Investig Magn Reson Imaging.
2016 Mar;20(1):36-43. 10.13104/imri.2016.20.1.36.
Non-Invasive in vivo Loss Tangent Imaging: Thermal Sensitivity Estimation at the Larmor Frequency
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea. donghyunkim@yonsei.ac.kr
- 2Center for Neuroscience Imaging Research, Institute for Basic Science, Sungkyunkwan University, Korea.
- KMID: 2161368
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2016.20.1.36
Abstract
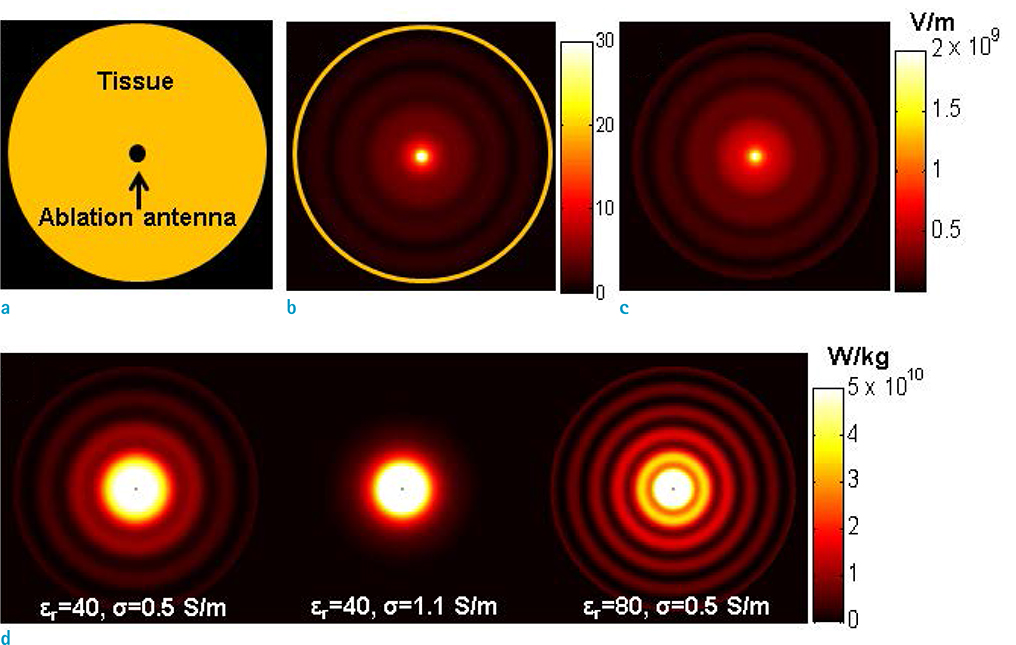
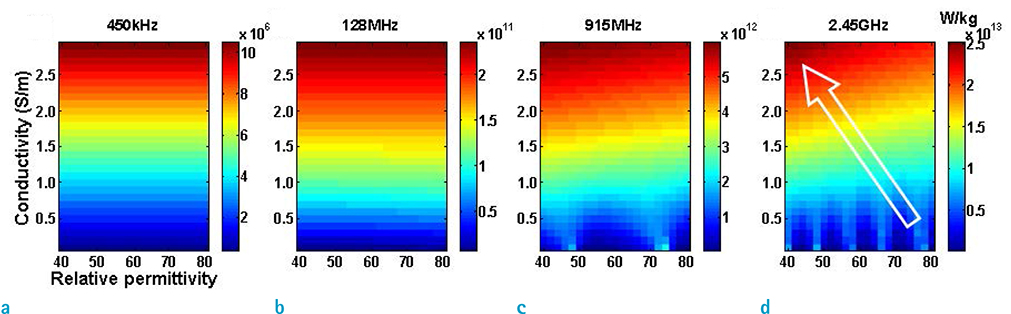
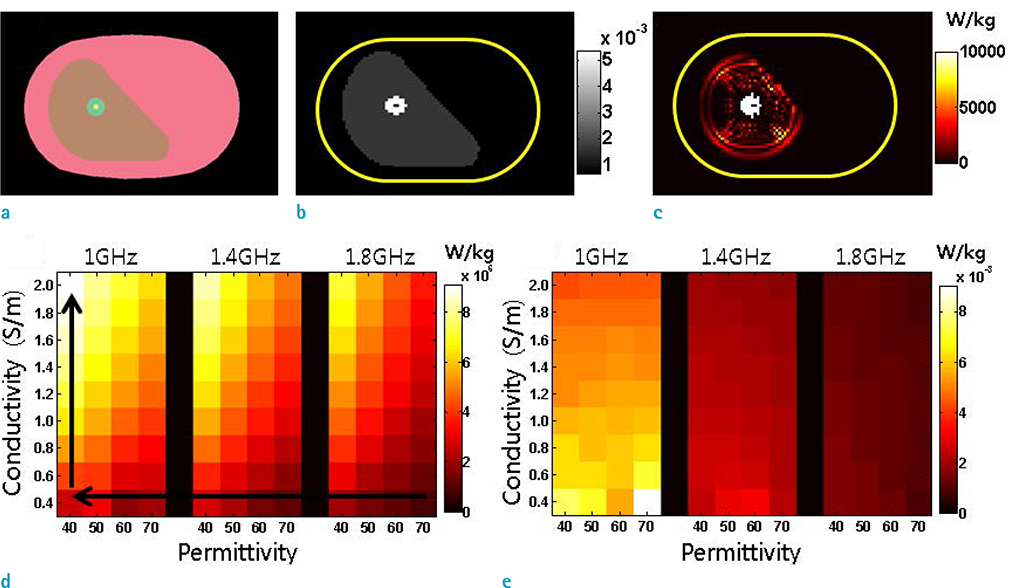
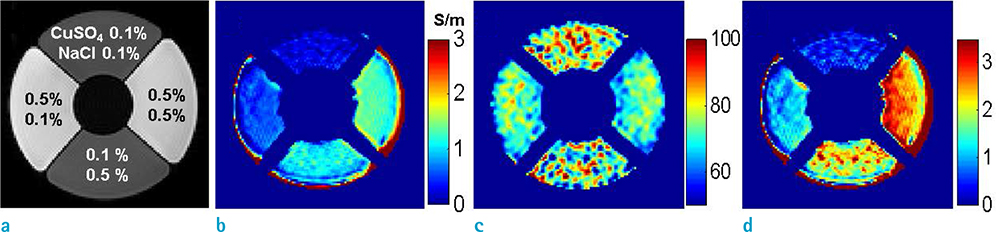
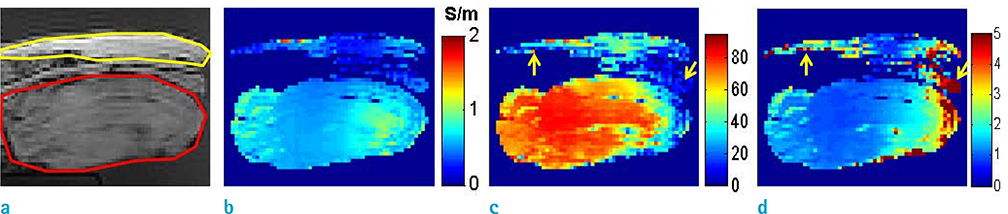
- Visualization of the tissue loss tangent property can provide distinct contrast and offer new information related to tissue electrical properties. A method for non-invasive imaging of the electrical loss tangent of tissue using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was demonstrated, and the effect of loss tangent was observed through simulations assuming a hyperthermia procedure. For measurement of tissue loss tangent, radiofrequency field maps (B1+ complex map) were acquired using a double-angle actual flip angle imaging MRI sequence. The conductivity and permittivity were estimated from the complex valued B1+ map using Helmholtz equations. Phantom and ex-vivo experiments were then performed. Electromagnetic simulations of hyperthermia were carried out for observation of temperature elevation with respect to loss tangent. Non-invasive imaging of tissue loss tangent via complex valued B1+ mapping using MRI was successfully conducted. Simulation results indicated that loss tangent is a dominant factor in temperature elevation in the high frequency range during hyperthermia. Knowledge of the tissue loss tangent value can be a useful marker for thermotherapy applications.
