J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2014 Oct;56(4):344-347. 10.3340/jkns.2014.56.4.344.
Very Late Stent Thrombosis after Sole Stent-Assisted Coiling at the Paraclinoid Giant Aneurysm : Could Prophylactic Antiplatelet Therapy Be Ceased at the Only 1 Year after Procedure?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. nslcy@dsmc.or.kr
- KMID: 2018087
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2014.56.4.344
Abstract
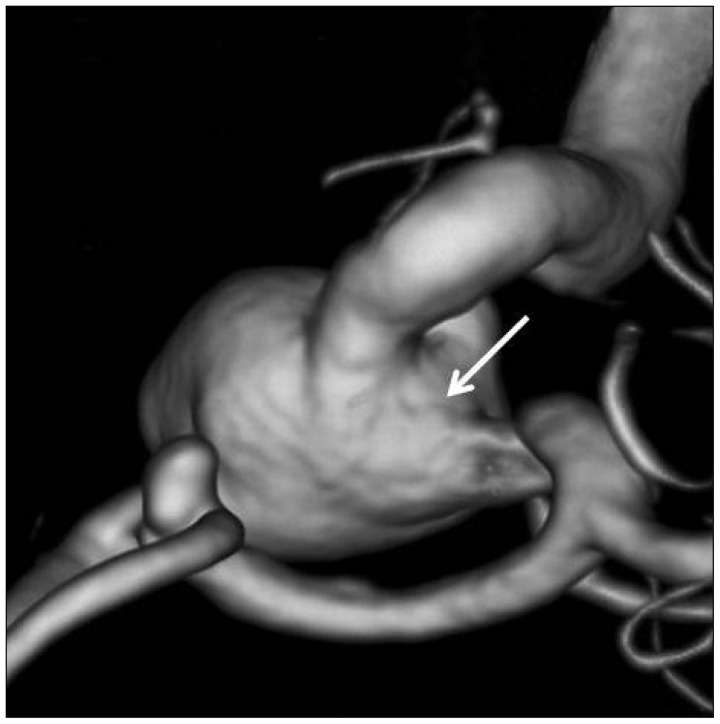
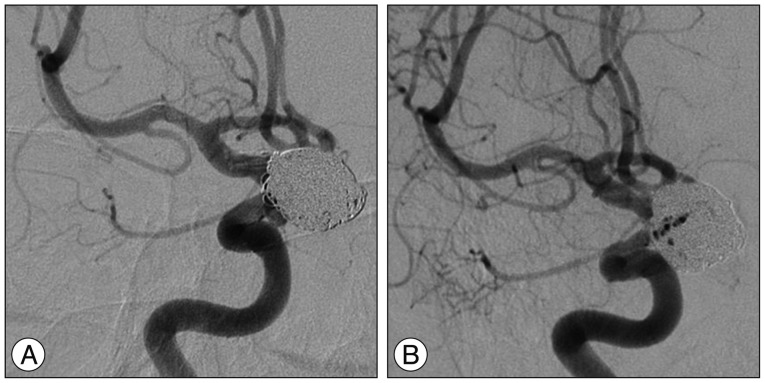
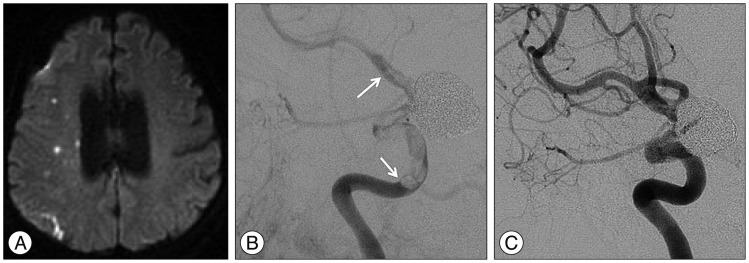
- Stent thrombosis is a major limitation of stent-assisted coiling, which is an effective method for treating wide-necked aneurysms. Although early in-stent thrombosis has been reported, very late stent thrombosis (VLST) (>1 year) has not been reported following implantation of a single self-expandable stent designed for coiling. Herein, the authors present a case of VLST that occurred 14 months after single stent implantation in a large paraclinoid aneurysm with an ultra-wide neck involving the parent artery circumferentially. This case indicates the need for establishing guidelines regarding the optimal duration of prophylactic antiplatelet therapy following stent-assisted coiling, which remains undefined in the neuroendovascular field.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Amenta PS, Dalyai RT, Kung D, Toporowski A, Chandela S, Hasan D, et al. Stent-assisted coiling of wide-necked aneurysms in the setting of acute subarachnoid hemorrhage : experience in 65 patients. Neurosurgery. 2012; 70:1415–1429. discussion 1429. PMID: 22186840.
Article2. Cutlip DE, Windecker S, Mehran R, Boam A, Cohen DJ, van Es GA, et al. Clinical end points in coronary stent trials : a case for standardized definitions. Circulation. 2007; 115:2344–2351. PMID: 17470709.3. Ebrahimi N, Claus B, Lee CY, Biondi A, Benndorf G. Stent conformity in curved vascular models with simulated aneurysm necks using flat-panel CT : an in vitro study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007; 28:823–829. PMID: 17494650.4. Farb A, Burke AP, Kolodgie FD, Virmani R. Pathological mechanisms of fatal late coronary stent thrombosis in humans. Circulation. 2003; 108:1701–1706. PMID: 14504181.
Article5. Farb A, Sangiorgi G, Carter AJ, Walley VM, Edwards WD, Schwartz RS, et al. Pathology of acute and chronic coronary stenting in humans. Circulation. 1999; 99:44–52. PMID: 9884378.
