J Cardiovasc Ultrasound.
2016 Mar;24(1):20-27. 10.4250/jcu.2016.24.1.20.
Incremental Value of Left Atrial Global Longitudinal Strain for Prediction of Post Stroke Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke
- Affiliations
-
- 1Cardiology Division, Severance Cardiovascular Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. cysprs@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Neurology, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2160991
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4250/jcu.2016.24.1.20
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is a well-established risk factor for stroke. Interestingly, ischemic stroke increases risk of incident AF in patients without prior diagnosed AF. For better risk stratification for post-stroke AF, we studied left atrial (LA) size and mechanical function using two-dimensional (2D) speckle tracking imaging in patients with acute ischemic stroke.
METHODS
A total of 227 patients (132 males, age 67 ± 12) with acute ischemic stroke without a history of AF underwent 2D transthoracic echocardiography and speckle tracking imaging for the assessment of LA volume index and global LA longitudinal strain (LALS). From clinical variables, the CHA2DS2-VASc score and National Institute of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) were calculated in each patient. Post-stroke AF was defined as newly diagnosed AF during the course after ischemic stroke.
RESULTS
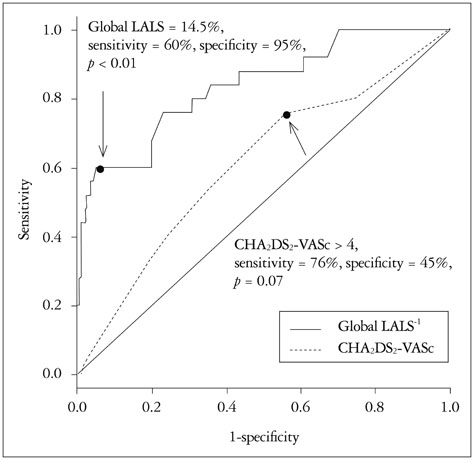
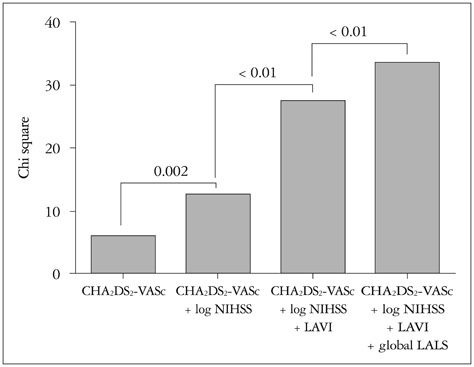
Post-stroke AF occurred in 25 patients (11%). Patients with post-stroke AF were older and showed a higher tendency of CHA2DS2-VASc score, significantly higher log NIHSS, larger LA volume index and lower global LALS than those without. In multivariate analysis, global LALS was an independent predictor for post-stroke AF (hazard ratio 0.90, 95% confidence interval 0.83.0.97, p < 0.01) after controlling for confounding factors. Furthermore, global LALS provided incremental predictive value for post-stroke AF over the CHA2DS2-VASc score, NIHSS, and LA volume index. The global LALS < 14.5% better distinguished post-stroke AF (area under the curve 0.837, sensitivity 60%, specificity 95%, p < 0.01) than CHA2DS2-VASc score.
CONCLUSION
Global LALS as a marker of LA mechanical function has incremental predictive value for post-stroke AF in patients with acute ischemic stroke.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Hannon N, Sheehan O, Kelly L, Marnane M, Merwick A, Moore A, Kyne L, Duggan J, Moroney J, McCormack PM, Daly L, Fitz-Simon N, Harris D, Horgan G, Williams EB, Furie KL, Kelly PJ. Stroke associated with atrial fibrillation--incidence and early outcomes in the north Dublin population stroke study. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2010; 29:43–49.2. Vingerhoets F, Bogousslavsky J, Regli F, Van Melle G. Atrial fibrillation after acute stroke. Stroke. 1993; 24:26–30.3. Sposato LA, Klein FR, Jáuregui A, Ferrúa M, Klin P, Zamora R, Riccio PM, Rabinstein A. Newly diagnosed atrial fibrillation after acute ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack: importance of immediate and prolonged continuous cardiac monitoring. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2012; 21:210–216.4. Schneider C, Malisius R, Krause K, Lampe F, Bahlmann E, Boczor S, Antz M, Ernst S, Kuck KH. Strain rate imaging for functional quantification of the left atrium: atrial deformation predicts the maintenance of sinus rhythm after catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J. 2008; 29:1397–1409.5. Sposato LA, Riccio PM, Hachinski V. Poststroke atrial fibrillation: cause or consequence? Critical review of current views. Neurology. 2014; 82:1180–1186.6. Kuppahally SS, Akoum N, Burgon NS, Badger TJ, Kholmovski EG, Vijayakumar S, Rao SN, Blauer J, Fish EN, Dibella EV, Macleod RS, McGann C, Litwin SE, Marrouche NF. Left atrial strain and strain rate in patients with paroxysmal and persistent atrial fibrillation: relationship to left atrial structural remodeling detected by delayed-enhancement MRI. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2010; 3:231–239.7. Benito B, Gay-Jordi G, Serrano-Mollar A, Guasch E, Shi Y, Tardif JC, Brugada J, Nattel S, Mont L. Cardiac arrhythmogenic remodeling in a rat model of long-term intensive exercise training. Circulation. 2011; 123:13–22.8. Mattle HP. Long-term outcome after stroke due to atrial fibrillation. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2003; 16:Suppl 1. 