Figure
Reference
-
1. van der Put RW, Kerkhof EM, Raaymakers BW, Jurgenliemk-Schulz IM, Lagendijk JJ. Contour propagation in MRI-guided radiotherapy treatment of cervical cancer: the accuracy of rigid, non-rigid and semi-automatic registrations. Phys Med Biol. 2009; 54:7135–7150.2. McDannold N, Clement GT, Black P, Jolesz F, Hynynen K. Transcranial magnetic resonance imaging-guided focused ultrasound surgery of brain tumors: initial findings in 3 patients. Neurosurgery. 2010; 66:323–332.3. Fuentes D, Walker C, Elliott A, Shetty A, Hazle JD, Stafford RJ. Magnetic resonance temperature imaging validation of a bioheat transfer model for laser-induced thermal therapy. Int J Hyperthermia. 2011; 27:453–464.4. Hynynen K, Pomeroy O, Smith DN, et al. MR imaging-guided focused ultrasound surgery of fibroadenomas in the breast: a feasibility study. Radiology. 2001; 219:176–185.5. Peyman A, Gabriel C, Benedickter HR, Frohlich J. Dielectric properties of human placenta, umbilical cord and amniotic fluid. Phys Med Biol. 2011; 56:N93–N98.6. Brace CL. Microwave tissue ablation: biophysics, technology, and applications. Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 2010; 38:65–78.7. Garrean S, Hering J, Saied A, Helton WS, Espat NJ. Radiofrequency ablation of primary and metastatic liver tumors: a critical review of the literature. Am J Surg. 2008; 195:508–520.8. Goldberg SN, Grassi CJ, Cardella JF, et al. Image-guided tumor ablation: standardization of terminology and reporting criteria. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2009; 20:S377–S390.9. Haemmerich D. Biophysics of radiofrequency ablation. Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 2010; 38:53–63.10. Pennes HH. Analysis of tissue and arterial blood temperatures in the resting human forearm. J Appl Physiol. 1948; 1:93–122.11. Gajsek P, Hurt WD, Ziriax JM, Mason PA. Parametric dependence of SAR on permittivity values in a man model. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2001; 48:1169–1177.12. Voigt T, Katscher U, Doessel O. Quantitative conductivity and permittivity imaging of the human brain using electric properties tomography. Magn Reson Med. 2011; 66:456–466.13. van Lier AL, Brunner DO, Pruessmann KP, et al. B1(+) phase mapping at 7 T and its application for in vivo electrical conductivity mapping. Magn Reson Med. 2012; 67:552–561.14. Seo JK, Kim MO, Lee J, et al. Error analysis of nonconstant admittivity for MR-based electric property imaging. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2012; 31:430–437.15. Choi N, Lee J, Kim MO, Shin J, Kim DH. A modified multiecho AFI for simultaneous B1(+) magnitude and phase mapping. Magn Reson Imaging. 2014; 32:314–320.16. van den Bergen B, Stolk CC, Berg JB, Lagendijk JJ, Van den. Ultra fast electromagnetic field computations for RF multi-transmit techniques in high field MRI. Phys Med Biol. 2009; 54:1253–1264.17. Christ A, Kainz W, Hahn EG, et al. The Virtual Family--development of surface-based anatomical models of two adults and two children for dosimetric simulations. Phys Med Biol. 2010; 55:N23–N38.18. Shin J, Kim MJ, Lee J, et al. Initial study on in vivo conductivity mapping of breast cancer using MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015; 42:371–378.19. Wen H. Noninvasive quantitative mapping of conductivity and dielectric distributions using RF wave propagation effects in high-field MRI. Proceedings of the SPIE. 2003; 5030:471–477.20. Hoult DI. The principle of reciprocity in signal strength calculations - a mathematical guide. Concept Magnetic Res. 2000; 12:173–187.21. Renou R, Ding M, Zhu H, Szymczyk A, Malfreyt P, Ghoufi A. Concentration dependence of the dielectric permittivity, structure, and dynamics of aqueous NaCl solutions: comparison between the Drude oscillator and electronic continuum models. J Phys Chem B. 2014; 118:3931–3940.22. Akilan C. Thermodynamic and related studies of aqueous copper (II) sulfate solutions. Australia: Murdoch University;2008. 87–134. PhD Dissertation.23. Weast RC, Astle MJ, Beyer WH. CRC handbook of chemistry and physics. 69th ed. Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press;1988.24. Wolf AV. Aqueous solutions and body fluids. Their concentrative properties and conversion tables. New York: Hoeber Medical Division Harper & Row Publishers;1966.25. Huang L, Schweser F, Herrmann KH, Kramer M, Deistung A, Reichenbach JR. A Monte Carlo method for overcoming the edge artifacts in MRI-based electrical conductivity mapping. In : Proc 22nd Annual Meeting of ISMRM; Milan, Italy: 2014. p. 3190.26. Stollberger R, Wach P. Imaging of the active B1 field in vivo. Magn Reson Med. 1996; 35:246–251.27. Peyman A, Holden SJ, Watts S, Perrott R, Gabriel C. Dielectric properties of porcine cerebrospinal tissues at microwave frequencies: in vivo, in vitro and systematic variation with age. Phys Med Biol. 2007; 52:2229–2245.28. Cole KS, Cole RH. Dispersion and absorption in dielectrics I. Alternating current characteristics. J Chem Phys. 1941; 9:34.29. Peyman A, Gabriel C. Cole-Cole parameters for the dielectric properties of porcine tissues as a function of age at microwave frequencies. Phys Med Biol. 2010; 55:N413–N419.30. Solazzo SA, Liu Z, Lobo SM, et al. Radiofrequency ablation: importance of background tissue electrical conductivity--an agar phantom and computer modeling study. Radiology. 2005; 236:495–502.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Quantitative Conductivity Estimation Error due to Statistical Noise in Complex B1+ Map
- Visual Field Ratio According to Distance in the Near Tangent Screen Test
- High-contrast spectroscopic photoacoustic characterization of thermal tissue ablation in the visible spectrum
- Design of a stimulation protocol to predict temperature distribution in subcutaneous tissue using the finite element model
- Problems of Application to McBride Disability Evaluation in Loss of Visual Effciency Patients