J Korean Diabetes.
2016 Mar;17(1):24-29. 10.4093/jkd.2016.17.1.24.
Mechanism of Hypoglycemia-Associated Cardiovascular Diseases
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. lwjatlas@amc.seoul.kr
- KMID: 2161127
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4093/jkd.2016.17.1.24
Abstract
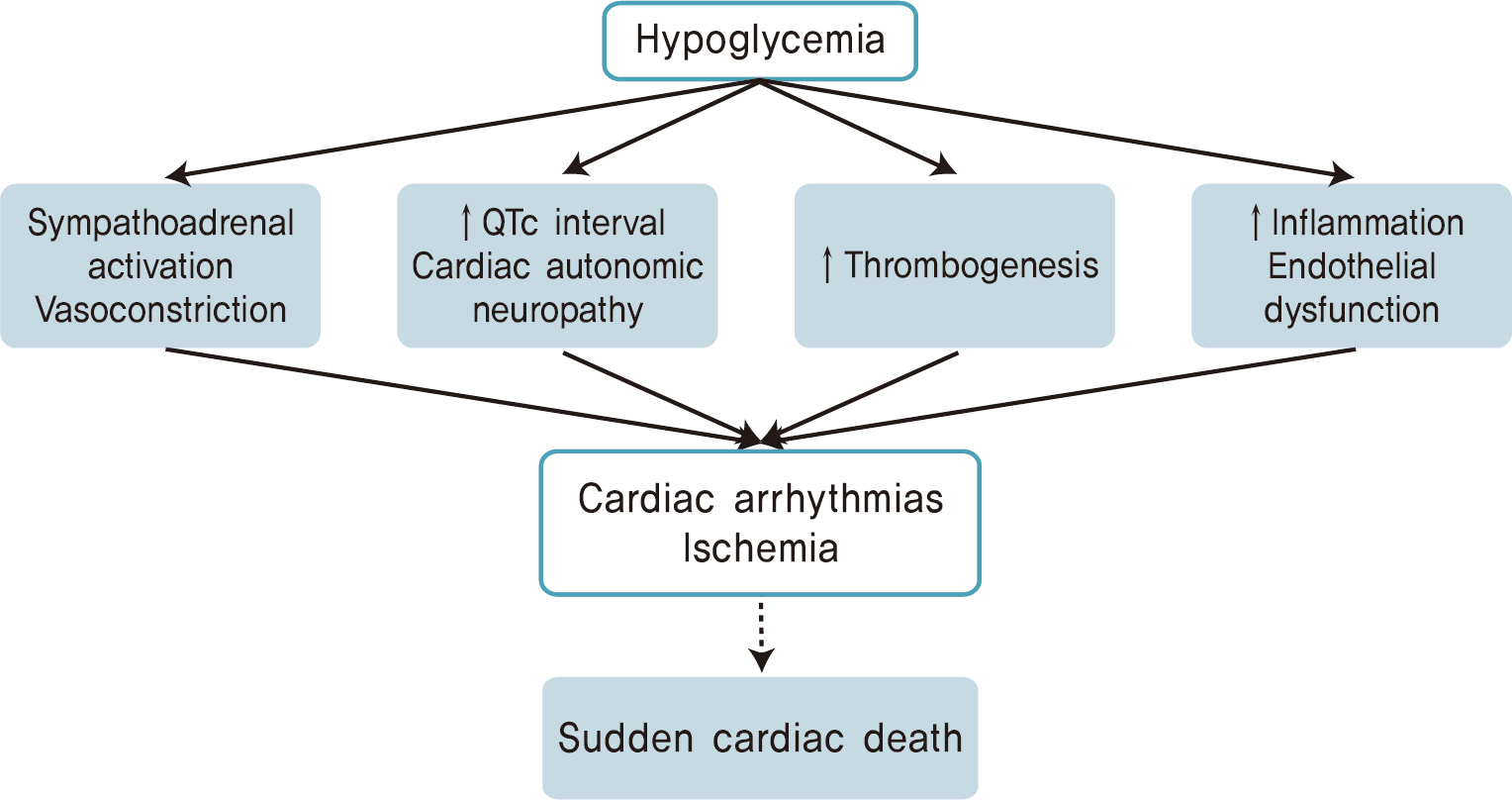
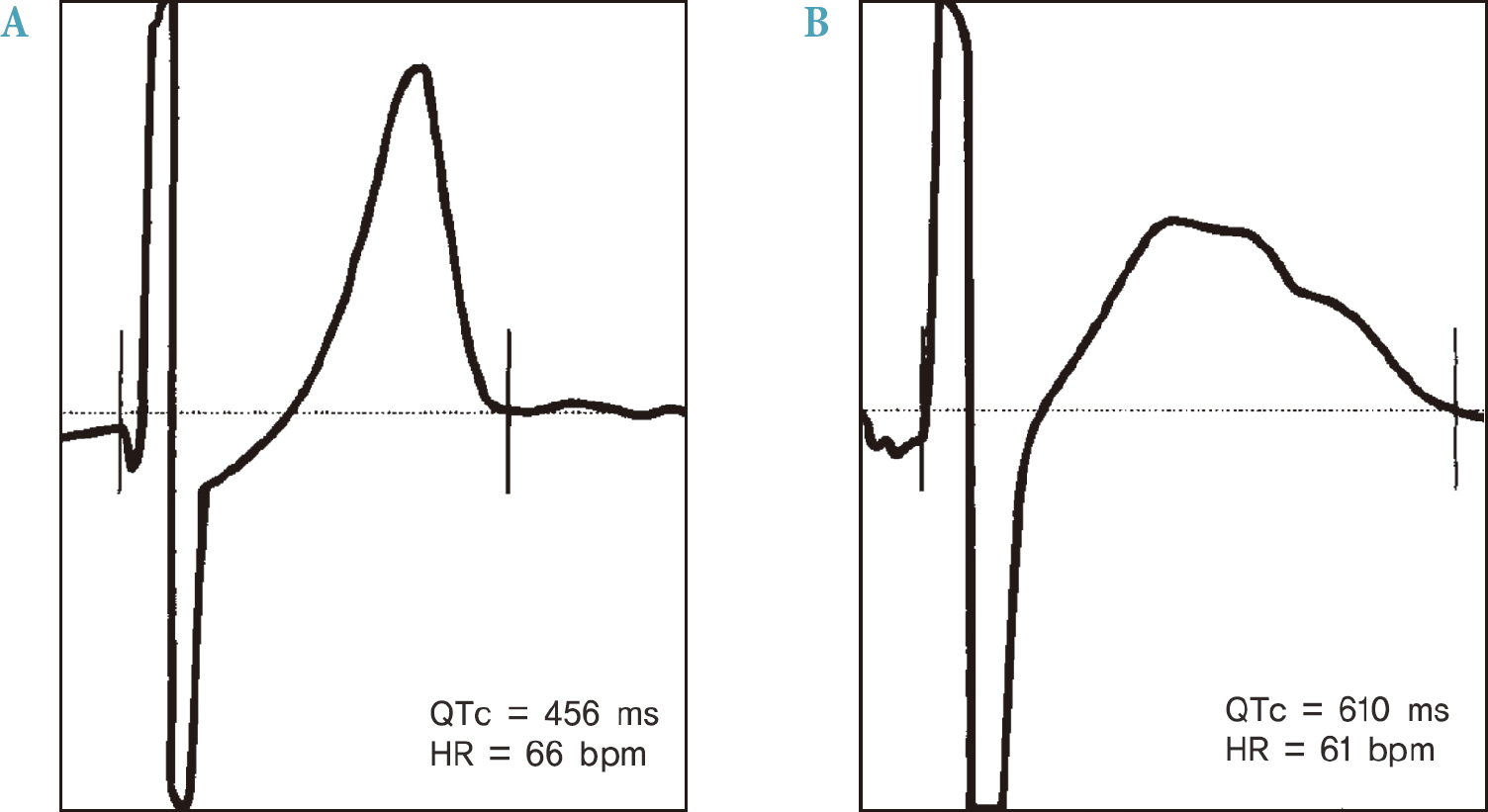
- Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death in patients with diabetes mellitus. However, the benefit of intensive glycemic control in reducing CVD is unclear. In large clinical trials, intensive glycemic control was associated with increased incidence of hypoglycemia and all-cause mortality. Although it is uncertain whether hypoglycemia is a direct cause of CVD, a marker of vulnerability, or both, numerous studies have reported that hypoglycemia is associated with increased cardiovascular events such as cardiac arrhythmia and ischemia. The potential mechanisms of hypoglycemia-associated CVD include sympathoadrenal activation, repolarization abnormality, cardiac autonomic neuropathy, increased thrombogenesis, inflammatory reaction, and endothelial