J Korean Med Sci.
2010 Oct;25(10):1522-1525. 10.3346/jkms.2010.25.10.1522.
Jervell and Lange-Nielsen Syndrome: Novel Compound Heterozygous Mutations in the KCNQ1 in a Korean Family
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Seoul National University Children's Hospital, Seoul, Korea. eunjbae@plaza.snu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2157860
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2010.25.10.1522
Abstract
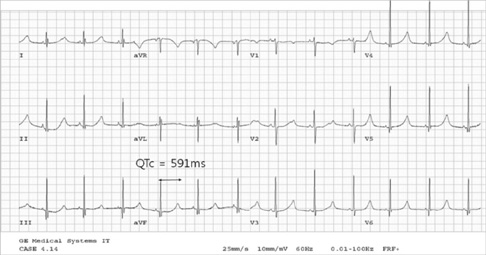
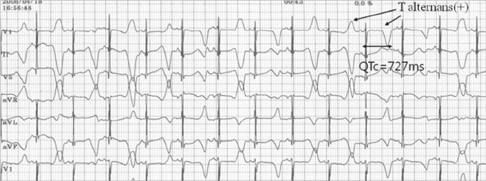
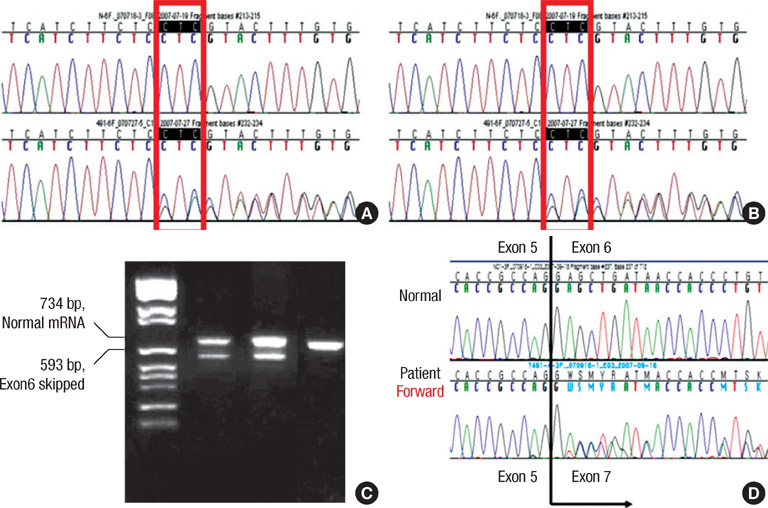
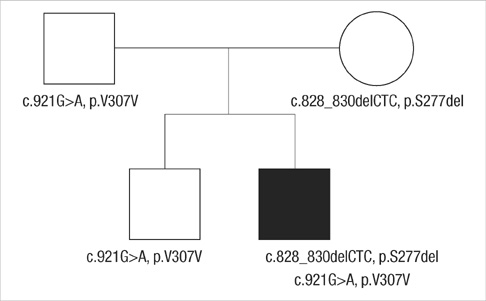
- The Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome (JLNS) is an autosomal recessive syndrome characterized by congenital deafness and cardiac phenotype (QT prolongation, ventricular arrhythmias, and sudden death). JLNS has been shown to occur due to homozygous mutation in KCNQ1 or KCNE1. There have been a few clinical case reports on JLNS in Korea; however, these were not confirmed by a genetic study. We identified compound heterozygous mutations in KCNQ1 in a 5-yr-old child with JLNS, who visited the hospital due to recurrent syncope and seizures and had congenital sensorineural deafness. His electrocardiogram revealed a markedly prolonged corrected QT interval with T wave alternans. The sequence analysis of the proband revealed the presence of novel compound heterozygous deletion/splicing error mutations (c.828-830 delCTC, p.S277del/c.921G>A, p.V307V). Each mutation in KCNQ1 was identified on the maternal and paternal side. With beta-blocker therapy the patient has remained symptom-free for three and a half years.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kannankeril PJ, Fish FA. Allen HD, Driscoll DJ, Shaddy RE, Feltes TF, editors. Disorders of cardiac rhythm and conduction. Moss and Adams' heart disease in infants, children, and adolescents including the fetus and young adult. 2008. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;328–331.2. Wang Z, Li H, Moss AJ, Robinson J, Zareba W, Knilans T, Bowles NE, Towbin JA. Compound heterozygous mutations in KvLQT1 cause Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome. Mol Genet Metab. 2002. 75:308–316.
