Korean J Gastroenterol.
2014 Dec;64(6):380-386. 10.4166/kjg.2014.64.6.380.
A Case of Splenic Hamartoma Diagnosed by Contrast-enhanced Ultrasonography and Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea. kimthy@medimail.co.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea.
- 3Institute of Health Sciences, Gyeongsang National University School of Medicine, Jinju, Korea.
- KMID: 2160672
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2014.64.6.380
Abstract
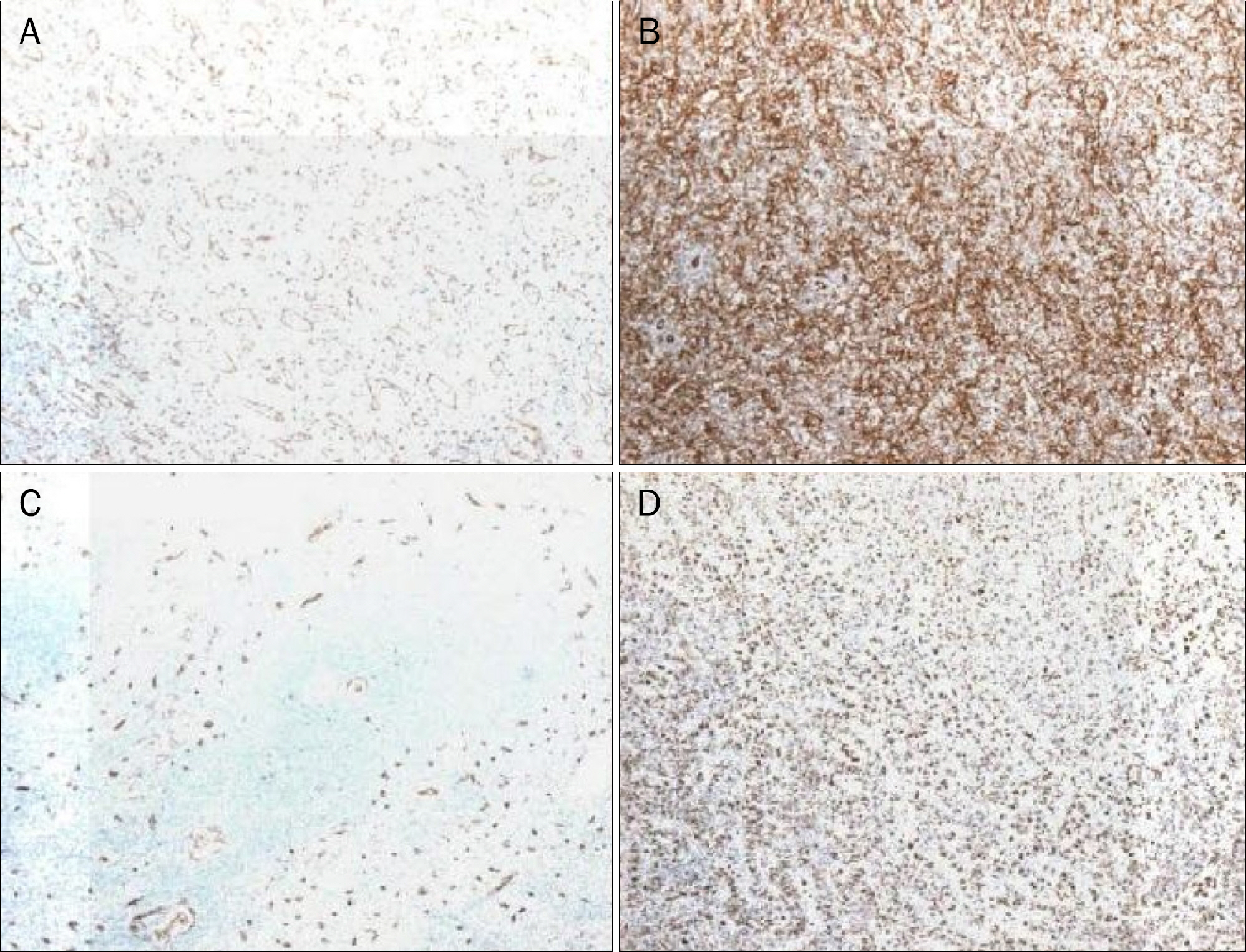
- Splenic hamartoma is a very rare benign tumor, which is usually found incidentally after splenectomy or autopsy. Although percutaneous needle biopsy can be performed, it carries a high risk of bleeding after the procedure. Therefore, diagnosis is usually made by surgical resection. Herein, we report a case of splenic hamartoma diagnosed by magnetic resonance imaging and contrast-enhanced ultrasonography, which enables visualization of the unique signals of microbubbles in the vessels in real time. Relevant literature is also reviewed.
