J Korean Med Sci.
2012 Nov;27(11):1398-1404. 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.11.1398.
Relationship between Irritable Bowel Syndrome, Worry and Stress in Adolescent Girls
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Family Medicine, St. Vincent's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, Suwon, Korea. hippo94@naver.com
- KMID: 2157953
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2012.27.11.1398
Abstract
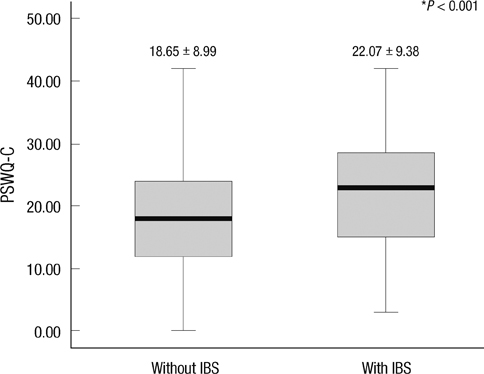
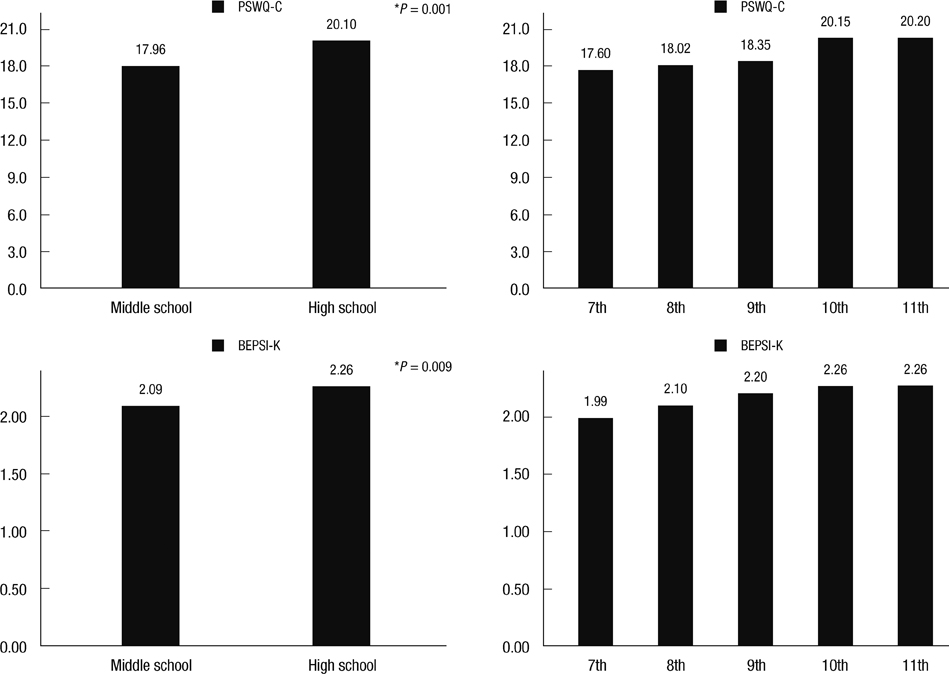
- The aim of this study is to investigate prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) among adolescents and difference in worry and stress between normal and IBS groups. Questionnaire survey was conducted at a girl's middle and high school. Students from seventh to eleventh grade participated in the examination on Rome II criteria, lifestyle and dietary habits. Worry and stress were measured with the Korean version Penn State Worry Questionnaire-Children and the Korean version Brief Encounter Psychosocial Instrument. Worry score was significantly higher in the IBS group (22.07 +/- 9.38, P < 0.001) than in the normal group (18.65 +/- 8.99) and was higher in high school students than in middle school students (P = 0.02). Stress score also was higher in the IBS group than in the normal group (P < 0.001) and was higher in the high school girls than in the middle school ones (P = 0.04). Of all the lifestyle factors influencing IBS preference for fatty foods, preference for salty foods, drinking alcohol and sleeping for less than six hours a day were found to be significant. Worry and stress seem to be associated with IBS symptoms. The findings of this study draw a clue that less worry and stress will help decrease IBS symptoms.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Irritable Bowel Syndrome May Be Associated with Elevated Alanine Aminotransferase and Metabolic Syndrome
Seung-Hwa Lee, Kyu-Nam Kim, Kwang-Min Kim, Nam-Seok Joo
Yonsei Med J. 2016;57(1):146-152. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.1.146.
