J Vet Sci.
2014 Sep;15(3):417-422. 10.4142/jvs.2014.15.3.417.
Laparoscopic left hepatectomy in swine: a safe and feasible technique
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Veterinary Surgery, College of Veterinary Medicine, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin 150030, China. hbwang1940@126.com
- 2Department of Histology and Embryology, Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150081, China.
- KMID: 2155625
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2014.15.3.417
Abstract
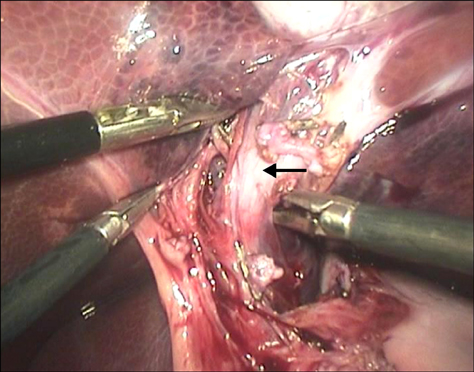
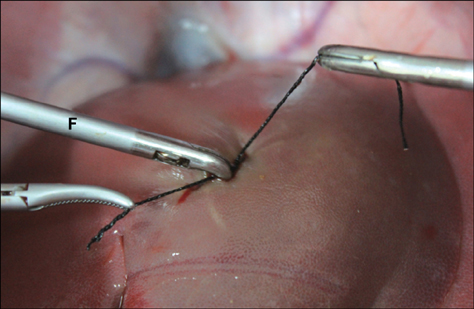
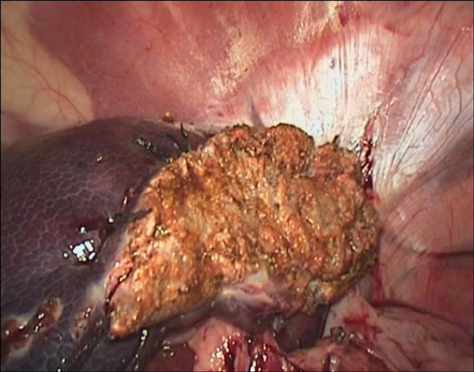
- A purely laparoscopic four-port approach was created for left hepatectomy in pigs. A polyethylene loop was placed on the left two hepatic lobes for traction and lift. Next, penetrating ligation of the lobes using of a double row of silk sutures was performed to control bleeding. A direct hepatic transection was completed using a monopolar hook electrode without meticulous dissection of the left hepatic vein. The raw surface of the liver was coagulated and sealed with fibrin glue. Lobes were retrieved through an enlarged portal. Laparoscopic hepatic lobectomy was completed in all pigs without the use of specialized instruments and with a mean operative time of 179 +/- 9 min. No significant perioperative complications were observed. The average weight of each resected lobe was 180 +/- 51 g. Complete blood count as well as serum organics and enzyme levels normalized after about 2 weeks. During necropsy, adhesion of the hepatic raw surface to the gastric wall and omentum were observed. No other abnormalities were identified. This minimally invasive left hepatectomy technique in swine could serve as a useful model for investigating liver diseases and regeneration, and offer preclinical information to improve hepatobiliary surgical procedures.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Abu Hilal M, McPhail MJ, Zeidan B, Zeidan S, Hallam MJ, Armstrong T, Primrose JN, Pearce NW. Laparoscopic versus open left lateral hepatic sectionectomy: a comparative study. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2008; 34:1285–1288.
Article2. Arkadopoulos N, Kostopanagiotou G, Nastos C, Papalois A, Papoutsidakis N, Kalimeris K, Defterevos G, Kanna T, Polyzois K, Kampouroglou G, Kypriotis D, Costopanagiotou C, Pafiti A, Tzanatos H, Smyrniotis V. Reversal of experimental posthepatectomy liver failure in pigs: a new application of hepatocyte bioreactors. Artif Organs. 2011; 35:29–36.
Article3. Belli G, Fantini C, D'Agostino A, Belli A, Cioffi L, Russolillo N. Laparoscopic left lateral hepatic lobectomy: a safer and faster technique. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2006; 13:149–154.
Article4. Buell JF, Koffron AJ, Thomas MJ, Rudich S, Abecassis M, Woodle ES. Laparoscopic liver resection. J Am Coll Surg. 2005; 200:472–480.
Article5. Cannon RM, Brock GN, Marvin MR, Buell JF. Laparoscopic liver resection: an examination of our first 300 patients. J Am Coll Surg. 2011; 213:501–507.
Article6. Chen YL, Chen WB, Wan YY, Li WG, Huang ZQ, Wu XT, Yang J, Yang L. Effects of partial portal vein arterialization on liver regeneration after hepatectomy in minipigs with obstructive jaundice. Chin Med J (Engl). 2012; 125:2302–2305.7. Consten EC, Dakin GF, Robertus JL, Bardaro S, Milone L, Gagner M. Perioperative outcome of laparoscopic left lateral liver resection is improved by using a bioabsorbable staple line reinforcement material in a porcine model. Surg Endosc. 2008; 22:1188–1193.
Article8. Court FG, Wemyss-Holden SA, Morrison CP, Teague BD, Laws PE, Kew J, Dennison AR, Maddern GJ. Segmental nature of the porcine liver and its potential as a model for experimental partial hepatectomy. Br J Surg. 2003; 90:440–444.
