J Korean Med Sci.
2012 Nov;27(11):1315-1319. 10.3346/jkms.2012.27.11.1315.
Phylogenetic Analysis of the 56-kDa Type-Specific Protein Genes of Orientia tsutsugamushi in Central Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Cheongju, Korea. hwjeong@chungbuk.ac.kr
- 2Department of Microbiology, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Cheongju, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 2157940
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2012.27.11.1315
Abstract
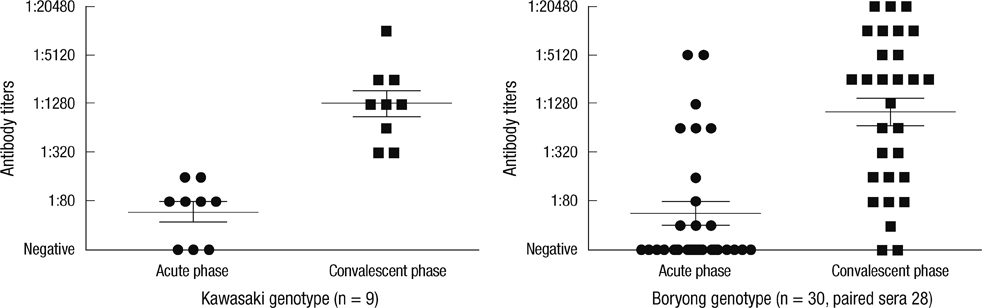
- There are several antigenic variants of Orientia tsutsugamushi. The 56-kDa type-specific antigen (TSA) is responsible for the antigenic variation. Nucleotide sequences of the 56-kDa TSA obtained from 44 eschar samples of Korean scrub typhus patients and from 40 representative strains retrieved from the GenBank database were analyzed phylogenetically. Clinical patient data were assessed based on the genotyping results. Of the 44 nucleotide sequences, 32 (72.7%) clustered with the Boryong genotype, which is the major genotype in Korea. Eleven nucleotide sequences (25%) clustered with the Kawasaki genotype, not identified in Korea until 2010. One nucleotide sequence was consistent with the Karp genotype. The clinical course of the patients infected with each genotype showed no differences. Diagnostic performance of the immunofluorescence assay (IFA) using the 56-kDa TSA from Gilliam, Karp and Boryong as test antigens were not different for the Boryong and Kawasaki genotypes. Although Boryong is still the predominant genotype, the results suggest that Kawasaki genotype is quite prevalent in Chungbuk province of Korea.
MeSH Terms
-
Aged
Bacterial Proteins/*genetics/metabolism
Base Sequence
DNA, Bacterial/analysis
Databases, Genetic
Female
Genotype
Humans
Male
Middle Aged
Open Reading Frames
Orientia tsutsugamushi/*classification/isolation & purification
Phylogeny
Republic of Korea
Scrub Typhus/diagnosis/metabolism/*microbiology
Sequence Analysis, DNA
Bacterial Proteins
DNA, Bacterial
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
High In Vitro Infectivity of a Doxycycline-Insensitive Strain of Orientia tsutsugamushi
Min Su Kim, Ji Hyeon Baek, Jin-Soo Lee, Moon-Hyun Chung, Sun Myoung Lee, Jae-Seung Kang
Infect Chemother. 2013;45(4):431-434. doi: 10.3947/ic.2013.45.4.431.
Reference
-
1. Ree HI, Cho MK, Lee IY, Jeon SH. Comparative epidemiological studies on vector/reservoir animals of tsutsugamushi disease between high and low endemic areas in Korea. Korean J Parasitol. 1995. 33:27–36.2. Tamura A, Takahashi K, Tsuruhara T, Urakami H, Miyamura S, Sekikawa H, Kenmotsu M, Shibata M, Abe S, Nezu H. Isolation of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi antigenically different from Kato, Karp, and Gilliam strains from patients. Microbiol Immunol. 1984. 28:873–882.3. Murata M, Yoshida Y, Osono M, Ohashi N, Oyanagi M, Urakami H, Tamura A, Nogami S, Tanaka H, Kawamura A Jr. Production and characterization of monoclonal strain-specific antibodies against prototype strains of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. Microbiol Immunol. 1986. 30:599–610.4. Yamashita T, Kasuya S, Noda S, Nagano I, Ohtsuka S, Ohtomo H. Newly isolated strains of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi in Japan identified by using monoclonal antibodies to Karp, Gilliam, and Kato strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1988. 26:1859–1860.5. Elisberg BL, Campbell JM, Bozeman FM. Antigenic diversity of rickettsia tsutsugamushi: epidemiologic and ecologic significance. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol. 1968. 12:18–25.6. Yamamoto S, Kawabata N, Tamura A, Urakami H, Ohashi N, Murata M, Yoshida Y, Kawamura A Jr. Immunological properties of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi, Kawasaki strain, isolated from a patient in Kyushu. Microbiol Immunol. 1986. 30:611–620.7. Manosroi J, Chutipongvivate S, Auwanit W, Manosroi A. Determination and geographic distribution of Orientia tsutsugamushi serotypes in Thailand by nested polymerase chain reaction. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2006. 