J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg.
2016 Mar;18(1):38-41. 10.7461/jcen.2016.18.1.38.
Open-cell Stent Deployment across the Wide Neck of a Large Middle Cerebral Aneurysm Using the Stent Anchor Technique
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Hiroshima University Graduate School of Biomedical and Health Sciences, Hiroshima, Japan. sakamoto@hiroshima-u.ac.jp
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Araki Neurosurgical Hospital, Hiroshima, Japan.
- KMID: 2161701
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2016.18.1.38
Abstract
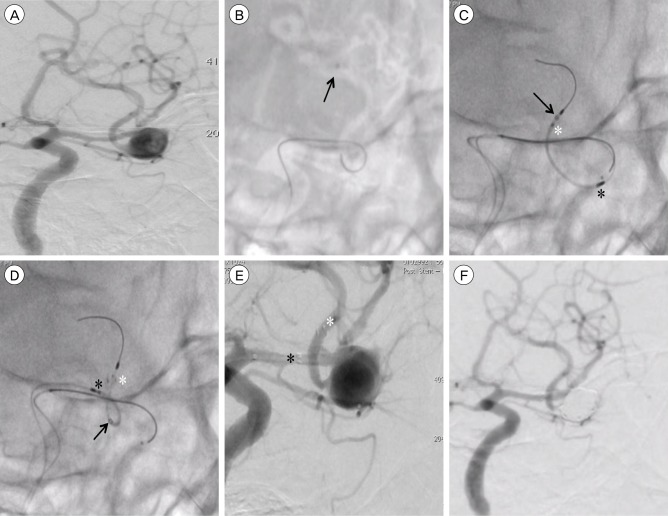
- We describe a case of successful open-cell stent deployment across the wide neck of a large middle cerebral artery aneurysm using the stent anchor technique. A microcatheter was looped through the aneurysm and navigated into a distal vessel across the aneurysm neck. Although the loop of the microcatheter in the aneurysm straightened as it was gently withdrawn, the microcatheter again protruded into the aneurysm by open-cell stent navigation. The stent was partially deployed in a vessel distal to the aneurysm neck, withdrawn slowly to straighten the loop of the microcatheter in the aneurysm, and completely deployed across the aneurysm neck. After successful stent deployment, stent-assisted coil embolization was performed without complications. The stent anchor technique was successfully used to deploy an open-cell stent across the aneurysm neck in this case of microcatheter protrusion into the aneurysm during stent navigation.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Edwards L, Kota G, Morris PP. The sea anchor technique: a novel method to aid in stent-assisted embolization of giant cerebral aneurysms. J Neurointerv Surg. 2013; 11. 5(6):e39. PMID: 22952247.
Article2. Effendi K, Sacho RH, Belzile F, Marotta TR. The wire anchor loop traction (WALT) maneuver. J Neurointerv Surg. 2016; 2. 8(2):e7. PMID: 25634903.
Article3. Fargen KM, Velat GJ, Lawson MF, Hoh BL, Mocco J. The stent anchor technique for distal access through a large or giant aneurysm. J Neurointerv Surg. 2013; 7. 5(4):e24. PMID: 22544820.
Article4. Kono K, Okada H, Terada T. A novel neck-sealing balloon technique for distal access through a giant aneurysm. Neurosurgery. 2013; 73(2 Suppl Operative):onsE302–onsE305. discussion onsE305-6PMID: 23756749.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Waffle-Cone Technique Using Solitaire AB Stent
- Temporary Semi-Jailing Technique for Coil Embolization of Wide-Neck Aneurysm with Small Caliber Parent Artery Following Incomplete Clipping
- Application of the Woven EndoBridge Device in the Treatment of Multiple Aneurysms of the Distal Posterior Cerebral Artery: A Case Report
- Balloon Anchor Technique for Pipeline Embolization Device Deployment Across the Neck of a Giant Intracranial Aneurysm
- Very Late Stent Thrombosis after Sole Stent-Assisted Coiling at the Paraclinoid Giant Aneurysm : Could Prophylactic Antiplatelet Therapy Be Ceased at the Only 1 Year after Procedure?