Ann Dermatol.
2015 Dec;27(6):694-701. 10.5021/ad.2015.27.6.694.
Treatment of Nodular Fasciitis Occurring on the Face
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology and Cutaneous Biology Research Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kychung@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2157445
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2015.27.6.694
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
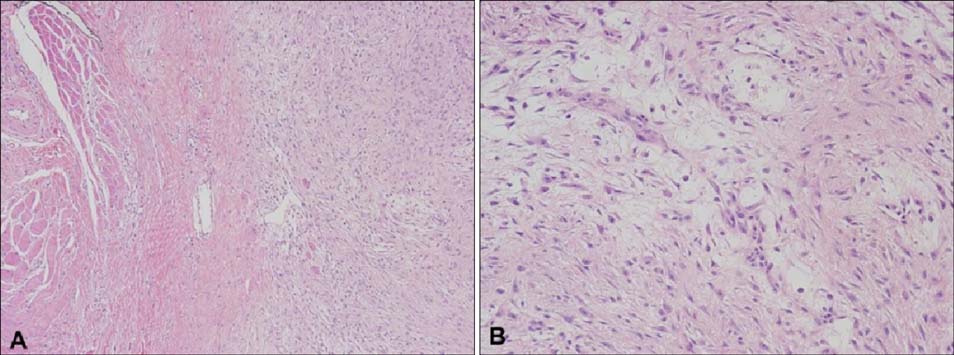
Surgical excision is generally recommended for the treatment of nodular fasciitis (NF) to rule out sarcoma. However, in cases of NF occurring on the face, the reported recurrence rate is higher and the surgical approach may result in considerable aesthetic concern.
OBJECTIVE
To describe our experience with NF occurring on the face and evaluate the outcomes of surgical and nonsurgical methods of treatment.
METHODS
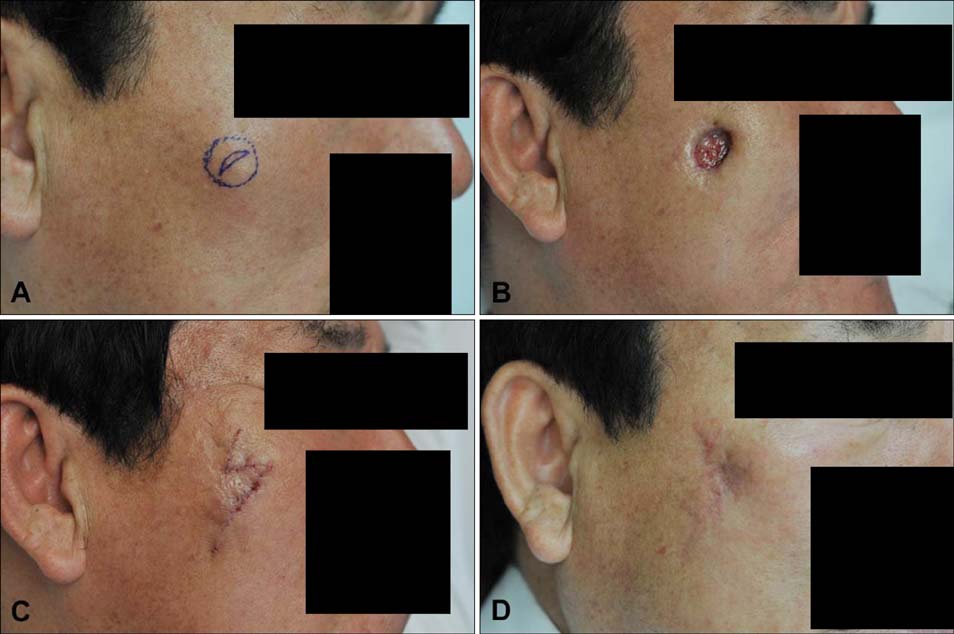
We performed a retrospective review of 16 patients with NF on the face. The patients were treated with surgical excision or nonsurgical methods such as triamcinolone intralesional injection (TA ILI) and pinhole method with a carbon dioxide (CO2) laser.
RESULTS
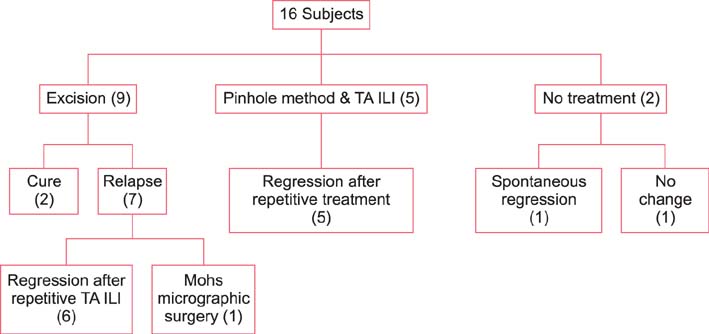
Among the 16 patients, surgical treatment was performed in 9 and recurrence occurred in 7 of these 9 patients (77.8%). The recurred lesions showed regression after repeated TA ILI. On the other hand, five patients underwent nonsurgical treatment after the histologic exclusion of malignancy. Their lesions showed regression after repeated pinhole treatment and TA ILI. In one case, NF spontaneously regressed. On a visual analogue scale, the nonsurgical approach showed superior results. However, the values were not statistically significant (6.90+/-1.56 vs. 5.61+/-1.36; p=0.163). The satisfaction level was lower in patients who experienced recurrence after surgical excision.