dysfunction. In this article, we review the evidence of an association of hypoglycemia with CVD in patients with diabetes and discuss the possible mechanisms through which hypoglycemia might result in adverse cardiovascular outcomes.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes Study Group. Gerstein HC, Miller ME, Byington RP, Goff DC Jr, Bigger JT, Buse JB, Cushman WC, Genuth S, IsmailBeigi F, Grimm RH Jr, Probstfield JL, Simons-Morton DG, Friedewald WT. Effects of intensive glucose lowering in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008; 358:2545–59.2. ADVANCE Collaborative Group. Patel A, MacMahon S, Chalmers J, Neal B, Billot L, Woodward M, Marre M, Cooper M, Glasziou P, Grobbee D, Hamet P, Harrap S, Heller S, Liu L, Mancia G, Mogensen CE, Pan C, Poulter N, Rodgers A, Williams B, Bompoint S, de Galan BE, Joshi R, Travert F. Intensive blood glucose control and vascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2008; 358:2560–72.3. Duckworth W, Abraira C, Moritz T, Reda D, Emanuele N, Reaven PD, Zieve FJ, Marks J, Davis SN, Hayward R, Warren SR, Goldman S, McCarren M, Vitek ME, Henderson WG, Huang GD. VADT Investigators. Glucose control and vascular complications in veterans with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2009; 360:129–39.
Article4. Goto A, Arah OA, Goto M, Terauchi Y, Noda M. Severe hypoglycaemia and cardiovascular disease: systematic review and metaanalysis with bias analysis. BMJ. 2013; 347:f4533.
Article5. Johnston SS, Conner C, Aagren M, Smith DM, Bouchard J, Brett J. Evidence linking hypoglycemic events to an increased risk of acute cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2011; 34:1164–70.
Article6. Zhao Y, Campbell CR, Fonseca V, Shi L. Impact of hypoglycemia associated with antihyperglycemic medications on vascular risks in veterans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2012; 35:1126–32.
Article7. Hsu PF, Sung SH, Cheng HM, Yeh JS, Liu WL, Chan WL, Chen CH, Chou P, Chuang SY. Association of clinical symptomatic hypoglycemia with cardiovascular events and total mortality in type 2 diabetes: a nationwide population-based study. Diabetes Care. 2013; 36:894–900.8. Moheet A, Seaquist ER. Hypoglycemia as a driver of cardiovascular risk in diabetes. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2013; 15:351.