MeSH Terms
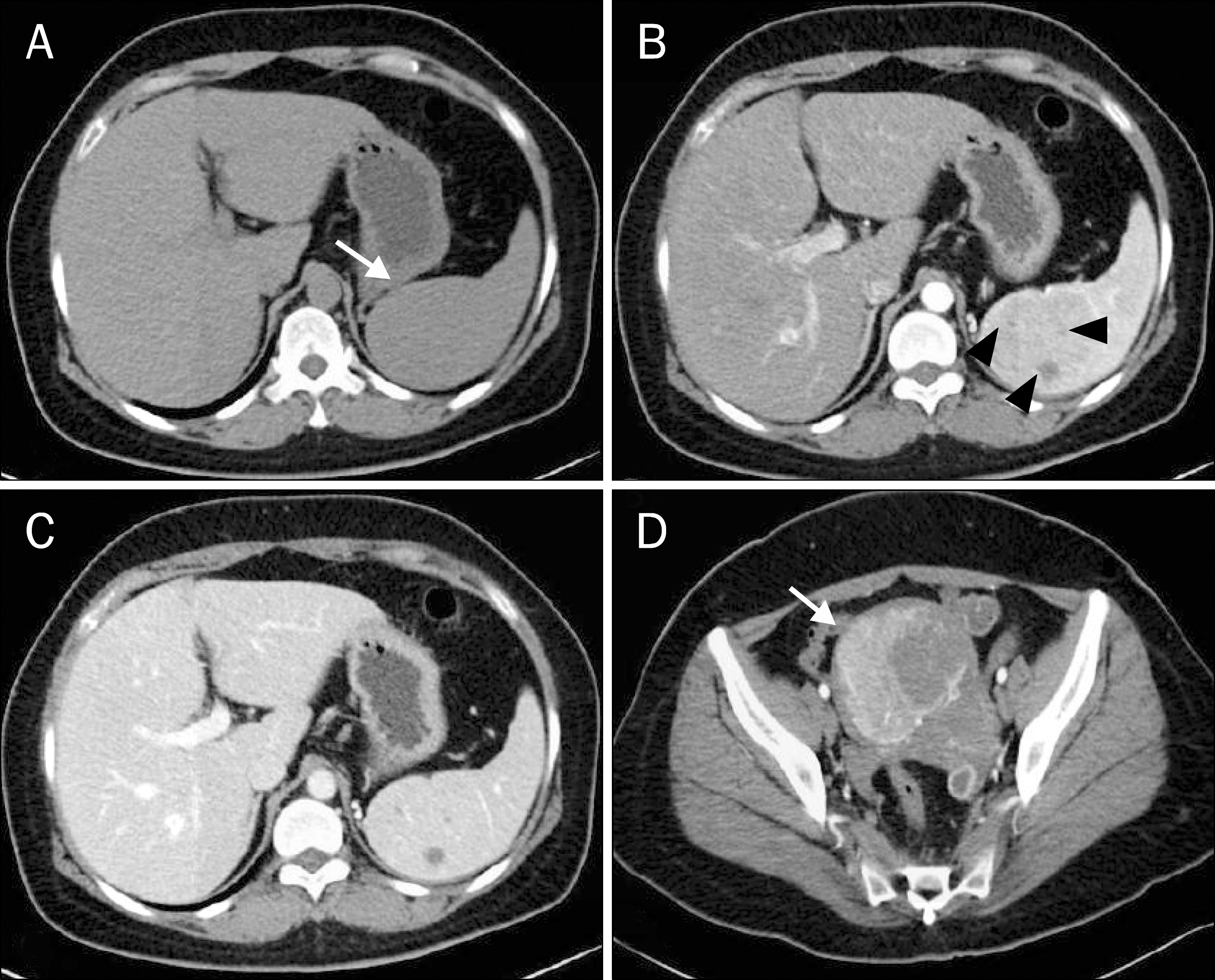
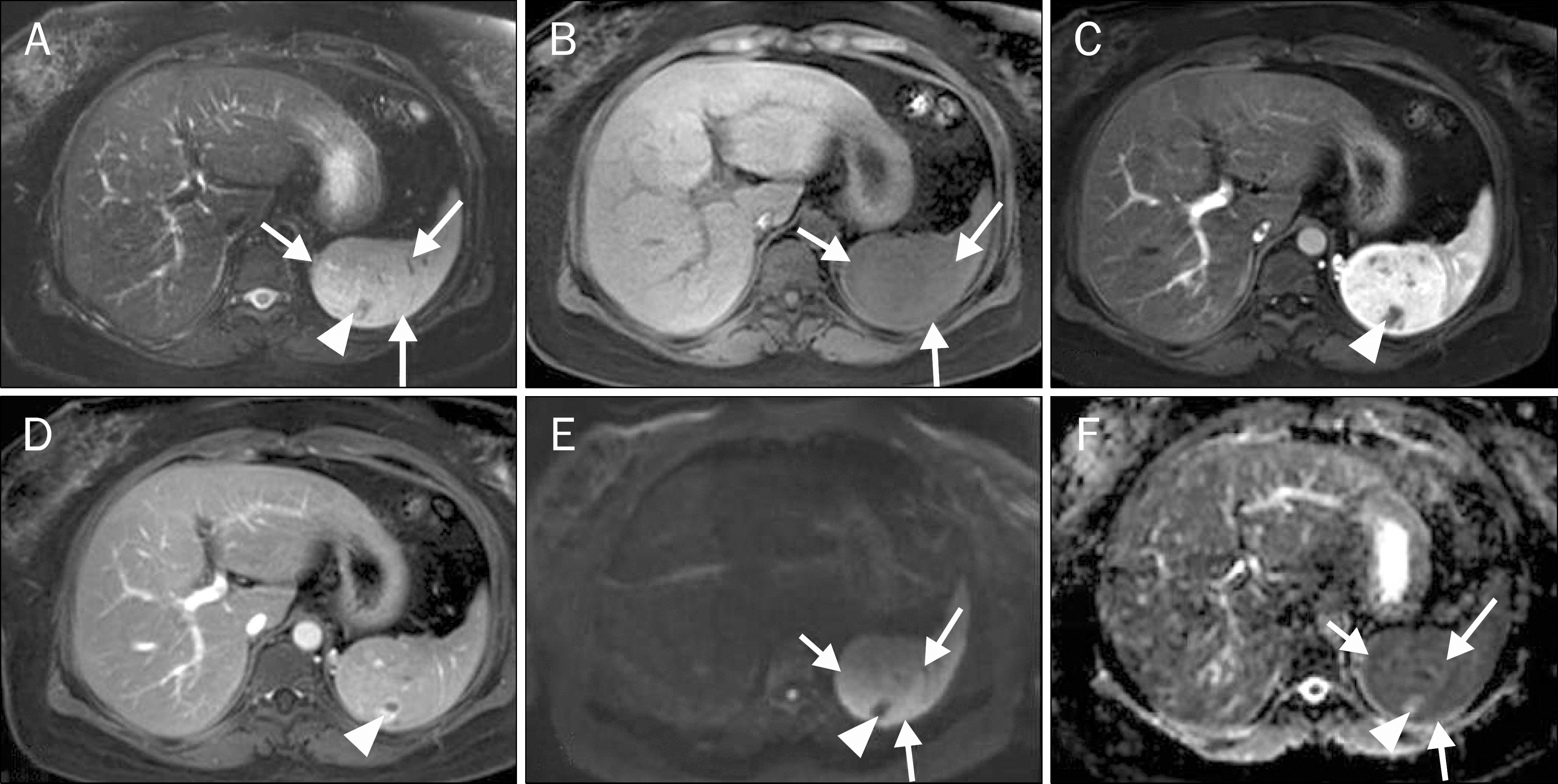
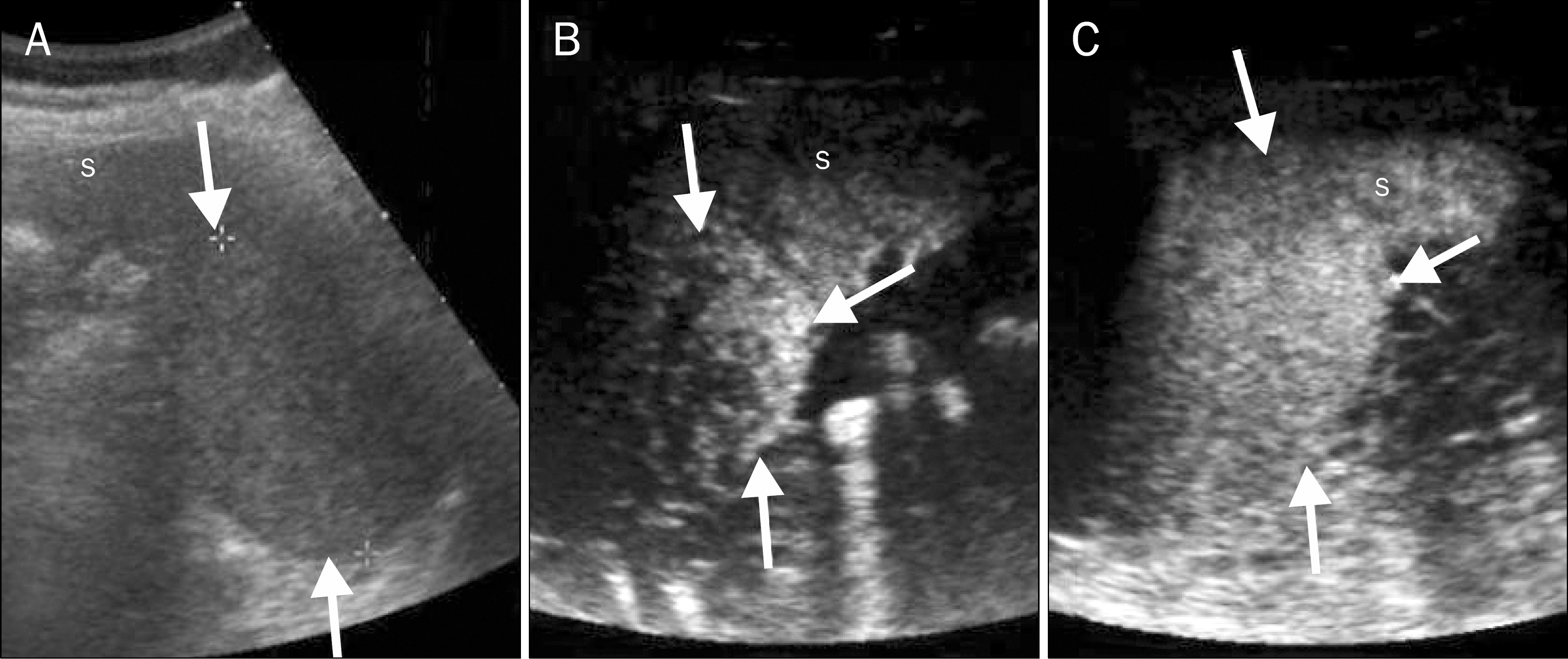
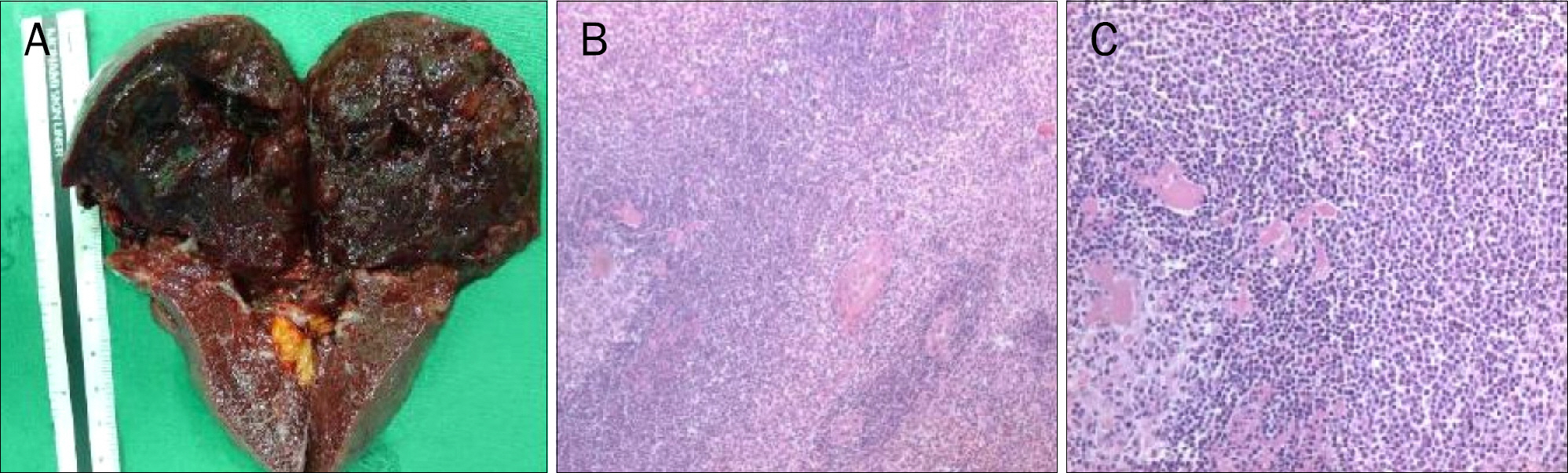
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Kraus MD, Fleming MD, Vonderheide RH. The spleen as a diagnostic specimen: a review of 10 years' experience at two tertiary care institutions. Cancer. 2001; 91:2001–2009.2. Silverman ML, LiVolsi VA. Splenic hamartoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 1978; 70:224–229.