Reference
-
1. Drossman DA, Camilleri M, Mayer EA, Whitehead WE. AGA technical review on irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 2002. 123:2108–2131.2. Han SH, Lee OY. Prevalence of irritable bowel syndrome in Korea : Population-based survey using the Rome II criteria. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006. 21:1687–1692.3. Everhart JE, Renault PF. Irritable bowel syndrome in an office-based practice in the United States. Gastroenterology. 1991. 100:998–1005.4. Mayer EA. Irritable Bowel Syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2008. 358:1692–1699.5. Lee OY. Psychosocial factors and visceral hypersensitivity in irritable bowel syndrome. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2006. 47:111–119.6. Creed FH. The relationship between psychosocial parameters and outcome in irritable bowel syndrome. Am J Med. 1999. 107:74S–80S.7. Brown TA, Barlow DH. Barlow DH, editor. Classification of anxiety and mood disorders. Anxiety and its disorders: the nature and treatment of anxiety and panic. 2002. New York: Guilford Press;292–327.8. Garakani A, Win T, Virk S, Gupta S, Kaplan D, Masand PS. Comorbidity of irritable bowel syndrome in psychiatric patients: a review. Am J Ther. 2003. 10:61–67.9. McGarth JE. A conceptual formulation for research on stress. Social psychologic factors in stress. 1970. New York: Holt, Reinhart & Winston;10–21.10. Jung JH, So YH. The relationship between entrance examination stress, anger and depression of physical education examinee. J Sport Leis Stud. 2008. 34:1407–1419.11. Kang MH, Jung EE. A study on stress coping strategies and thought suppressions of adolescents with excessive worry. Korean J Youth Stud. 2003. 10:439–460.12. Borkovec TD, Robinson E, Pruzinsky T, DePree JA. Preliminary exploration of worry: some characteristics and processes. Behav Res Ther. 1983. 21:9–16.13. Orton GL. A comparative study of children's worries. J Psychol. 1982. 110:153–162.14. Brown JM, O'Keeffe J, Sanders S, Baker B. Developmental changes in children's cognition to stressful and painful situation. J Pediatr Psychol. 1986. 11:343–357.15. Muris P, Meesters C, Merckelbach H, Hülsenbeck P. Worry in children is related to perceived parental rearing and attachment. Behav Res Ther. 2000. 38:487–497.16. Bell-Dolan DJ, Last CG, Strauss CC. Symptoms of anxiety disorders in normal children. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 1990. 29:759–765.17. Son YJ, Jun EY, Park JH. Prevalence and risk factors of irritable bowel syndrome in Korean adolescent girls: a school-based study. Int J Nurs Stud. 2009. 46:76–84.18. Thompson WG, Dotevall G, Drossman DA. Irritable bowel syndrome: guidelines for the diagnosis. Gastroenterol Int. 1989. 2:92–95.19. Drossman DA, Li Z, Anduzzi E, Temple RD, Talley NJ, Thompson WG. U.S. householder survey of functional gastrointestinal disorders. Dig Dis Sci. 1993. 38:1569–1580.20. Thompson WG, Longstreth GF, Drossman DA, Heaton KW, Irvine EJ, Mueller-Lissner SA. Drossman DA, Talley NJ, Thompson WG, Whitehead WE, Corazziari E, editors. Functional bowel disorders and functional abdominal pain. Rome II: functional gastrointestinal disorders: diagnosis, pathophysiology, and treatment. 2000. 2nd ed. McLean, VA: Degnon Associates, Inc.;351–432.21. Ji SW, Park HJ, Choi JP, Lee TH, Lee DY, Lee SI. Validation of Rome II criteria for functional gastrointestinal disorders in Korean patients. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2003. 