J Korean Med Sci.
2006 Feb;21(1):1-4. 10.3346/jkms.2006.21.1.1.
Increased Expression of Sodium Transporters in Rats Chronically Inhibited of Nitric Oxide Synthesis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physiology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. julee@chonnam.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 2157772
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2006.21.1.1
Abstract
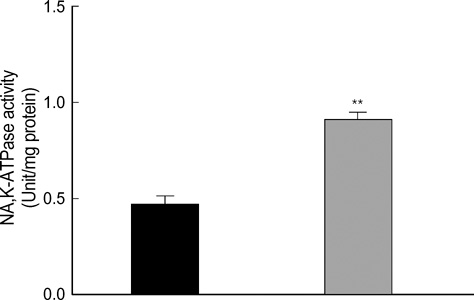
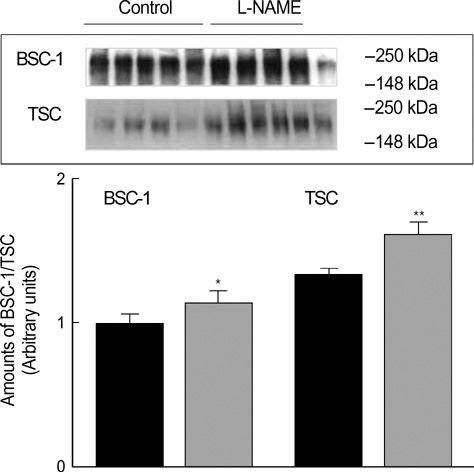
- The present study was done to determine whether endogenous nitric oxide (NO) plays a role in the regulation of sodium transporters in the kidney. Male Sprague-Dawley rats were treated with NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME, 100 mg/L drinking water) for 4 weeks. Control rats were supplied with tap water without drugs. Expression of Na, K-ATPase, type 3 Na/H exchanger (NHE3), Na/K/2Cl cotransporter (BSC1), and thiazide-sensitive Na/Cl cotransporter (TSC) proteins was determined in the kidney by Western blot analysis. Catalytic activity of Na,K-ATPase was also determined. The treatment with L-NAME significantly and steadily increased the systemic blood pressure. Total and fractional excretion of urinary sodium decreased significantly, while creatinine clearance remained unaltered. Neither plasma renin activity nor aldosterone concentration was significantly altered. The alpha1 subunit expression and the catalytic activity of Na, K-ATPase were increased in the kidney. The expression of NHE3, BSC1 and TSC was also increased significantly. These results suggest that endogenously-derived NO exerts a tonic inhibitory effect on the expression of sodium transporters, including Na, K-ATPase, NHE3, BSC1, and TSC, in the kidney.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Blotting, Western
Carrier Proteins/*biosynthesis
Enzyme Inhibitors/pharmacology
Kidney/drug effects/metabolism
Male
NG-Nitroarginine Methyl Ester/*pharmacology
Na(+)-K(+)-Exchanging ATPase/biosynthesis
Nitric Oxide Synthase/*antagonists & inhibitors/metabolism
Rats
Rats, Sprague-Dawley
Receptors, Drug/biosynthesis
Sodium/*metabolism
Sodium Chloride Symporters/biosynthesis
Sodium-Hydrogen Antiporter/biosynthesis
Sodium-Potassium-Chloride Symporters/biosynthesis
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Altered Nitric Oxide System in Cardiovascular and Renal Diseases
JongUn Lee, Eun Hui Bae, Seong Kwon Ma, Soo Wan Kim
Chonnam Med J. 2016;52(2):81-90. doi: 10.4068/cmj.2016.52.2.81.
Reference
-
1. Lahera V, Salom MG, Fiksen-Olsen MJ, Raij L, Romero JC. Effects of NG-monomethyl-L-arginine and L-arginine on acetylcholine response. Hypertension. 1990. 15:659–663.2. Kashgarian M, Biemesderfer D, Caplan M, Forbush B 3rd. Monoclonal antibody to Na, K-ATPase: immunocytochemical localization along nephron segments. Kidney Int. 1985. 28:899–913.3. Amemiya M, Loffing J, Lotscher M, Kaissling B, Alpern RJ, Moe OW. Expression of NHE-3 in the apical membrane of rat renal proximal tubule and thick ascending limb. Kidney Int. 1995. 48:1206–1215.
