J Korean Med Sci.
2005 Dec;20(6):941-946. 10.3346/jkms.2005.20.6.941.
A Sporadic Outbreak of Human Brucellosis in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, Korea. lhbmd@chonbuk.ac.kr
- 2Division of Zoonoses, Center for Immunology and Pathology, National Institute of Health, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2157741
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2005.20.6.941
Abstract
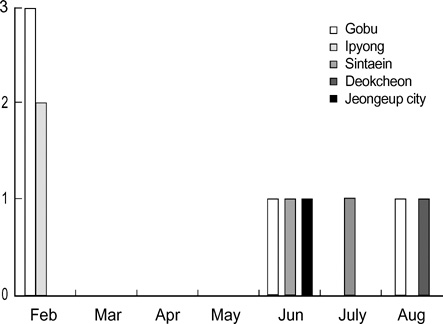
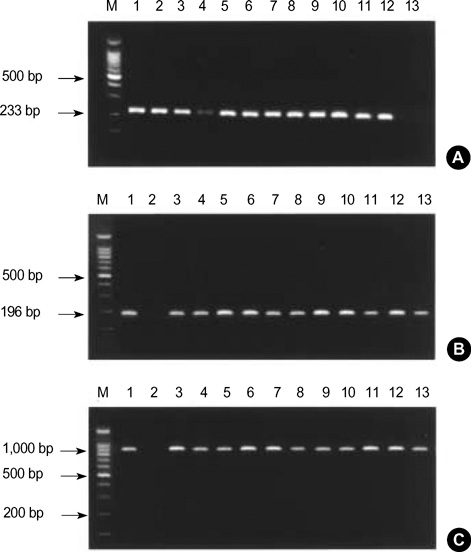
- Eleven cases of human brucellosis occurred among livestock workers and a veterinarian who lived and worked in a rural area around Jeongeup City, Jeollabuk-Do, Korea from February 2003 to August 2003. Eight of the patients had taken care of Korean native cattle that were infected with bovine brucellosis and had already been slaughtered. Two of the patients had taken care of dairy cattle, and one case was a veterinarian who acquired the disease through an accidental contact with infected cattle while assisting in calf delivery. Eleven cases were identified by serologic work ups and four cases were identified via positive blood cultures. This study shows that the Republic of Korea is no longer free of human brucellosis, Brucella abortus biotype 1. We reviewed the patients' characteristics and serologic data during the oneyear follow up period, and we also discuss on the efficacy and side effects of the rifampin and doxycyline regimen used for the treatment of human brucellosis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Animal Husbandry
Animals
Anti-Bacterial Agents/adverse effects/therapeutic use
Antibodies, Bacterial/blood
Base Sequence
Brucella abortus/genetics/immunology/isolation and purification
Brucellosis/drug therapy/*epidemiology/microbiology/transmission
Brucellosis, Bovine/transmission
Cattle
DNA, Bacterial/genetics
Disease Outbreaks
Doxycycline/adverse effects/therapeutic use
Female
Humans
Korea/epidemiology
Male
Middle Aged
Occupational Diseases/drug therapy/epidemiology/immunology/microbiology
Rifampin/adverse effects/therapeutic use
Veterinarians
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Is Human Brucellosis Endemics in Korea?
Eun-Kyung Kim, Joo-Hee Hwang, Jeong-Hwan Hwang, Chang-Seop Lee
Yonsei Med J. 2017;58(1):259-260. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2017.58.1.259.Chemoprophylaxis and Serological Follow-Up in Brucella abortus Exposed Laboratory Workers
Chang-Seop Lee, Hye-Soo Lee, Jae-Hyeon Lee, Jin-Hee Park, Young-Sil Choi, Kyu-Jam Hwang, Heung-Bum Lee
Infect Chemother. 2008;40(2):107-109. doi: 10.3947/ic.2008.40.2.107.Efficacy of strain RB51 vaccine in protecting infection and vertical transmission against Brucella abortus in Sprague-Dawley rats
Md. Ariful Islam, Mst. Minara Khatun, Byeong-Kirl Baek, Sung-Il Lee
J Vet Sci. 2009;10(3):211-218. doi: 10.4142/jvs.2009.10.3.211.
Reference
-
1. Corbel MJ. Brucellosis: an overview. Emerg Infect Dis. 1997. 3:213–221.
Article2. Takahashi H, Tanaka S, Yoshida K, Hoshino H, Sasaki H, Takahashi K, Kimura K, Fujii N, Kimura H, Mori M, Abe S. An unusual case of brucellosis in Japan: difficulties in the differential diagnosis from pulmonary tuberculosis. Intern Med. 1996. 35:310–314.