CONCLUSION
Surgical treatment for NF on the face showed a noticeable recurrence rate and resulted in scarring. Therefore, considering the possibility of spontaneous regression, the nonsurgical method can be considered as an alternative treatment option for NF on the face.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Yanagisawa A, Okada H. Nodular fasciitis with degeneration and regression. J Craniofac Surg. 2008; 19:1167–1170.
Article2. Bernstein KE, Lattes R. Nodular (pseudosarcomatous) fasciitis, a nonrecurrent lesion: clinicopathologic study of 134 cases. Cancer. 1982; 49:1668–1678.
Article3. Kang SK, Kim HH, Ahn SJ, Choi JH, Sung KJ, Moon KC, et al. Intradermal nodular fasciitis of the face. J Dermatol. 2002; 29:310–314.
Article4. Ko CJ. Dermal hypertrophies and benign fibroblastic/myofibroblastic tumors. In : Goldsmith LA, Fitzpatrick TB, editors. Fitzpatrick's dermatology in general medicine. 8th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill;2012. p. 715–716.5. Graham BS, Barrett TL, Goltz RW. Nodular fasciitis: response to intralesional corticosteroids. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999; 40:490–492.
Article6. Shimizu S, Hashimoto H, Enjoji M. Nodular fasciitis: an analysis of 250 patients. Pathology. 1984; 16:161–166.
Article7. de Feraudy S, Fletcher CD. Intradermal nodular fasciitis: a rare lesion analyzed in a series of 24 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2010; 34:1377–1381.8. Whang SW, Lee KY, Cho SB, Lee SJ, Kang JM, Kim YK, et al. Burn scars treated by pinhole method using a carbon dioxide laser. J Dermatol. 2006; 33:869–872.
Article9. Lee SJ, Yeo IK, Kang JM, Chung WS, Kim YK, Kim BJ, et al. Treatment of hypertrophic burn scars by combination laser-cision and pinhole method using a carbon dioxide laser. Lasers Surg Med. 2014; 46:380–384.
Article10. Spinelli N, Khorassani N. Nodular fasciitis: an uncommon disease with common medical management challenges at a remote Naval Hospital. Mil Med. 2013; 178:e1051–e1054.
Article11. Thompson LD, Fanburg-Smith JC, Wenig BM. Nodular fasciitis of the external ear region: a clinicopathologic study of 50 cases. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2001; 5:191–198.
Article12. Lin XY, Wang L, Zhang Y, Dai SD, Wang EH. Variable Ki67 proliferative index in 65 cases of nodular fasciitis, compared with fibrosarcoma and fibromatosis. Diagn Pathol. 2013; 8:50.
Article13. Souza e Souza Id, Rochael MC, Farias RE, Vieira RB, Vieira JS, Schimidt NC. Nodular fasciitis on the zygomatic region: a rare presentation. An Bras Dermatol. 2013; 88:6 Suppl 1. 89–92.
Article14. Engellau J, Persson A, Bendahl PO, Akerman M, Domanski HA, Bjerkehagen B, et al. Expression profiling using tissue microarray in 211 malignant fibrous histiocytomas confirms the prognostic value of Ki-67. Virchows Arch. 2004; 445:224–230.
Article15. Alonso-Castro L, Boixeda P, Segura-Palacios JM, de Daniel-Rodríguez C, Jiménez-Gómez N, Ballester-Martínez A. Dermatofibromas treated with pulsed dye laser: Clinical and dermoscopic outcomes. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2012; 14:98–101.
Article16. Wang AS, Larsen L, Chang S, Phan T, Jagdeo J. Treatment of a symptomatic dermatofibroma with fractionated carbon dioxide laser and topical corticosteroids. J Drugs Dermatol. 2013; 12:1483–1484.17. Lanigan SW, Robinson TW. Cryotherapy for dermatofibromas. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1987; 12:121–123.
Article18. Cho SB, Lee SJ, Kang JM, Kim YK, Kim TY, Kim DH. The treatment of burn scar-induced contracture with the pinhole method and collagen induction therapy: a case report. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2008; 22:513–514.
Article19. Chung BY, Han SS, Kim BW, Chang SE, Lee MW. Effective treatment of congenital melanocytic nevus and nevus sebaceous using the pinhole method with the erbium-doped yttrium aluminium garnet laser. Ann Dermatol. 2014; 26:651–653.
Article