Ann Dermatol.
2011 Sep;23(Suppl 1):S8-S10. 10.5021/ad.2011.23.S1.S8.
Hypohidrotic Ectodermal Dysplasia Associated with Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency
- Affiliations
-
- 1Celal Bayar University Faculty of Medicine, Department of Dermatology, ManIsa, Turkey. draylinturel@hotmail.com
- 2Celal Bayar University Faculty of Medicine, Department of Pediatrics, ManIsa, Turkey.
- KMID: 2156740
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2011.23.S1.S8
Abstract
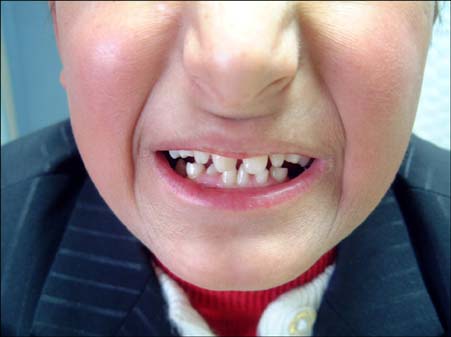
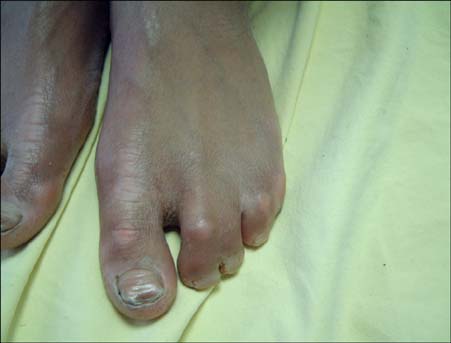
- Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia (HED) is a syndrome characterized by hypodontia, hypotrichosis, and partial or total ecrine sweat gland deficiency. The most prevalent form of HED is inherited as an X linked pattern. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G-6-PD) deficiency is an X-linked recessive disease, which leads to hemolytic anemia and jaundice. It is expressed in males, while heterozygous females are usually clinically normal. A 12-year-old boy with the complaints of hair and eyebrow disturbances, teeth disfigurement, decreased sweating, and xerosis presented to the outpatient clinic. Dermatological examination revealed sparse hair and eyebrows, conical-shaped teeth, xerosis, syndactylia, transverse grooves, and discoloration of nails. Laboratory findings indicated anemia. His 3-year-old sister also had sparse hair and eyebrows, xerosis, and syndactylia. We learned that the patient had a previous history of neonatal jaundice and a diagnosis of G-6-PD deficiency. Although it has been shown that loci of ectodermal dysplasia and G-6-PD deficiency genes are near to one another, we did not find any case study reporting on occurrence of these two genetic diseases together. With the aspect of this rare and interesting case, the relationship between HED and G-6-PD deficiency was defined.
MeSH Terms
-
Ambulatory Care Facilities
Anemia
Anemia, Hemolytic
Anodontia
Child
Ectoderm
Ectodermal Dysplasia
Eyebrows
Female
Glucose-6-Phosphate
Glucosephosphate Dehydrogenase
Glucosephosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency
Hair
Humans
Hypotrichosis
Infant, Newborn
Jaundice
Jaundice, Neonatal
Male
Nails
Preschool Child
Siblings
Sweat
Sweat Glands
Sweating
Syndactyly
Tooth
Glucose-6-Phosphate
Glucosephosphate Dehydrogenase
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lind LK, Stecksén-Blicks C, Lejon K, Schmitt-Egenolf M. EDAR mutation in autosomal dominant hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia in two Swedish families. BMC Med Genet. 2006. 7:80.
Article2. Lanzkowsky P. Lanzkowsky P, editor. Hemolytic anemia. Manual of pediatric hematology and oncology. 2005. 4th ed. New York: Elsevier;136–198.
Article3. Harper J, Trembath RC. Burns T, Breathnach S, Burns T, Breathnach S, Cox N, Griffiths C, editors. Genetics and genodermatoses. Rook's textbook of dermatology. 2004. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Blackwell Publishing;12–85.4. Martínez F, Millán JM, Orellana C, Prieto F. X-linked anhidrotic (hypohidrotic) ectodermal dysplasia caused by a novel mutation in EDA1 gene: 406T > G (Leu55Arg). J Invest Dermatol. 1999. 113:285–286.
Article5. Itin PH, Fistarol SK. Ectodermal dysplasias. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet. 2004. 131C:45–51.
Article6. Lu PD, Schaffer JV. Hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. Dermatol Online J. 2008. 14:22.
Article7. Motil KJ, Fete TJ, Fraley JK, Schultz RJ, Foy TM, Ochs U, et al. Growth characteristics of children with ectodermal dysplasia syndromes. Pediatrics. 2005. 116:e229–e234.
Article8. Lau HK, Li CH, Lee AC. Acute massive haemolysis in children with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency. Hong Kong Med J. 2006. 12:149–151.9. Anees M, Mumtaz A, Rizwan SM, Amin J, Moin H, Sharif MM. Hematuria: a rare presentation of G6PD deficiency. Gomal J Med Sci. 2005. 3:27–29.10. de Gurrola GC, Araúz JJ, Durán E, Aguilar-Medina M, Ramos-Payán R, Noemí García-Magallanes N, et al. Kernicterus by glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency: a case report and review of the literature. J Med Case Reports. 2008. 2:146.
Article11. Filippi G, Rinaldi A, Crisponi G, Daniels GL, Siniscalco M. X-mapping in man: evidence against measurable linkage between anhidrotic ectodermal dysplasia and G6PD deficiency. J Med Genet. 1979. 16:223–224.
Article