J Korean Med Sci.
2015 Jun;30(6):788-792. 10.3346/jkms.2015.30.6.788.
Seizure Frequencies and Number of Anti-epileptic Drugs as Risk Factors for Sudden Unexpected Death in Epilepsy
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. jkkang@amc.seoul.kr
- 2Department of Clinical Epidemiology and Biostatistics, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Psychiatry, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2160609
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2015.30.6.788
Abstract
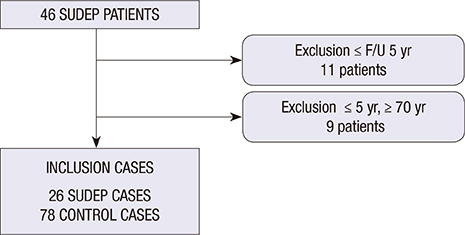
- The purpose of this study was to investigate the association between clinical variables and sudden unexpected death in epilepsy (SUDEP) and identify risk factors for SUDEP. SUDEP is one of the most frequent causes of death in patients with epilepsy. Previous studies have reported possible risk factors associated with SUDEP, but there need to be elucidated yet. The cases were 26 patients with SUDEP and three control patients were included for each case, matched for age, sex, and date of initial clinical visit. All demographic and clinical characteristics, including age, sex, disease duration, classification of epilepsy, age at seizure onset, kind and number of antiepileptic drugs, were compared between cases and controls. Seizure frequency was higher in SUDEP cases than in controls (P=0.035). Univariate analysis using conditional logistic regression showed that higher seizure frequency (odds ratio [OR]=3.1, P=0.021) and the number of antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) (OR=2.0, P=0.009) were significantly associated with SUDEP. Only the number of AEDs remained significant in multivariate analysis (OR=1.8, P=0.026). Frequent seizures and multi-drug therapy were associated with SUDEP. This may suggest that the severity of epilepsy is associated with SUDEP, regardless of the type of AED used.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Tomson T, Walczak T, Sillanpaa M, Sander JW. Sudden unexpected death in epilepsy: a review of incidence and risk factors. Epilepsia. 2005; 46:54–61.2. Schraeder PL, Lathers CM. Paroxysmal autonomic dysfunction, epileptogenic activity and sudden death. Epilepsy Res. 1989; 3:55–62.3. Nashef L, Walker F, Allen P, Sander JW, Shorvon SD, Fish DR. Apnoea and bradycardia during epileptic seizures: relation to sudden death in epilepsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1996; 60:297–300.4. Johnston SC, Horn JK, Valente J, Simon RP. The role of hypoventilation in a sheep model of epileptic sudden death. Ann Neurol. 1995; 37:531–537.5. Bardai A, Lamberts RJ, Blom MT, Spanjaart AM, Berdowski J, van der Staal AR, Brouwer HJ, Koster RW, Sander JW, Thijs RD, et al. Epilepsy is a risk factor for sudden cardiac arrest in the general population. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e42749.6. Beal E. Epilepsy: risk factors for sudden unexpected death in epilepsy-combined analysis from case-control studies. Nat Rev Neurol. 2011; 7:188.7. Hesdorffer DC, Tomson T, Benn E, Sander JW, Nilsson L, Langan Y, Walczak TS, Beghi E, Brodie MJ, Hauser A, et al. ILAE Commission on Epidemiology. Subcommission on Mortality. Combined analysis of risk factors for SUDEP. Epilepsia. 2011; 52:1150–1159.8. Hesdorffer DC, Tomson T, Benn E, Sander JW, Nilsson L, Langan Y, Walczak TS, Beghi E, Brodie MJ, Hauser WA. Do antiepileptic drugs or generalized tonic-clonic seizure frequency increase SUDEP risk? A combined analysis. Epilepsia. 2012; 53:249–252.9. Lamberts RJ, Thijs RD, Laffan A, Langan Y, Sander JW. Sudden unexpected death in epilepsy: people with nocturnal seizures may be at highest risk. Epilepsia. 2012; 53:253–257.10. Nilsson L, Ahlbom A, Farahmand BY, Asberg M, Tomson T. Risk factors for suicide in epilepsy: a case control study. Epilepsia. 2002; 43:644–651.11. Nilsson L, Farahmand BY, Persson PG, Thiblin I, Tomson T. Risk factors for sudden unexpected death in epilepsy: a case-control study. Lancet. 1999; 353:888–893.12. Opeskin K, Berkovic SF. Risk factors for sudden unexpected death in epilepsy: a controlled prospective study based on coroners cases. Seizure. 2003; 12:456–464.13. Leestma JE, Walczak T, Hughes JR, Kalelkar MB, Teas SS. A prospective study on sudden unexpected death in epilepsy. Ann Neurol. 1989; 26:195–203.14. Shorvon S, Tomson T. Sudden unexpected death in epilepsy. Lancet. 2011; 378:2028–2038.15. Kwon OY, Park SP. Depression and anxiety in people with epilepsy. J Clin Neurol. 2014; 10:175–188.16. Tennis P, Cole TB, Annegers JF, Leestma JE, McNutt M, Rajput A. Cohort study of incidence of sudden unexplained death in persons with seizure disorder treated with antiepileptic drugs in Saskatchewan, Canada. Epilepsia. 1995; 36:29–36.17. Walczak TS, Leppik IE, D’Amelio M, Rarick J, So E, Ahman P, Ruggles K, Cascino GD, Annegers JF, Hauser WA. Incidence and risk factors in sudden unexpected death in epilepsy: a prospective cohort study. Neurology. 2001; 56:519–525.18. Feldman AE, Gidal BE. QTc prolongation by antiepileptic drugs and the risk of torsade de pointes in patients with epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav. 2013; 26:421–426.19. Tomson T, Kennebäck G. Arrhythmia, heart rate variability, and antiepileptic drugs. Epilepsia. 1997; 38:S48–S51.20. Saetre E, Abdelnoor M, Amlie JP, Tossebro M, Perucca E, Taubøll E, Anfinsen OG, Isojärvi J, Gjerstad L. Cardiac function and antiepileptic drug treatment in the elderly: a comparison between lamotrigine and sustained-release carbamazepine. Epilepsia. 2009; 50:1841–1849.21. Danielsson BR, Lansdell K, Patmore L, Tomson T. Effects of the antiepileptic drugs lamotrigine, topiramate and gabapentin on hERG potassium currents. Epilepsy Res. 2005; 63:17–25.22. Walczak T. Do antiepileptic drugs play a role in sudden unexpected death in epilepsy? Drug Saf. 2003; 26:673–683.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Sudden Unexpected Death in Epilepsy
- Antiepileptic Drugs
- Near-Sudden Unexpected Death of Epilepsy (SUDEP) Caused by Ventricular Fibrillation Following Seizure in a Post-Stroke Epilepsy Patient
- Depression and Anxiety in the Epileptic Patients: the Association With Demographic and Seizure-Related Variables
- Epilepsy and Oxidative Stress