Article9. D'Angelica M. Laparoscopic partial hepatectomy. Surg Pract. 2005; 9:90–93.10. Eiriksson K, Fors D, Rubertsson S, Arvidsson D. Laparoscopic left lobe liver resection in a porcine model: a study of the efficacy and safety of different surgical techniques. Surg Endosc. 2009; 23:1038–1042.
Article11. Frezza EE, Wachtel MS. A proposed canine model of laparoscopic nonanatomic liver resection. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 2006; 16:15–20.
Article12. Herrero Fonollosa E, Cugat Andorra E, García-Domingo MI, Rivero Deniz J, Camps Lasa J, Rodríguez Campos A, Riveros Caballero M, Marco Molina C. Laparoscopic left lateral sectionectomy. Presentation of our technique. Cir Esp. 2011; 89:650–656.
Article13. Hisakura K, Murata S, Fukunaga K, Myronovych A, Tadano S, Kawasaki T, Kohno K, Ikeda O, Pak S, Ikeda N, Nakano Y, Matsuo R, Konno K, Kobayashi E, Saito T, Yasue H, Ohkohchi N. Platelets prevent acute liver damage after extended hepatectomy in pigs. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2010; 17:855–864.
Article14. Kurian MS, Gagner M, Murakami Y, Andrei V, Jossart G, Schwartz M. Hand-assisted laparoscopic donor hepatectomy for living related transplantation in the porcine model. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2002; 12:232–237.
Article15. Kwon YS, Jang KH, Jang IH. The effects of Korean red ginseng (ginseng radix rubra) on liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy in dogs. J Vet Sci. 2003; 4:83–92.
Article16. Ladurner R, Traub F, Schenk M, Königsrainer A, Glatzle J. Cellular liver regeneration after extended hepatic resection in pigs. HPB Surg. 2009; 2009:306740.
Article17. Lai PB, Lee KF, Wong J, Li AK. Techniques for liver resection: a review. Surgeon. 2007; 5:166–174.
Article18. Laurence JM, Lam VWT, Langcake ME, Hollands MJ, Crawford MD, Pleass HCC. Laparoscopic hepatectomy, a systematic review. Anz J Surg. 2007; 77:948–953.
Article19. Lin E, Gonzalez R, Venkatesh KR, Mattar SG, Bowers SP, Fugate KM, Heffron TG, Smith CD. Can current technology be integrated to facilitate laparoscopic living donor hepatectomy? Surg Endosc. 2003; 17:750–753.
Article20. Liska V, Treska V, Mirka H, Benes J, Vycital O, Bruha J, Pitule P, Skalicky T, Sutnar A, Chlumska A, Racek J, Trefil L, Finek J, Holubec L. Immediately preoperative use of biological therapy does not influence liver regeneration after large resection-porcine experimental model with monoclonal antibody against epidermal growth factor. In Vivo. 2012; 26:683–691.21. May LR, Mehler SJ. Complications of hepatic surgery in companion animals. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 2011; 41:935–948.
Article22. Pinto PA, Montgomery RA, Ryan B, Robert W, Hsu T, Kavoussi P, Klein AS, Kavoussi LR, Molmenti EP. Laparoscopic procurement model for living donor liver transplantation. Clin Transplant. 2003; 17:Suppl 9. 39–43.
Article23. Rao A, Rao G, Ahmed I. Laparoscopic vs. open liver resection for malignant liver disease. A systematic review. Surgeon. 2012; 10:194–201.
Article24. Robles Campos R, Marín Hernández C, Löpez Conesa A, Abellán B, Pastor Pérez P, Parrilla Paricio P. Laparoscopic resection of the left segments of the liver: the "ideal technique" in experienced centres? Cir Esp. 2009; 85:214–221.
Article25. Saidi RF, Ahad A, Escobar R, Nalbantoglu I, Adsay V, Jacobs MJ. Comparison between staple and vessel sealing device for parynchemal transection in laparoscopic liver surgery in a swine model. HPB (Oxford). 2007; 9:440–443.
Article26. Shimoda M, Iwasaki Y, Okada T, Kubota K. Edaravone inhibits apoptosis caused ischemia/reperfusion injury in a porcine hepatectomy model. World J Gastroenterol. 2012; 18:3520–3526.
Article27. Vibert E, Perniceni T, Levard H, Denet C, Shahri NK, Gayet B. Laparoscopic liver resection. Br J Surg. 2006; 93:67–72.
Article28. Wu JS, Strasberg SM, Luttmann DR, Meininger TA, Talcott MR, Soper NJ. Laparoscopic hepatic lobectomy in the porcine model. Surg Endosc. 1998; 12:232–235.
Article29. Yoon YS, Han HS, Choi YS, Lee SI, Jang JY, Suh KS, Kim SW, Lee KU, Park YH. Total laparoscopic left lateral sectionectomy performed in a child with benign liver mass. J Pediatr Surg. 2006; 41:e25–e28.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Successful laparoscopic living donor right hepatectomy in a case with challenging portal vein variation
- Laparoscopic left hepatectomy in patients with intrahepatic duct stones and recurrent pyogenic cholangitis
- The Feasibility of Laparoscopic Hepatectomy for the Patients with Left Intrahepatic Stones
- Laparoscopic living donor hepatectomy
- The Feasibility of Laparoscopic Hepatectomy for the Patients with Left Intrahepatic Stones