Ann Surg Treat Res.
2016 Apr;90(4):194-200. 10.4174/astr.2016.90.4.194.
Validity of breast-specific gamma imaging for Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System 4 lesions on mammography and/or ultrasound
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, Konkuk University Medical Center, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. 20110364@kuh.ac.kr
- 2Department of Nuclear Medicine, Konkuk University Medical Center, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, Konkuk University Medical Center, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2160948
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2016.90.4.194
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The purpose of this study was to assess the breast-specific gamma imaging (BSGI) in Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) 4 lesions on mammography and/or ultrasound.
METHODS
We performed a retrospective review of 162 patients who underwent BSGI in BI-RADS 4 lesions on mammography and/or ultrasound.
RESULTS
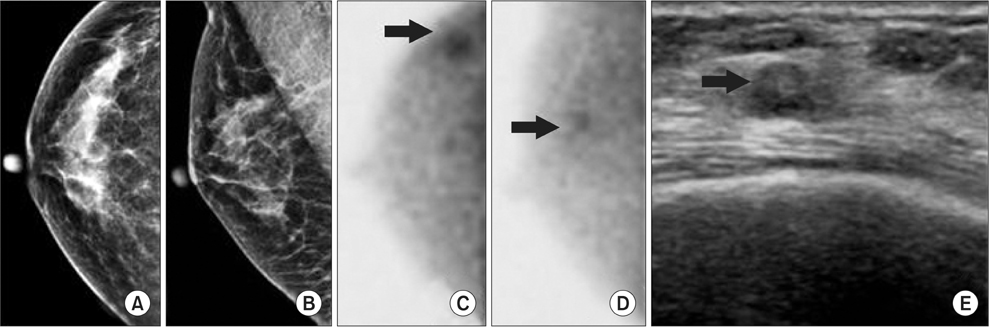
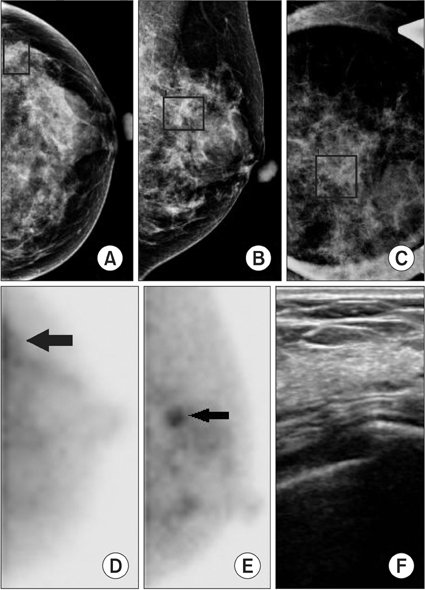
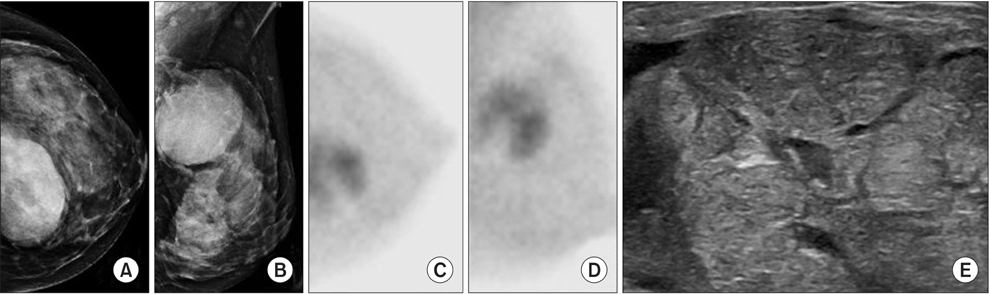
Of the 162 breast lesions, 66 were malignant tumors and 96 were benign tumors. Sensitivity and specificity of BSGI were 90.9% and 78.1%, and positive predictive value and negative predictive value were 74.1% and 92.6%. The sensitivity or specificity of mammography and ultrasound were 74.2% and 56.3% and 87.9% and 19.8%, respectively. The sensitivity and specificity of BSGI for breast lesions ≤1 cm were 88.0% and 86.8%, while the values of beast lesions >1 cm were 92.7% and 61.5%. The sensitivity or specificity of BSGI and mammography for patients with dense breasts were 92.0% and 81.3% and 72.0% and 50.0%, respectively. 26 patients showed neither a nodule nor microcalcification on ultrasound, but showed suspicious calcification on mammography. The sensitivity and specificity of BSGI with microcalcification only lesion were 75.0% and 94.4%.
CONCLUSION
This study demonstrated that BSGI had shown high sensitivity and specificity, as well as positive and negative predictive values in BI-RADS 4 lesions on ultrasound and/or mammography. BSGI showed excellent results in dense breasts, in lesions that are less than 1 cm in size and lesions with suspicious microcalcification only.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Wound healing and postsurgical complications in breast cancer surgery: a comparison between PEAK PlasmaBlade and conventional electrosurgery – a preliminary report of a case series
Corrado Chiappa, Anna Fachinetti, Carlo Boeri, Veronica Arlant, Stefano Rausei, Gianlorenzo Dionigi, Francesca Rovera
Ann Surg Treat Res. 2018;95(3):129-134. doi: 10.4174/astr.2018.95.3.129.