Article3. Ferguson ER, Sardi A, Beckman EN. Spontaneous rupture of splenic hamartoma. J La State Med Soc. 1993; 145:48–52.4. Koh YW, Lee H, Choi G, Kwon GY, Kim EJ, Huh J. Primary splenic vascular lesions: a clinicopathologic, immunophenotypic and radiopathologic correlation study of 40 cases. Korean J Pathol. 2010; 44:502–512.
Article5. Zukerberg LR, Kaynor BL, Silverman ML, Harris NL. Splenic hamartoma and capillary hemangioma are distinct entities: immunohistochemical analysis of CD8 expression by endothelial cells. Hum Pathol. 1991; 22:1258–1261.
Article6. Ali TZ, Beyer G, Taylor M, Volpe C, Papadimitriou JC. Splenic hamartoma: immunohistochemical and ultrastructural profile of two cases. Int J Surg Pathol. 2005; 13:103–111.
Article7. Wang JH, Ma XL, Ren FY, et al. Multi-modality imaging findings of splenic hamartoma: a report of nine cases and review of the literature. Abdom Imaging. 2013; 38:154–162.
Article8. Fernandez-Canton G, Capelastegui A, Merino A, Astigarraga E, Larena JA, Diaz-Otazu R. Atypical MRI presentation of a small splenic hamartoma. Eur Radiol. 1999; 9:883–885.
Article9. Stang A, Keles H, Hentschke S, et al. Incidentally detected splenic lesions in ultrasound: does contrast-enhanced ultrasonography improve the differentiation of benign hemangioma/ha- martoma from malignant lesions? Ultraschall Med. 2011; 32:582–592.10. Makino Y, Imai Y, Fukuda K, et al. Sonazoid-enhanced ultrasonography for the diagnosis of an intrapancreatic accessory spleen: a case report. J Clin Ultrasound. 2011; 39:344–347.
Article11. Chou YH, Chiou HJ, Tiu CM, Chiou SY, Hsia CY, Tsay SH. Splenic hamartoma: presentation on contrast-enhanced sonography. J Clin Ultrasound. 2004; 32:425–428.12. Gorg C. The forgotten organ: contrast enhanced sonography of the spleen. Eur J Radiol. 2007; 64:189–201.13. Stang A, Keles H, Hentschke S, et al. Differentiation of benign from malignant focal splenic lesions using sulfur hexa-fluoride-filled microbubble contrast-enhanced pulse-inversion sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2009; 193:709–721.
Article14. Yu X, Yu J, Liang P, Liu F. Real-time contrast-enhanced ultrasound in diagnosing of focal spleen lesions. Eur J Radiol. 2012; 81:430–436.
Article15. Caremani M, Occhini U, Caremani A, et al. Focal splenic lesions: US findings. J Ultrasound. 2013; 16:65–74.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Invasive Ductal Carcinoma Arising within a Mammary Hamartoma: Case Report
- Biliary hamartoma presented as a single mass
- Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography of the liver using SonoVue
- Recent development of diagnostic imaging of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Benefits of contrast-enhanced ultrasonography for interventional procedures