Article3. Park MS, Woo YS, Lee MJ, Shim SK, Lee HK, Choi YS, Lee WH, Kim KH, Park MY. The first case of human brucellosis in Korea. Infect Chemother. 2003. 35:461–466.4. Sohn JY, Lee KU, Yoo JC, Park MS, Park KS, Lee IT, Kim BH, Kim YJ, Ko KS, Park HJ. Studies on zoonosis brucellosis. Report of NIH Korea. 1986. 23:281–295.5. Lee YW, Lee KU, Lee SM, Park MS, Park KS, Lee MS, Park KW, Byun HS. Studies on bacteriological and serological diagnosis of human brucellosis. Report of NIH Korea. 1988. 25:257–266.6. Yeom JS, Jung HC, Nam JH, Choi YH, Song YG, Kim E, Kim HS, Suh I, Kim JM. Seroepidemiologic study of brucellosis in Cheju Island. Korean J Infect Dis. 1998. 30:165–172.7. Monthly Report on Notifiable Diseases. (Livestock and Poultry). Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry, Republic of Korea. [accessed on 3 March 2005]. http://www.maf.go.kr/index.jsp.8. CDC. Case definition of brucellosis. MMWR. 1997. 46:1–55.9. Baldi PC, Miguel SE, Fossati CA, Wallach JC. Serological follow-up of human brucellosis by measuring IgG antibodies to lipopolysaccharide and cytoplasmic proteins of Brucella species. Clin Infect Dis. 1996. 22:446–455.
Article10. Gazapo E, Gonzalez Lahoz J, Subiza JL, Baquero M, Gil J, de la Concha EG. Changes in IgM and IgG antibody concentrations in brucellosis over time: importance for diagnosis and follow-up. J Infect Dis. 1989. 159:219–225.
Article11. Chung JS, Cho YJ, Park CK. Isolation and biotyping of Brucella abortus from dairy cattle in Kyungbuk area, Korea. Korean J Vet Res. 1988. 28:339–343.12. Baek BK, Lim CW, Rahman MS, Kim CH, Oluoch A, Kakoma I. Brucella abortus infection in indigenous Korean dogs. Can J Vet Res. 2003. 67:312–314.13. Memish Z, Mah MW, Al Mahmoud S, Al Shaalan M, Khan MY. Brucella bacteraemia: clinical and laboratory observations in 160 patients. J Infect. 2000. 40:59–63.
Article14. Noviello S, Gallo R, Kelly M, Limberger RJ, DeAngelis K, Cain L, Wallace B, Dumas N. Laboratory-acquired brucellosis. Emerg Infect Dis. 2004. 10:1848–1850.
Article15. Robichaud S, Libman M, Behr M, Rubin E. Prevention of laboratory-acquired brucellosis. Clin Infect Dis. 2004. 38:e119–e122.16. Gee JE, De BK, Levett PN, Whitney AM, Novak RT, Popovic T. Use of 16S rRNA gene sequencing for rapid confirmatory identification of Brucella isolates. J Clin Microbiol. 2004. 42:3649–3654.
Article17. Moyer NP, Evins GM, Pigott NE, Hudson JD, Farshy CE, Feeley JC, Hausler WJ Jr. Comparison of serologic screening tests for brucellosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987. 25:1969–1972.
Article18. Matar GM, Khneisser IA, Abdelnoor AM. Rapid laboratory confirmation of human brucellosis by PCR analysis of a target sequence on the 31-kilodalton Brucella antigen DNA. J Clin Microbiol. 1996. 34:477–478.
Article19. Navarro E, Escribano J, Fernandez J, Solera J. Comparison of three different PCR methods for detection of Brucella spp in human blood samples. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2002. 34:147–151.20. Irmak H, Buzgan T, Evirgen O, Akdeniz H, Demiroz AP, Abdoel TH, Smits HL. Use of the Brucella IgM and IgG flow assays in the serodiagnosis of human brucellosis in an area endemic for brucellosis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2004. 70:688–694.
Article21. Ariza J, Pellicer T, Pallares R, Foz A, Gudiol F. Specific antibody profile in human brucellosis. Clin Infect Dis. 1992. 14:131–140.
Article22. Solera J, Rodriguez-Zapata M, Geijo P, Largo J, Paulino J, Saez L, Martinez-Alfaro E, Sanchez L, Sepulveda MA, Ruiz-Ribo MD. Doxycycline-rifampin versus doxycycline-streptomycin in treatment of human brucellosis due to Brucella melitensis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1995. 39:2061–2067.23. Montejo JM, Alberola I, Glez-Zarate P, Alvarez A, Alonso J, Canovas A, Aguirre C. Open, randomized therapeutic trial of six antimicrobial regimens in the treatment of human brucellosis. Clin Infect Dis. 1993. 16:671–676.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Diagnosis of human brucellosis
- A Case Report of Human Brucellosis Found by Zoonoses Surveillance System Based on One Health
- Epidemiology of brucellosis among cattle in Korea from 2001 to 2011
- Brucellar Spondylodiscitis in an Endemic Bovine Brucellosis Region of Korea: A Case Report
- Brucella Epididymorchitis: A Rare Cause of Testicular Mass