Reference
-
1. Kim KS, Kim Z, Shim EJ, Kim NH, Jung SY, Kim J, et al. The reality in the followup of breast cancer survivors: survey of Korean Breast Cancer Society. Ann Surg Treat Res. 2015; 88:133–139.2. Kolb TM, Lichy J, Newhouse JH. Comparison of the performance of screening mammography, physical examination, and breast US and evaluation of factors that influence them: an analysis of 27,825 patient evaluations. Radiology. 2002; 225:165–175.3. Rosenberg RD, Hunt WC, Williamson MR, Gilliland FD, Wiest PW, Kelsey CA, et al. Effects of age, breast density, ethnicity, and estrogen replacement therapy on screening mammographic sensitivity and cancer stage at diagnosis: review of 183,134 screening mammograms in Albuquerque, New Mexico. Radiology. 1998; 209:511–518.4. Berg WA, Gutierrez L, NessAiver MS, Carter WB, Bhargavan M, Lewis RS, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of mammography, clinical examination, US, and MR imaging in preoperative assessment of breast cancer. Radiology. 2004; 233:830–849.5. Berg WA, Blume JD, Cormack JB, Mendelson EB, Lehrer D, Bohm-Velez M, et al. Combined screening with ultrasound and mammography vs mammography alone in women at elevated risk of breast cancer. JAMA. 2008; 299:2151–2163.6. Liberman M, Sampalis F, Mulder DS, Sampalis JS. Breast cancer diagnosis by scintimammography: a meta-analysis and review of the literature. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2003; 80:115–126.7. Howarth D, Sillar R, Clark D, Lan L. Technetium-99m sestamibi scintimammography: the influence of histopathological characteristics, lesion size and the presence of carcinoma in situ in the detection of breast carcinoma. Eur J Nucl Med. 1999; 26:1475–1481.8. Brem RF, Rapelyea JA, Zisman G, Mohtashemi K, Raub J, Teal CB, et al. Occult breast cancer: scintimammography with high-resolution breast-specific gamma camera in women at high risk for breast cancer. Radiology. 2005; 237:274–280.9. Goldsmith SJ, Parsons W, Guiberteau MJ, Stern LH, Lanzkowsky L, Weigert J, et al. SNM practice guideline for breast scintigraphy with breast-specific gammacameras 1.0. J Nucl Med Technol. 2010; 38:219–224.10. Sharma S, Sharma MC, Sarkar C. Morphology of angiogenesis in human cancer: a conceptual overview, histoprognostic perspective and significance of neoangiogenesis. Histopathology. 2005; 46:481–489.11. Delmon-Moingeon LI, Piwnica-Worms D, Van den Abbeele AD, Holman BL, Davison A, Jones AG. Uptake of the cation hexakis (2-methoxyisobutylisonitrile)-technetium-99m by human carcinoma cell lines in vitro. Cancer Res. 1990; 50:2198–2202.12. Sampalis FS, Denis R, Picard D, Fleiszer D, Martin G, Nassif E, et al. International prospective evaluation of scintimammography with (99m)technetium sestamibi. Am J Surg. 2003; 185:544–549.13. Keto JL, Kirstein L, Sanchez DP, Fulop T, McPartland L, Cohen I, et al. MRI versus breast-specific gamma imaging (BSGI) in newly diagnosed ductal cell carcinoma-insitu: a prospective head-to-head trial. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012; 19:249–252.14. Brem RF, Fishman M, Rapelyea JA. Detection of ductal carcinoma in situ with mammography, breast specific gamma imaging, and magnetic resonance imaging: a comparative study. Acad Radiol. 2007; 14:945–950.15. Kim SH, Kim MH, Oh KK. Analysis and comparison of breast density according to age on mammogram between Korean and western women. J Korean Radiol Soc. 2000; 42:1009–1014.16. Brem RF, Floerke AC, Rapelyea JA, Teal C, Kelly T, Mathur V. Breast-specific gamma imaging as an adjunct imaging modality for the diagnosis of breast cancer. Radiology. 2008; 247:651–657.17. Brem RF, Ioffe M, Rapelyea JA, Yost KG, Weigert JM, Bertrand ML, et al. Invasive lobular carcinoma: detection with mammography, sonography, MRI, and breast-specific gamma imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009; 192:379–383.18. Waxman AD. The role of (99m)Tc methoxyisobutylisonitrile in imaging breast cancer. Semin Nucl Med. 1997; 27:40–54.19. Cutrone JA, Khalkhali I, Yospur LS, Diggles L, Weinberg I, Pong EM, et al. Tc-99m Sestamibi Scintimammography for the Evaluation of Breast Masses in Patients with Radiographically Dense Breasts. Breast J. 1999; 5:383–388.20. Ling CM, Coffey CM, Rapelyea JA, Torrente J, Teal CB, McSwain AP, et al. Breast-specific gamma imaging in the detection of atypical ductal hyperplasia and lobular neoplasia. Acad Radiol. 2012; 19:661–666.21. Elvecrog EL, Lechner MC, Nelson MT. Nonpalpable breast lesions: correlation of stereotaxic large-core needle biopsy and surgical biopsy results. Radiology. 1993; 188:453–455.22. Gisvold JJ, Goellner JR, Grant CS, Donohue JH, Sykes MW, Karsell PR, et al. Breast biopsy: a comparative study of stereotaxically guided core and excisional techniques. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1994; 162:815–820.23. Hahn SY, Shin JH, Han BK, Ko EY. Sonographically-guided vacuum-assisted biopsy with digital mammography-guided skin marking of suspicious breast microcalcifications: comparison of outcomes with stereotactic biopsy in Asian women. Acta Radiol. 2011; 52:29–34.