Article3. Lehnart SE, Ackerman MJ, Benson DW Jr, Brugada R, Clancy CE, Donahue JK, George AL Jr, Grant AO, Groft SC, January CT, Lathrop DA, Lederer WJ, Makielski JC, Mohler PJ, Moss A, Nerbonne JM, Olson TM, Przywara DA, Towbin JA, Wang LH, Marks AR. Inherited arrhythmias: a National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and Office of Rare Diseases workshop consensus report about the diagnosis, phenotyping, molecular mechanisms, and therapeutic approaches for primary cardiomyopathies of gene mutations affecting ion channel function. Circulation. 2007. 116:2325–2345.4. Oudit GY, Ramirez RJ, Backx PH. Zipes DP, Jalife J, editors. Voltage-regulated potassium channels. Cardiac electrophysiology: from cell to bedside. 2004. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders;28–29.
Article5. Neyroud N, Tesson F, Denjoy I, Leibovici M, Donger C, Barhanin J, Faure S, Gary F, Coumel P, Petit C, Schwartz K, Guicheney P. A novel mutation in the potassium channel gene KVLQT1 causes the Jervell and Lange-Nielsen cardioauditory syndrome. Nat Genet. 1997. 15:186–189.
Article6. Schulze-Bahr E, Wang Q, Wedekind H, Haverkamp W, Chen Q, Sun Y, Rubie C, Hordt M, Towbin JA, Borggrefe M, Assmann G, Qu X, Somberg JC, Breithardt G, Oberti C, Funke H. KCNE1 mutations cause jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome. Nat Genet. 1999. 17:267–268.
Article7. Neyroud N, Richard P, Vignier N, Donger C, Denjoy I, Demay L, Shkolnikova M, Pesce R, Chevalier P, Hainque B, Coumel P, Schwartz K, Guicheney P. Genomic organization of the KCNQ1 K+ channel gene and identification of C-terminal mutations in the long-QT syndrome. Circ Res. 1999. 84:290–297.8. Tranebjaerg L, Bathen J, Tyson J, Bitner-Glindzicz M. Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome: a Norwegian perspective. Am J Med Genet. 1999. 89:137–146.9. Ning L, Moss AJ, Zareba W, Robinson J, Rosero S, Ryan D, Qi M. Novel compound heterozygous mutations in the KCNQ1 gene associated with autosomal recessive long QT syndrome (Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome). Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2003. 8:246–250.
Article10. Napolitano C, Priori SG, Schwartz PJ, Bloise R, Ronchetti E, Nastoli J, Bottelli G, Cerrone M, Leonardi S. Genetic testing in the long QT syndrome: development and validation of an efficient approach to genotyping in clinical practice. JAMA. 2005. 294:2975–2980.11. Schwartz PJ, Spazzolini C, Crotti L, Bathen J, Amlie JP, Timothy K, Shkolnikova M, Berul CI, Bitner-Glindzicz M, Toivonen L, Horie M, Schulze-Bahr E, Denjoy I. The Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome: natural history, molecular basis, and clinical outcome. Circulation. 2006. 113:783–790.12. Richter S, Brugada P. Risk-stratifying Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome from clinical data. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 2006. 17:1169–1171.
Article13. Tyson J, Tranebjaerg L, McEntagart M, Larsen LA, Christiansen M, Whiteford ML, Bathen J, Aslaksen B, Sorland SJ, Lund O, Pembrey ME, Malcolm S, Bitner-Glindzicz M. Mutational spectrum in the cardioauditory syndrome of Jervell and Lange-Nielsen. Hum Genet. 2000. 107:499–503.
Article14. Tester DJ, Will ML, Haglund CM, Ackerman MJ. Compendium of cardiac channel mutations in 541 consecutive unrelated patients referred for long QT syndrome genetic testing. Heart Rhythm. 2005. 2:507–517.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Large Deletion in KCNQ1 Identified in a Family with Jervell and Lange-Nielsen Syndrome
- A Case of Congenital Long QT Syndrome Associated with Deafness and Syncope
- A Case of Congenital Long QT Syndrome with Reccurent Syncope
- Novel Compound Heterozygous Mutations in CTSC Gene in a Chinese Family with Papillon–Lefevre Syndrome
- A family with X-linked Cornelia de Lange syndrome due to a novel SMC1A missense mutation identified by multi-gene panel sequencing