55:185–190.8. Fournier PE, Siritantikorn S, Rolain JM, Suputtamongkol Y, Hoontrakul S, Charoenwat S, Losuwanaluk K, Parola P. Detection of new genotypes of Orientia tsutsugamushi infecting humans in Thailand. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2008. 14:168–173.9. Chang WH. Tsutsugamushi disease in Korea. 1994. Seoul: Seohung Press;56–57.10. Kim DM, Yun NR, Neupane GP, Shin SH, Ryu SY, Yoon HJ, Wie SH, Kim WJ, Lee CY, Choi JS, et al. Differences in clinical features according to Boryoung and Karp genotypes of Orientia tsutsugamushi. PLoS One. 2011. 6:e22731.11. Chu H, Park SH, Kim EJ, Hwang KJ, Shim SK, Park S, Park MY. Phylogenetic clustering of 4 prevalent virulence genes in Orientia tsutsugamushi isolates from human patients. J Microbiol. 2010. 48:124–128.12. Ree HI, Kim TE, Lee IY, Jeon SH, Hwang UW, Chang WH. Determination and geographical distribution of Orientia tsutsugamushi serotypes in Korea by nested polymerase chain reaction. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2001. 65:528–534.13. Higgins DG, Bleasby AJ, Fuchs R. CLUSTAL V: improved software for multiple sequence alignment. Comput Appl Biosci. 1992. 8:189–191.14. Perriere G, Gouy M. WWW-query: an on-line retrieval system for biological sequence banks. Biochimie. 1996. 78:364–369.15. Lee YM, Kim DM, Lee SH, Jang MS, Neupane GP. Phylogenetic analysis of the 56 kDa protein genes of Orientia tsutsugamushi in Southwest Area of Korea. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2011. 84:250–254.16. Park SW, Lee CK, Kwak YG, Moon C, Kim BN, Kim ES, Kang JM, Lee CS. Antigenic drift of Orientia tsutsugamushi in South Korea as identified by the sequence analysis of a 56-kDa protein-encoding gene. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2010. 83:930–935.17. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Current trends of scrub typhus. Commun Dis Monthly Rep. 2004. 15:245–252.18. Shim SK, Choi EN, Yu KO, Park HJ, Kim CM, Kee KH, Park JK, Park PH, Yoon MH, Park SH, et al. Characterisation of Orientia tsutsugamushi genotypes from wild rodents and chigger mites in Korea. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2009. 15:Suppl 2. 311–312.19. Chang WH. Current status of tsutsugamushi disease in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 1995. 10:227–238.20. Seong SY, Kim HR, Huh MS, Park SG, Kang JS, Han TH, Choi MS, Chang WH, Kim IS. Induction of neutralizing antibody in mice by immunization with recombinant 56 kDa protein of Orientia tsutsugamushi. Vaccine. 1997. 15:1741–1747.21. Seong SY, Park SG, Huh MS, Jang WJ, Kim HR, Han TH, Choi MS, Chang WH, Kim IS. Mapping of antigenic determinant regions of the Bor56 protein of Orientia tsutsugamushi. Infect Immun. 1997. 65:5250–5256.22. Choi MS, Seong SY, Kang JS, Kim YW, Huh MS, Kim IS. Homotypic and heterotypic antibody responses to a 56-kilodalton protein of Orientia tsutsugamushi. Infect Immun. 1999. 67:6194–6197.23. Lee JH, Cho NH, Kim SY, Bang SY, Chu H, Choi MS, Kim IS. Fibronectin facilitates the invasion of Orientia tsutsugamushi into host cells through interaction with a 56-kDa type-specific antigen. J Infect Dis. 2008. 198:250–257.24. Ohashi N, Nashimoto H, Ikeda H, Tamura A. Diversity of immunodominant 56-kDa type-specific antigen (TSA) of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. Sequence and comparative analyses of the genes encoding TSA homologues from four antigenic variants. J Biol Chem. 1992. 267:12728–12735.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Genetic Heterogeneity in 56 kDa gene of Orientia tsutsugamushi Genotype Karp
- Analysis of antigenic characteristics of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi Boryong strain and antigenic heterogeneity of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi using monoclonal antibodies
- Seroprevalence and Phylogenetic Analysis of Orientia tsutsugamushi from Apodemus peninsulae in Korea
- The Attachment of Detergent-Extracted Outer Membrane Proteins of Orientia tsutsugamushi to the Host Cell Surface
- Molecular Cloning of the Major Immunogen of Orientia tsutsugamushi Thai Strains and Development Passive Hemagglutination Test