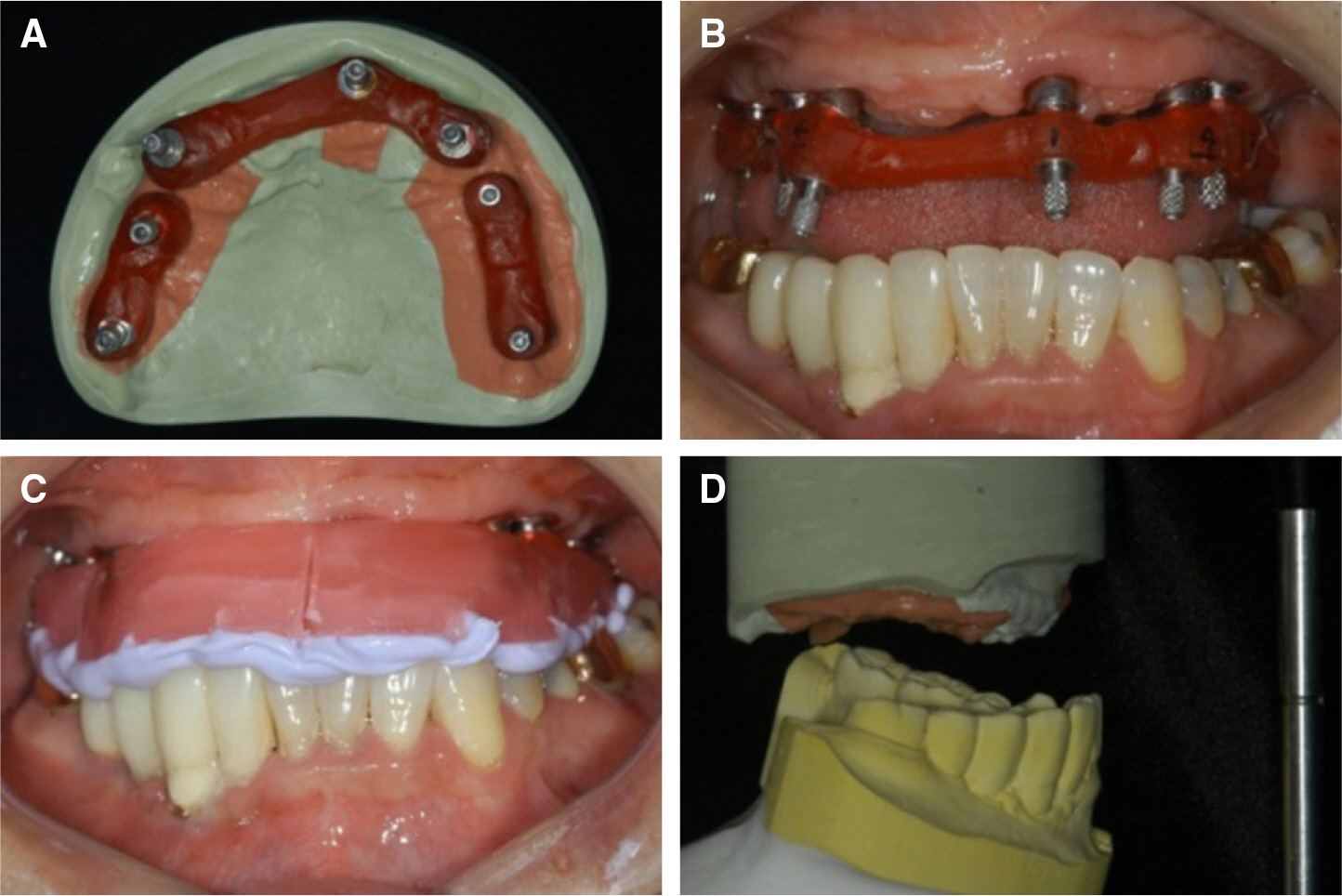
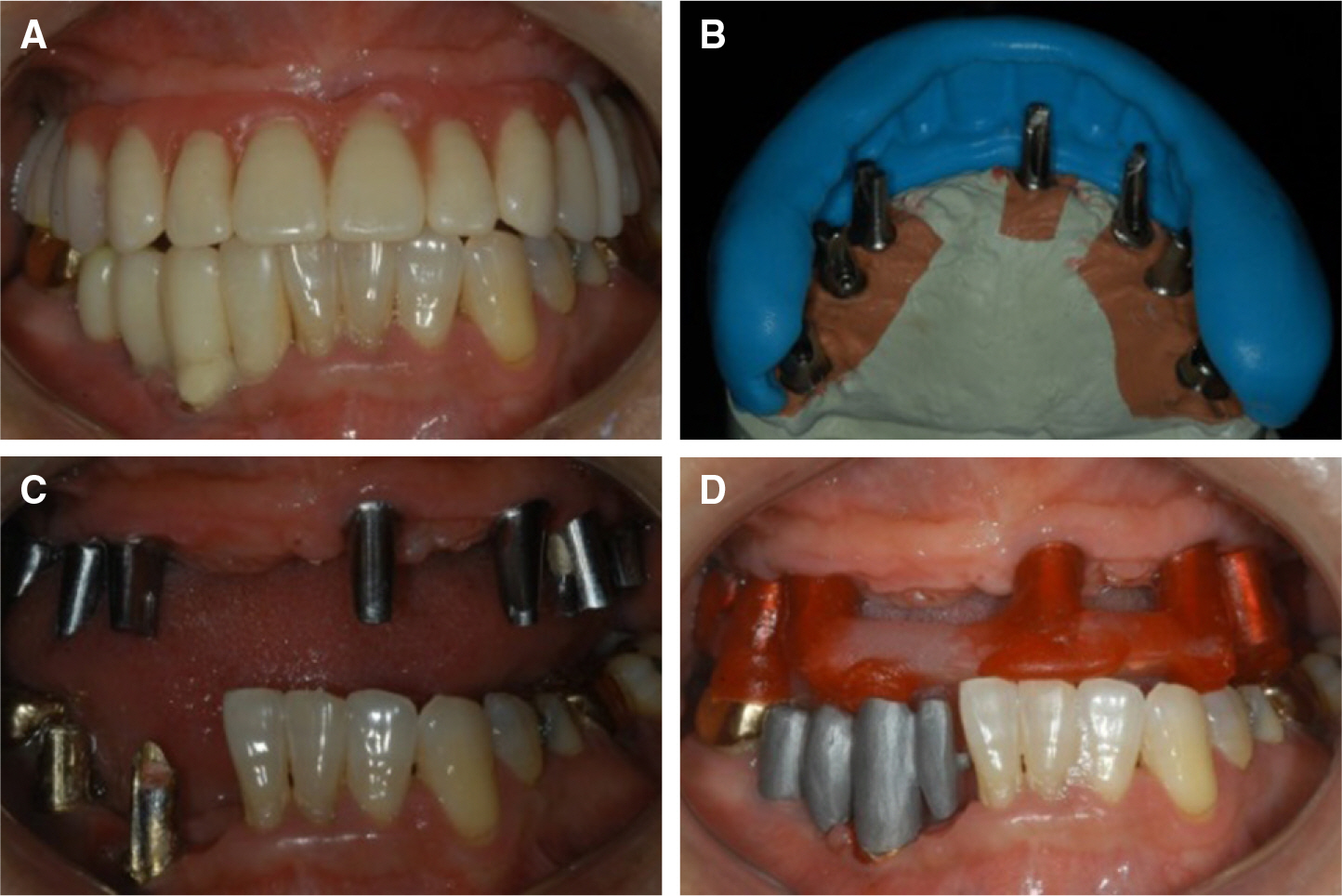
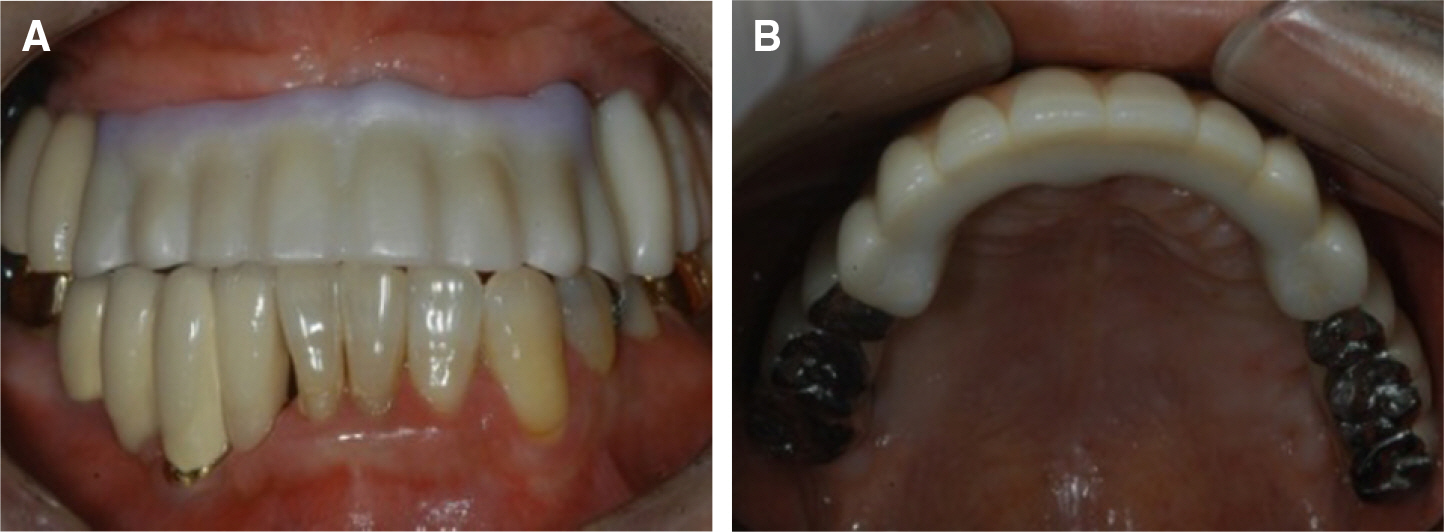
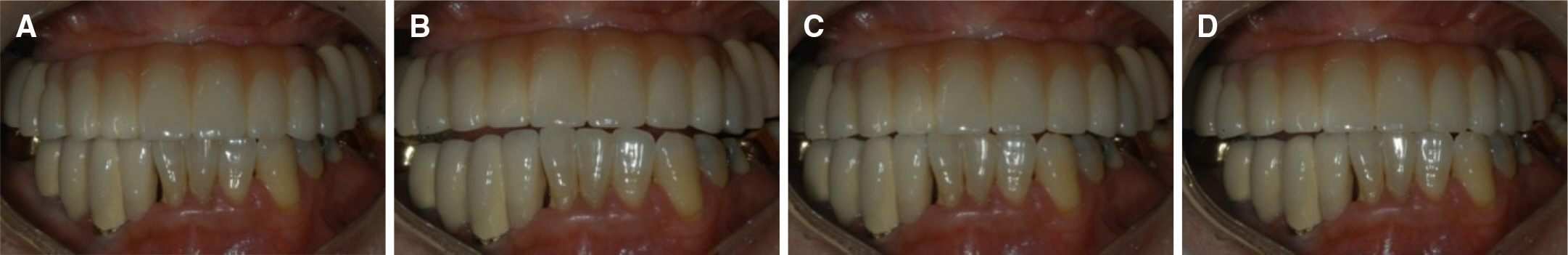
- Implant fixed prosthesis for the complete edentulous maxilla provides significant benefits in the aspects of functions and esthetics compared with the conventional denture. Implant supported fixed prosthesis are totally supported by implant, and thus stabilizes the prosthesis to the maximum degree as possible. Also, the improved retention and stability of fixed prosthesis enhance patients' psychological and psychosocial health. This clinical presentation describes a maxillary full arch implant-supported fixed prosthesis in complete maxillary edentulous patient who showed vertical and horizontal alveolar bone resorption in the anterior ridge. To rehabilitate the esthetics and proper lip support, the zirconia framework was fabricated and the pink porcelain was veneered to reproduce the natural gingival tissue. After 9 months of follow up, the restorations were maintained without complications and the patient was satisfied with the restoration both functionally and esthetically.