3–8.9. Francis DA, Heron JR, Clarke M. Ambulatory electrocardiographic monitoring in patients with transient focal cerebral ischaemia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1984; 47:256–259.10. Kessler DK, Kessler KM. Is ambulatory electrocardiography useful in the evaluation of patients with recent stroke? Chest. 1995; 107:916–918.11. Jabaudon D, Sztajzel J, Sievert K, Landis T, Sztajzel R. Usefulness of ambulatory 7-day ECG monitoring for the detection of atrial fibrillation and flutter after acute stroke and transient ischemic attack. Stroke. 2004; 35:1647–1651.12. Sposato LA, Cipriano LE, Saposnik G, Ruíz Vargas E, Riccio PM, Hachinski V. Diagnosis of atrial fibrillation after stroke and transient ischaemic attack: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2015; 14:377–387.13. Vianna-Pinton R, Moreno CA, Baxter CM, Lee KS, Tsang TS, Appleton CP. Two-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography of the left atrium: feasibility and regional contraction and relaxation differences in normal subjects. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2009; 22:299–305.14. Sarvari SI, Haugaa KH, Stokke TM, Ansari HZ, Leren IS, Hegbom F, Smiseth OA, Edvardsen T. Strain echocardiographic assessment of left atrial function predicts recurrence of atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015; 07. 27. [Epub]. DOI: 10.1093/ehjci/jev185.15. Cameli M, Lisi M, Righini FM, Massoni A, Natali BM, Focardi M, Tacchini D, Geyer A, Curci V, Di Tommaso C, Lisi G, Maccherini M, Chiavarelli M, Massetti M, Tanganelli P, Mondillo S. Usefulness of atrial deformation analysis to predict left atrial fibrosis and endocardial thickness in patients undergoing mitral valve operations for severe mitral regurgitation secondary to mitral valve prolapse. Am J Cardiol. 2013; 111:595–601.16. Habibi M, Lima JA, Khurram IM, Zimmerman SL, Zipunnikov V, Fukumoto K, Spragg D, Ashikaga H, Rickard H, Marine JE, Calkins H, Nazarian S. Association of left atrial function and left atrial enhancement in patients with atrial fibrillation: cardiac magnetic resonance study. Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015; 8:e002769.17. Shaikh AY, Maan A, Khan UA, Aurigemma GP, Hill JC, Kane JL, Tighe DA, Mick E, McManus DD. Speckle echocardiographic left atrial strain and stiffness index as predictors of maintenance of sinus rhythm after cardioversion for atrial fibrillation: a prospective study. Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2012; 10:48.18. Adams HP Jr, Bendixen BH, Kappelle LJ, Biller J, Love BB, Gordon DL, Marsh EE 3rd. Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke. 1993; 24:35–41.19. Lip GY, Nieuwlaat R, Pisters R, Lane DA, Crijns HJ. Refining clinical risk stratification for predicting stroke and thromboembolism in atrial fibrillation using a novel risk factor-based approach: the euro heart survey on atrial fibrillation. Chest. 2010; 137:263–272.20. Lang RM, Bierig M, Devereux RB, Flachskampf FA, Foster E, Pellikka PA, Picard MH, Roman MJ, Seward J, Shanewise JS, Solomon SD, Spencer KT, Sutton MS, Stewart WJ. Chamber Quantification Writing Group. American Society of Echocardiography's Guidelines and Standards Committee. European Association of Echocardiography. Recommendations for chamber quantification: a report from the American Society of Echocardiography's Guidelines and Standards Committee and the Chamber Quantification Writing Group, developed in conjunction with the European Association of Echocardiography, a branch of the European Society of Cardiology. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2005; 18:1440–1463.21. Obokata M, Negishi K, Kurosawa K, Tateno R, Tange S, Arai M, Amano M, Kurabayashi M. Left atrial strain provides incremental value for embolism risk stratification over CHA2DS2-VASc score and indicates prognostic impact in patients with atrial fibrillation. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2014; 27:709–716.e4..22. Shih JY, Tsai WC, Huang YY, Liu YW, Lin CC, Huang YS, Tsai LM, Lin LJ. Association of decreased left atrial strain and strain rate with stroke in chronic atrial fibrillation. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 2011; 24:513–519.23. Stroke Prevention in Atrial Fibrillation Investigators Committee on Echocardiography. Transesophageal echocardiography in atrial fibrillation: standards for acquisition and interpretation and assessment of interobserver variability. J Am Soc Echocardiogr. 