Article4. Gamba G, Miyanoshita A, Lombardi M, Lytton J, Lee WS, Hediger MA, Hebert SC. Molecular cloning, primary structure, and characterization of two members of the mammalian electroneutral sodium-(potassium)-chloride cotransporter family expressed in kidney. J Biol Chem. 1994. 269:17713–17722.
Article5. Knepper MA, Kim GH, Fernandez Llama P, Ecelbarger C. Regulation of thick ascending limb transport by vasopressin. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999. 10:628–634.
Article6. Roczniak A, Burns KD. Nitric oxide stimulates guanylate cyclase and regulates sodium transport in rabbit proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1996. 270:F106–F115.
Article7. McKee M, Scavone C, Nathanson JA. Nitric oxide, cGMP, and hormone regulation of active sodium transport. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1994. 91:12056–12060.
Article8. Varela M, Herrera M, Garvin JL. Inhibition of Na-K-ATPase in thick ascending limbs by NO depends on O2 - and is diminished by a high-salt diet. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2004. 287:F224–F230.9. Ortiz PA, Hong NJ, Garvin JL. NO decreases thick ascending limb chloride absorption by reducing Na+-K+-2Cl- cotransporter activity. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2001. 281:F819–F825.10. Nakanishi K, Hara N, Nagai Y. Salt-sensitive hypertension in conscious rats induced by chronic nitric oxide blockade. Am J Hypertens. 2002. 15:150–156.
Article11. Salazar FJ, Alberola A, Pinilla JM, Romero JC, Quesada T. Salt-induced increase in arterial pressure during nitric oxide synthesis inhibition. Hypertension. 1993. 22:49–55.
Article12. Nakanishi K, Mattson DL, Cowley AW Jr. Role of renal medullary blood flow in the development of L-NAME hypertension in rats. Am J Physiol. 1995. 268:R317–R323.
Article13. Norby JG. Coupled assay of Na+,K+-ATPase activity. Methods Enzymol. 1988. 156:116–119.14. Lee J, Choi KC, Yeum CH, Kim W, Yoo K, Park JW, Yoon PJ. Impairment of endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation in chronic two-kidney, one clip hypertensive rats. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1995. 10:619–623.15. Kang DG, Kim JW, Lee J. Effects of nitric oxide synthesis inhibition on the Na,K-ATPase activity in the kidney. Pharmacol Res. 2000. 41:123–127.
Article16. Roczniak A, Burns KD. Nitric oxide stimulates guanylate cyclase and regulates sodium transport in rabbit proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1996. 270:F106–F115.
Article17. Stoos BA, Garvin JL. Actions of nitric oxide on renal epithelial transport. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1997. 24:591–594.
Article18. Plato CF, Stoos BA, Wang D, Garvin JL. Endogenous nitric oxide inhibits chloride transport in the thick ascending limb. Am J Physiol. 1999. 276:F159–F163.19. Ortiz PA, Hong NJ, Garvin JL. NO decreases thick ascending limb chloride absorption by reducing Na+-K+-2Cl- cotransporter activity. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2001. 281:F819–F825.20. He H, Podymow T, Zimpelmann J, Burns KD. NO inhibits Na+-K+-2Cl- cotransport via a cytochrome P-450-dependent pathway in renal epithelial cells (MMDD1). Am J Physiol. 2003. 284:F1235–F1244.21. Kim GH, Masilamani S, Turner R, Mitchell C, Wade JB, Knepper MA. The thiazide-sensitive Na-Cl cotransporter is an aldosterone-induced protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998. 95:14552–14557.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Altered Expression of Sodium Transporters and Water Channels in the Submandibular Gland of Rats Treated with Nitric Oxide Synthesis Inhibitors
- Altered Regulation of NHE3, NBC1 and Nitric Oxide System in the Kidney of Rats with Maleic Acid-nduced Metabolic Acidosis
- Endogenous Nitric Oxide Inhibits Na,K-ATPase Activity in the Kidney
- Changes in Endothelin Receptor Type B and Neuronal Nitric Oxide Synthase in Puromycin Aminonucleoside-Induced Nephrotic Syndrome
- The Expression of NADPH-diaphorase in Corneal Neovascularization of streptozotocin Induced Diabetic Rat