J Korean Med Sci.
2015 Jun;30(6):757-762. 10.3346/jkms.2015.30.6.757.
Determination of Rifaximin Treatment Period According to Lactulose Breath Test Values in Nonconstipated Irritable Bowel Syndrome Subjects
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Family Practice and Community Health, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. ktwonm@hanmail.net
- 2Department of Gastroenterology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- 3Department of Family Medicine, Cha University, Cha Bundang Medical Centre, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 2160605
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2015.30.6.757
Abstract
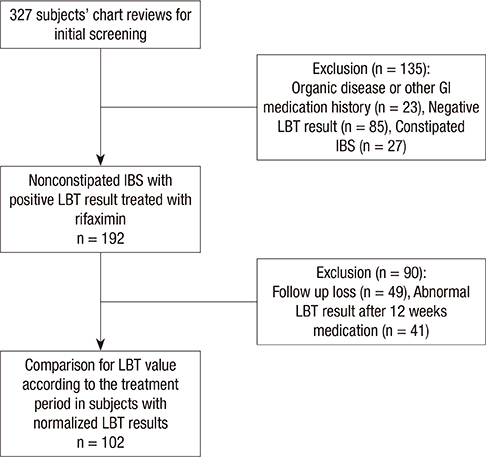
- Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO) can partly explain irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and rifaximin has been observed to improve abdominal symptoms in nonconstipated IBS patients. However, there are few reports on the association of the rifaximin treatment periods with the results of a lactulose breath test (LBT). Therefore, we performed a retrospective review of patient charts to investigate the relation between the rifaximin treatment periods with LBT results in nonconstipated IBS patients. We also evaluated the time to achieve a symptomatic improvement in the IBS patients as compared to the changes in the LBT. We reviewed the charts for patients who showed IBS symptoms with documented positive results for LBT during their initial visit and who had a follow-up LBT after treatment with rifaximin. The LBT values were compared to the subjects' symptom scores. A total of 102 subjects had a follow-up LBT to assess LBT normalization. The subjects were divided into groups according to treatment periods of 4 weeks (n = 36), 8 weeks (n = 43), and 12 weeks (n = 23). The groups with a longer treatment exhibited an increase in the hydrogen gas value at 90 min and its sum during 90 min at the initial LBT. There were significant differences in hydrogen gas value at 90 min and in its sum during 90 min at the initial LBT between the groups treated for 4 and 12 weeks. The most significant treatment response was observed during the first 4 weeks for all treatment groups. Symptomatic improvement occurred earlier than LBT normalization in the treatment period over 4 weeks. The results indicate that different rifaximin treatment periods are needed in accordance with LBT levels to effectively eradicate SIBO.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Biomarkers/analysis
Breath Tests/*methods
Constipation
Drug Administration Schedule
Drug Monitoring/*methods
Female
Gastrointestinal Agents/administration & dosage
Humans
Irritable Bowel Syndrome/*diagnosis/*drug therapy
Lactulose/*analysis
Male
Middle Aged
Reproducibility of Results
Rifamycins/*administration & dosage
Sensitivity and Specificity
Treatment Outcome
Biomarkers
Gastrointestinal Agents
Lactulose
Rifamycins
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mitchell CM, Drossman DA. Survey of the AGA membership relating to patients with functional gastrointestinal disorders. Gastroenterology. 1987; 92:1282–1284.2. Pimentel M, Morales W, Chua K, Barlow G, Weitsman S, Kim G, Amichai MM, Pokkunuri V, Rook E, Mathur R, et al. Effects of rifaximin treatment and retreatment in nonconstipated IBS subjects. Dig Dis Sci. 2011; 56:2067–2072.3. Pyleris E, Giamarellos-Bourboulis E, Koussoulas B, Barbatzas C. Prevalence of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in a Greek cohort: relationship with irritable bowel syndrome. Barcelona, Spain: United European Gastroenterology Week;2010. p. 23–27.4. Van Citters GW, Lin HC. Management of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2005; 7:317–320.5. Pimentel M, Lembo A, Chey WD, Zakko S, Ringel Y, Yu J, Mareya SM, Shaw AL, Bortey E, Forbes WP, et al. TARGET Study Group. Rifaximin therapy for patients with irritable bowel syndrome without constipation. N Engl J Med. 2011; 364:22–32.6. Pimentel M, Park S, Mirocha J, Kane SV, Kong Y. The effect of a nonabsorbed oral antibiotic (rifaximin) on the symptoms of the irritable bowel syndrome: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med. 2006; 145:557–563.7. Hoover WW, Gerlach EH, Hoban DJ, Eliopoulos GM, Pfaller MA, Jones RN. Antimicrobial activity and spectrum of rifaximin, a new topical rifamycin derivative. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 1993; 16:111–118.8. Sharara AI, Aoun E, Abdul-Baki H, Mounzer R, Sidani S, Elhajj I. A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial of rifaximin in patients with abdominal bloating and flatulence. Am J Gastroenterol. 2006; 101:326–333.9. Lauritano EC, Gabrielli M, Lupascu A, Santoliquido A, Nucera G, Scarpellini E, Vincenti F, Cammarota G, Flore R, Pola P, et al. Rifaximin dose-finding study for the treatment of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2005; 22:31–35.10. Ford AC, Bercik P, Morgan DG, Bolino C, Pintos-Sanchez MI, Moayyedi P. Characteristics of functional bowel disorder patients: a cross-sectional survey using the Rome III criteria. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2014; 39:312–321.11. Bond JH Jr, Levitt MD, Prentiss R. Investigation of small bowel transit time in man utilizing pulmonary hydrogen (H2) measurements. J Lab Clin Med. 1975; 85:546–555.12. Joseph F Jr, Rosenberg AJ. Breath hydrogen testing: diseased versus normal patients. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1988; 7:787–788.13. Di Stefano M, Corazza GR. Treatment of small intestine bacterial over growth and related symptoms by rifaximin. Chemotherapy. 2005; 51:103–109.14. Canavan C, West J, Card T. The epidemiology of irritable bowel syndrome. Clin Epidemiol. 2014; 6:71–80.15. Scarpignato C, Pelosini I. Experimental and clinical pharmacology of rifaximin, a gastrointestinal selective antibiotic. Digestion. 2006; 73:13–27.16. Scarpellini E, Gabrielli M, Lauritano CE, Lupascu A, Merra G, Cammarota G, Cazzato IA, Gasbarrini G, Gasbarrini A. High dosage rifaximin for the treatment of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2007; 25:781–786.17. Chatterjee S, Park S, Low K, Kong Y, Pimentel M. The degree of breath methane production in IBS correlates with the severity of constipation. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007; 102:837–841.18. Davidson GP, Robb TA, Kirubakaran CP. Bacterial contamination of the small intestine as an important cause of chronic diarrhea and abdominal pain: diagnosis by breath hydrogen test. Pediatrics. 1984; 74:229–235.19. Pimentel M, Mayer AG, Park S, Chow EJ, Hasan A, Kong Y. Methane production during lactulose breath test is associated with gastrointestinal disease presentation. Dig Dis Sci. 2003; 48:86–92.20. Calanni F, Renzulli C, Fogli MV, Barbanti M. Comment on: Rifaximin in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome. Is there a high risk for development of antimicrobial resistance? J Clin Gastroenterol. 2013; 47:814.21. Menees SB, Maneerattannaporn M, Kim HM, Chey WD. The efficacy and safety of rifaximin for the irritable bowel syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012; 107:28–35. quiz 6.22. Ghoshal UC. How to interpret hydrogen breath tests. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2011; 17:312–317.23. Yu D, Cheeseman F, Vanner S. Combined oro-caecal scintigraphy and lactulose hydrogen breath testing demonstrate that breath testing detects oro-caecal transit, not small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in patients with IBS. Gut. 2011; 60:334–340.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- How to Interpret Hydrogen Breath Tests
- Usefulness of Lactulose Breath Test for the Prediction of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Association between Symptoms of Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Methane and Hydrogen on Lactulose Breath Test
- Obesity Is Inversely Related to Hydrogen-Producing Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth in Non-Constipation Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Slow Transit Constipation Associated With Excess Methane Production and Its Improvement Following Rifaximin Therapy: A Case Report