1996; 9:556–566.24. Manning WJ, Weintraub RM, Waksmonski CA, Haering JM, Rooney PS, Maslow AD, Johnson RG, Douglas PS. Accuracy of transesophageal echocardiography for identifying left atrial thrombi. A prospective, intraoperative study. Ann Intern Med. 1995; 123:817–822.25. Beppu S, Nimura Y, Sakakibara H, Nagata S, Park YD, Izumi S. Smoke-like echo in the left atrial cavity in mitral valve disease: its features and significance. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1985; 6:744–749.26. Vincelj J, Sokol I, Jaksić O. Prevalence and clinical significance of left atrial spontaneous echo contrast detected by transesophageal echocardiography. Echocardiography. 2002; 19:319–324.27. DeLong ER, DeLong DM, Clarke-Pearson DL. Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: a nonparametric approach. Biometrics. 1988; 44:837–845.28. Secondary prevention in non-rheumatic atrial fibrillation after transient ischaemic attack or minor stroke. EAFT (European Atrial Fibrillation Trial) Study Group. Lancet. 1993; 342:1255–1262.29. Fauchier L, Clementy N, Pelade C, Collignon C, Nicolle E, Lip GY. Patients wth ischemic stroke and incident atrial fibrillation: a nationwide cohort study. Stroke. 2015; 46:2432–2437.30. Benjamin EJ, Levy D, Vaziri SM, D'Agostino RB, Belanger AJ, Wolf PA. Independent risk factors for atrial fibrillation in a population-based cohort. The Framingham Heart Study. JAMA. 1994; 271:840–844.31. Psaty BM, Manolio TA, Kuller LH, Kronmal RA, Cushman M, Fried LP, White R, Furberg CD, Rautaharju PM. Incidence of and risk factors for atrial fibrillation in older adults. Circulation. 1997; 96:2455–2461.32. Huxley RR, Filion KB, Konety S, Alonso A. Meta-analysis of cohort and case-control studies of type 2 diabetes mellitus and risk of atrial fibrillation. Am J Cardiol. 2011; 108:56–62.33. Schnabel RB, Sullivan LM, Levy D, Pencina MJ, Massaro JM, D'Agostino RB Sr, Newton-Cheh C, Yamamoto JF, Magnani JW, Tadros TM, Kannel WB, Wang TJ, Ellinor PT, Wolf PA, Vasan RS, Benjamin EJ. Development of a risk score for atrial fibrillation (Framingham Heart Study): a community-based cohort study. Lancet. 2009; 373:739–745.34. Hammerstingl C, Schwekendiek M, Momcilovic D, Schueler R, Sinning JM, Schrickel JW, Mittmann-Braun E, Nickenig G, Lickfett L. Left atrial deformation imaging with ultrasound based two-dimensional speckle-tracking predicts the rate of recurrence of paroxysmal and persistent atrial fibrillation after successful ablation procedures. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2012; 23:247–255.35. Yasuda R, Murata M, Roberts R, Tokuda H, Minakata Y, Suzuki K, Tsuruta H, Kimura T, Nishiyama N, Fukumoto K, Aizawa Y, Tanimoto K, Takatsuki S, Abe T, Fukuda K. Left atrial strain is a powerful predictor of atrial fibrillation recurrence after catheter ablation: study of a heterogeneous population with sinus rhythm or atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015; 16:1008–1014.36. Tops LF, Delgado V, Bertini M, Marsan NA, Den Uijl DW, Trines SA, Zeppenfeld K, Holman E, Schalij MJ, Bax JJ. Left atrial strain predicts reverse remodeling after catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011; 57:324–331.37. Cameli M, Caputo M, Mondillo S, Ballo P, Palmerini E, Lisi M, Marino E, Galderisi M. Feasibility and reference values of left atrial longitudinal strain imaging by two-dimensional speckle tracking. Cardiovasc Ultrasound. 2009; 7:6.38. Kim DG, Lee KJ, Lee S, Jeong SY, Lee YS, Choi YJ, Yoon HS, Kim JH, Jeong KT, Park SC, Park M. Feasibility of two-dimensional global longitudinal strain and strain rate imaging for the assessment of left atrial function: a study in subjects with a low probability of cardiovascular disease and normal exercise capacity. Echocardiography. 2009; 26:1179–1187.39. Verdejo HE, Becerra E, Zalaquet R, Del Campo A, Garcia L, Troncoso R, Chiong M, Marin A, Castro PF, Lavandero S, Gabrielli L, Corbalán R. Atrial function assessed by speckle tracking echocardiography is a good predictor of postoperative atrial fibrillation in elderly patients. Echocardiography. 2016; 33:242–248.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Mechanism of and Preventive Therapy for Stroke in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation
- Cardioembolic Stroke in Atrial Fibrillation-Rationale for Preventive Closure of the Left Atrial Appendage
- Non-medication Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation
- Epicardial Fat Thickness, Free Fatty Acid Can Predict Acute Ischemic Stroke in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation?
- Relation of Stroke Risk Factors to Severity and Disability after Ischemic Stroke