J Korean Neurotraumatol Soc.
2008 Dec;4(2):93-96. 10.13004/jknts.2008.4.2.93.
Traumatic Interhemispheric Subdural Hematoma Presenting the Falx Syndrome after Decompressive Craniectomy: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Wonju College of Medicine, Yonsei University, Wonju, Korea. junghh@yonsei.ac.kr
- KMID: 2156157
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13004/jknts.2008.4.2.93
Abstract
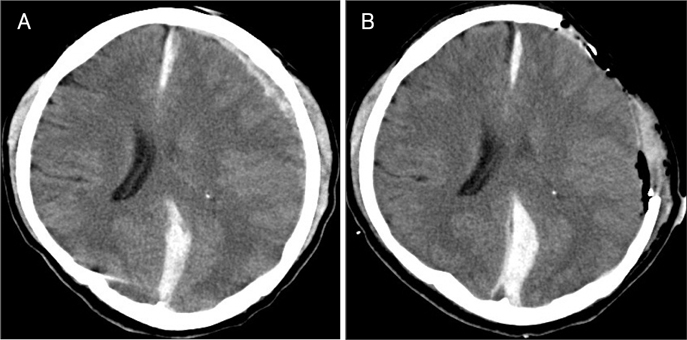
- Interhemispheric subdural hematoma (ISH) had been considered very rare until identification with image studies, such as brain computed tomography (BCT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). There are still some controversies in the management ISH, will be treated surgically or medically. We present one case of traumatic ISH which showed the falx syndrome after decompressive craniectomy for convexity subdural hematoma and was treated surgically with good outcome. Surgical treatment should be considered for symptomatic ISH patient, because ISH did not migrate over the convexity, as showed in our case.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Aring C, Evans J. Aberrant location of subdural hematoma. Arch Neurol Psychiat (Chicago). 1940; 44:1296–1306.
Article2. Bartels RH, Verhagen WI, Prick MJ, Dalman JE. Interhemispheric subdural hematoma in adults: case reports and a review of the literature. Neurosurgery. 1995; 36:1210–1214.3. Fein JM, Rovit RL. Interhemispheric subdural hematoma secondary to hemorrhage from a calloso-marginal artery aneurysm. Neuroradiology. 1970; 1:183–186.
Article4. Fruin AH, Juhl G, Taylon C. Interhemispheric subdural hematoma, case report. J Neurosurg. 1984; 60:1300–1302.5. Glista GG, Reichman O, Brumlik J, Fine M. Interhemispheric subdural hematoma. Surg Neurol. 1978; 10:119–122.6. Ho SU, Spehlmann R, Ho H. CT scan in interhemispheric subdural hematoma. Neurology. 1977; 27:1097–1098.7. Houtteville JP, Toumi K, Theron J, Derlon J, Benazza A, Hubert P. Interhemispheric subdural heamatomas: seven case and review of the literature. Br J Neurosurg. 1988; 2:357–367.8. Lee KJ, Koh EJ, Choi HY. Interhemispheric chronic subdural hematoma showing falx syndrome: case report. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2002; 32:268–271.9. Ogsbury JS, Schneck SA, Lehman RA. Aspects of interhemispheric subdural haematoma, including the falx syndrome. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1978; 41:72–75.
Article10. Sadrolhefazi A, Bloomfield S, Stephen M. Interhemispheric and bilateral chronic subdural hematoma. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2000; 11:455–463.
Article11. Takeda N, Kurihara F, Matsuoka H, Kose S, Tamaki N, Matsumoto S. Three cases of acute interhemispheric subdural hematoma. No Shinkei Geka. 1988; 16:87–92.12. Urculo E, Martinez L, Gereka L, Olasgasti V, Olascoaga V, Urcola J. The spontaneous reabsortion of posttraumatic interhemispheric subdural hematoma. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1996; 138:776–777.13. Wilberger JE Jr, Harris M, Diamond D. Acute subdural hematoma: morbidity, mortality, and operative timing. J Neurosurg. 1991; 74:212–218.
Article14. Zimmerman RA, Bilaniuk L, Bruce D, Schut L, Uzzell B, Goldberg H. Computed tomography of craniocerebral injury in abused child. Radiology. 1979; 130:687–690.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Paradoxical Herniation after Decompressive Craniectomy for Acute Subdural Hematoma
- Acute Interhemispheric Subdural Hematoma Presenting as Falx Syndrome
- Interhemispheric Chronic Subdural Hematoma Showing Falx Syndrome: Case Report
- Interhemispheric Subdural Hematoma Presenting with Falx Syndrome after Trauma
- "Syndrome of the Sinking Skin-Flap" Secondary to the Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt after Craniectomy