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1.Misch CE. Contemporary Implant Dentistry. 3rd ed.St. Louis: CV Mosby;2009. p. 3–25.2.Feine JS., Carlsson GE., Awad MA., Chehade A., Duncan WJ., Gizani S., Head T., Lund JP., MacEntee M., Mericske-Stern R., Mojon P., Morais J., Naert I., Payne AG., Penrod J., Stoker GT., Tawse-Smith A., Taylor TD., Thomason JM., Thomson WM., Wismeijer D. The McGill consensus statement on overdentures. Mandibular two-implant overdentures as first choice standard of care for edentulous patients. Montreal, Quebec, May 24-25, 2002. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2002. 17:601–2.3.Drago C., Carpentieri J. Treatment of maxillary jaws with dental implants: guidelines for treatment. J Prosthodont. 2011. 20:336–47.
Article4.Misch CE. Contemporary Implant Dentistry. 3rd ed.St. Louis: CV Mosby;2009. p. 92–104.5.Wheeler RC. The permanent maxillary central incisors. In Wheeler RC (ed): Dental Anatomy, Physiology and Occlusion. 5th ed.Philadelphia: Saunders;1974. p. 144.6.Seibert JS. Reconstruction of deformed, partially edentulous ridges, using full thickness onlay grafts. Part I. Technique and wound healing. Compend Contin Educ Dent. 1983. 4:437–53.7.Misch CE. Contemporary Implant Dentistry. 3rd ed.St. Louis: CV Mosby;2009. p. 367–88.8.Misch CE. Dental Implant Prosthetics. 2nd ed.Elsevier: Mosby;2014. p. 829–73.9.Al-Amleh B., Lyons K., Swain M. Clinical trials in zirconia: a systematic review. J Oral Rehabil. 2010. 37:641–52.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Full mouth rehabilitation of fully edentulous patient with implant-supported fixed prosthesis preceding bone graft: A case report
- Implant Surgery for Fixed Implant-supported Prostheses in the Edentulous Mandible: A Case Report
- ‘All-on-4’ fixed implant supported prosthesis restoration using digital workflow: a case report
- Implant supported prosthetic rehabilitation of severely atrophic mandible with fixed detachable prosthesis
- A case of maxilla implant overdenture using Pekkton telescopic attachment with severe alveolar bone resorption