Article6. Fargen KM, Hoh BL, Welch BG, Pride GL, Lanzino G, Boulos AS, et al. Long-term results of enterprise stent-assisted coiling of cerebral aneurysms. Neurosurgery. 2012; 71:239–244. discussion 244. PMID: 22472556.
Article7. Fiorella D, Hsu D, Woo HH, Tarr RW, Nelson PK. Very late thrombosis of a pipeline embolization device construct : case report. Neurosurgery. 2010; 67(3 Suppl Operative):onsE313–onsE314. discussion onsE314. PMID: 20679914.8. Grewe PH, Deneke T, Machraoui A, Barmeyer J, Müller KM. Acute and chronic tissue response to coronary stent implantation : pathologic findings in human specimen. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2000; 35:157–163. PMID: 10636274.
Article9. Grines CL, Bonow RO, Casey DE Jr, Gardner TJ, Lockhart PB, Moliterno DJ, et al. Prevention of premature discontinuation of dual antiplatelet therapy in patients with coronary artery stents : a science advisory from the American Heart Association, American College of Cardiology, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, American College of Surgeons, and American Dental Association, with representation from the American College of Physicians. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007; 49:734–739. PMID: 17291948.10. Kanaan H, Jankowitz B, Aleu A, Kostov D, Lin R, Lee K, et al. In-stent thrombosis and stenosis after neck-remodeling device-assisted coil embolization of intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurgery. 2010; 67:1523–1532. discussion 1532-1533. PMID: 21107183.
Article11. Kim DJ, Suh SH, Lee JW, Kim BM, Lee JW, Huh SK, et al. Influences of stents on the outcome of coil embolized intracranial aneurysms : comparison between a stent-remodeled and non-remodeled treatment. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2010; 152:423–429. PMID: 19806305.
Article12. King SB 3rd, Smith SC Jr, Hirshfeld JW Jr, Jacobs AK, Morrison DA, Williams DO, et al. 2007 focused update of the ACC/AHA/SCAI 2005 guideline update for percutaneous coronary intervention : a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008; 51:172–209. PMID: 18191745.
Article13. Krischek O, Miloslavski E, Fischer S, Shrivastava S, Henkes H. A comparison of functional and physical properties of self-expanding intracranial stents [Neuroform3, Wingspan, Solitaire, Leo+, Enterprise]. Minim Invasive Neurosurg. 2011; 54:21–28. PMID: 21506064.
Article14. Lee CY, Ryu CW, Koh JS, Kim EJ. Total occlusion of the internal carotid artery by subacute in-stent thrombosis and subsequent spontaneous recanalization after stent-assisted coil embolization. Neurointervention. 2011; 6:38–41. PMID: 22125748.
Article15. Lin RJ, Tang SC, Jeng JS. Stroke due to late in-stent thrombosis following carotid stenting. Acta Neurol Taiwan. 2011; 20:161–162. PMID: 21739397.16. Lopes D, Sani S. Histological postmortem study of an internal carotid artery aneurysm treated with the Neuroform stent. Neurosurgery. 2005; 56:E416. discussion E416. PMID: 15670395.
Article17. Luo CB, Teng MM, Chang FC, Lin CJ, Guo WY, Chang CY. Stent-assisted coil embolization of intracranial aneurysms : a single center experience. J Chin Med Assoc. 2012; 75:322–328. PMID: 22824046.
Article18. Mocco J, Fargen KM, Albuquerque FC, Bendok BR, Boulos AS, Carpenter JS, et al. Delayed thrombosis or stenosis following enterprise-assisted stent-coiling : is it safe? Midterm results of the interstate collaboration of enterprise stent coiling. Neurosurgery. 2011; 69:908–913. discussion 913-914. PMID: 21670718.19. Szikora I, Berentei Z, Kulcsar Z, Barath K, Berez A, Bose A, et al. Endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms with parent vessel reconstruction using balloon and self expandable stents. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2006; 148:711–723. discussion 723. PMID: 16708169.
Article20. Thorell WE, Chow MM, Woo HH, Masaryk TJ, Rasmussen PA. Y-configured dual intracranial stent-assisted coil embolization for the treatment of wide-necked basilar tip aneurysms. Neurosurgery. 2005; 56:1035–1040. discussion 1035-1040. PMID: 15854251.21. Valgimigli M, Campo G, Monti M, Vranckx P, Percoco G, Tumscitz C, et al. Short- versus long-term duration of dual-antiplatelet therapy after coronary stenting : a randomized multicenter trial. Circulation. 2012; 125:2015–2026. PMID: 22438530.
Article22. Wright RS, Anderson JL, Adams CD, Bridges CR, Casey DE Jr, Ettinger SM, et al. 2011 ACCF/AHA focused update incorporated into the ACC/AHA 2007 Guidelines for the Management of Patients with Unstable Angina/Non-ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction : a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines developed in collaboration with the American Academy of Family Physicians, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, and the Society of Thoracic Surgeons. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011; 57:e215–e367. PMID: 21545940.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Late Stent Thrombosis Associated with Late Stent Malapposition after Drug-Eluting Stenting: A Case Report
- A Complicated Case of Endovascular Stent Assisted Coil Embolization of an Aneurysm
- Delayed Self-expansion Phenomenon as a Complication of Neuroform Stent Assisted Coiling for Ruptured Intracranial Aneurysm
- Feasibility of single antiplatelet therapy after stent assisted coiling for ruptured intracranial aneurysms
- Two cases of acute ischemic stroke associated with strut exposure in the cerebral artery lumen after stent-assisted coil embolization