41:183–189.22. Lee KT, Yoo JH, Kim BK, Cheong HK. Prevalence and risk factors of irritable bowel syndrome in Korean high school students. Korean J Epidemiol. 2007. 29:21–33.23. Hollingshead AB. Four factor index of social status. 1975. (thesis).24. Moon JS, Lee SY, Nam CM, Choi JM, Choe BK, Seo JW, Oh K, Jang MJ, Hwang SS, Yoo MH, et al. 2007 Korean National Growth Charts: review of developmental process and an outlook. Korean J Pediatr. 2008. 51:1–25.25. Kang SG, Shin JH, Hwang YN, Lee EJ, Song SW. Relations between worry, attachment styles and perceived parental rearing in primary school children. J Korean Acad Fam Med. 2008. 29:854–866.26. Kang SG, Shin JH, Song SW. Reliability and validity of the Korean version of the Penn State Worry Questionnaire in primary school children. J Korean Med Sci. 2010. 25:1210–1216.27. Guillemin F, Bombardier C, Beaton D. Cross-cultural adaptation of health-related quality of life measures: literature review and proposed guidelines. J Clin Epidemiol. 1993. 46:1417–1432.28. Beaton DE, Bombardier C, Guillemin F, Ferraz MB. Guidelines for the process of cross-cultural adaptation of self-report measures. Spine. 2000. 25:3186–3191.29. Yim JH, Bae JM, Choi SS, Kim SW, Hwang HS, Huh BY. The validity of modified Korean-translated BEPSI (Brief Encounter Psychosocial Instrument) as instrument of stress measurement in outpatient clinic. J Korean Acad Fam Med. 1996. 17:42–53.30. Keefer L, Sanders K, Sykes MA, Blanchard EB, Lackner JM, Krasner S. Towards a better understanding of anxiety in irritable bowel syndrome: a preliminary look at worry and intolerance of uncertainty. J Cogn Psychother. 2005. 19:163–172.31. Gros DF, Antony MM, McCabe RE, Swinson RP. Frequency and severity of the symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome across the anxiety disorders and depression. J Anxiety Disord. 2009. 23:290–296.32. Butler G, Matthews A. Cognitive processes in anxiety. Adv Behav Res Ther. 1983. 5:551–565.33. Russel M, Davey GC. The relationship between life events measures and anxiety and its cognitive correlates. Pers Individ Dif. 1993. 14:317–322.34. Crane C, Martin M. Perceived vulnerability to illness in individuals with irritable bowel syndrome. J Psychosom Res. 2002. 53:1115–1122.35. Han SH, Lee OY, Lee YS, Kim KB, Yoon BC, Choi HS. Anxiety, depression and sleep disturbance in female constipation predominant irritable bowel syndrome. Korean J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2005. 11:66–71.36. Kearney DJ, Brown-Chang J. Complementary and alternative medicine for IBS in adults: mind-body interventions. Nat Clin Pract Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2008. 5:624–636.37. Krystal AD, Goforth HW, Roth T. Effects of antipsychotic medications on sleep in schizophrenia. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2008. 23:150–160.38. Shen YH, Nahas R. Complementary and alternative medicine for treatment of irritable bowel syndrome. Can Fam Physician. 2009. 55:143–148.39. Keefer L, Blanchard EB. A one year follow-up of relaxation response meditation as a treatment for irritable bowel syndrome. Behav Res Ther. 2002. 40:541–546.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Study on the Relationship between Irritable Bowel Syndrome(IBS) and Nurses' Occupational Stress
- Irritable bowel syndrome
- The Effect of Stress on Gastrointestinal Physiology in Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Frequency of Irritable Bowel Syndrome, Entrance Examination Stress, Mental Health, and Quality of Life among Adolescent Women
- Model Predicting Irritable Bowel Syndrome Severity in University Students