Article9. Wright RJ, Newby DE, Stirling D, Ludlam CA, Macdonald IA, Frier BM. Effects of acute insulin-induced hypoglycemia on indices of inflammation: putative mechanism for aggravating vascular disease in diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2010; 33:1591–7.10. Desouza C, Salazar H, Cheong B, Murgo J, Fonseca V. Association of hypoglycemia and cardiac ischemia: a study based on continuous monitoring. Diabetes Care. 2003; 26:1485–9.11. Judson WE, Hollander W. The effects of insulin-induced hypoglycemia in patients with angina pectoris; before and after intravenous hexamethonium. Am Heart J. 1956; 52:198–209.12. Koivikko ML, Karsikas M, Salmela PI, Tapanainen JS, Ruokonen A, Seppänen T, Huikuri HV, Perkiömäki JS. Effects of controlled hypoglycaemia on cardiac repolarisation in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2008; 51:426–35.
Article13. Robinson RT, Harris ND, Ireland RH, Lee S, Newman C, Heller SR. Mechanisms of abnormal cardiac repolarization during insulin-induced hypoglycemia. Diabetes. 2003; 52:1469–74.
Article14. Frier BM, Schernthaner G, Heller SR. Hypoglycemia and cardiovascular risks. Diabetes Care. 2011; 34(Suppl 2):S132–7.
Article15. Marques JL, George E, Peacey SR, Harris ND, Macdonald IA, Cochrane T, Heller SR. Altered ventricular repolarization during hypoglycaemia in patients with diabetes. Diabet Med. 1997; 14:648–54.
Article16. Chow E, Bernjak A, Williams S, Fawdry RA, Hibbert S, Freeman J, Sheridan PJ, Heller SR. Risk of cardiac arrhythmias during hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular risk. Diabetes. 2014; 63:1738–47.
Article17. Gerritsen J, Dekker JM, TenVoorde BJ, Kostense PJ, Heine RJ, Bouter LM, Heethaar RM, Stehouwer CD. Impaired autonomic function is associated with increased mortality, especially in subjects with diabetes, hypertension, or a history of cardiovascular disease: the Hoorn Study. Diabetes Care. 2001; 24:1793–8.18. Cryer PE. Mechanisms of hypoglycemia-associated autonomic failure and its component syndromes in diabetes. Diabetes. 2005; 54:3592–601.
Article19. Davis SN, Galassetti P, Wasserman DH, Tate D. Effects of antecedent hypoglycemia on subsequent counterregulatory responses to exercise. Diabetes. 2000; 49:73–81.
Article20. Adler GK, Bonyhay I, Failing H, Waring E, Dotson S, Freeman R. Antecedent hypoglycemia impairs autonomic cardiovascular function: implications for rigorous glycemic control. Diabetes. 2009; 58:360–6.21. Wright RJ, Frier BM. Vascular disease and diabetes: is hypoglycaemia an aggravating factor? Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2008; 24:353–63.
Article22. Gogitidze Joy N, Hedrington MS, Briscoe VJ, Tate DB, Ertl AC, Davis SN. Effects of acute hypoglycemia on inflammatory and pro-atherothrombotic biomarkers in individuals with type 1 diabetes and healthy individuals. Diabetes Care. 2010; 33:1529–35.
Article23. Razavi Nematollahi L, Kitabchi AE, Stentz FB, Wan JY, Larijani BA, Tehrani MM, Gozashti MH, Omidfar K, Taheri E. Proinflammatory cytokines in response to insulin-induced hypoglycemic stress in healthy subjects. Metabolism. 2009; 58:443–8.
Article24. Dandona P, Chaudhuri A, Dhindsa S. Proinflammatory and prothrombotic effects of hypoglycemia. Diabetes Care. 2010; 33:1686–7.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Severe Hypoglycemia and Cardiovascular Disease in Type 2 Diabetes
- Treatment Strategy for Diabetes with Cardiovascular Disease
- Hypoglycemic Morbidity and Mortality in Diabetes
- Letter: Cardiovascular Disease Predicts Severe Hypoglycemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes (Diabetes Metab J 2015; 39:498-506)
- Response: Cardiovascular Disease Predicts Severe Hypoglycemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes (Diabetes Metab J 2015; 39:498-506)