J Vet Sci.
2014 Sep;15(3):409-415. 10.4142/jvs.2014.15.3.409.
Antibiotic resistance and molecular characterization of ophthalmic Staphylococcus pseudintermedius isolates from dogs
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Veterinary Internal Medicine, College of Veterinary Medicine, Konkuk University, Seoul 143-701, Korea. parkhee@konkuk.ac.kr
- 2Department of Veterinary Microbiology, College of Veterinary Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul 151-742, Korea.
- KMID: 2155624
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2014.15.3.409
Abstract
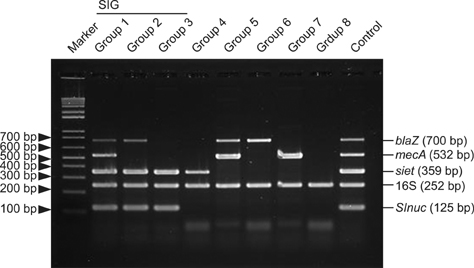
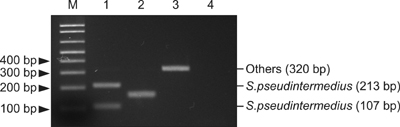
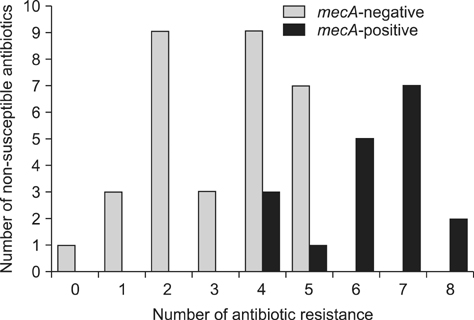
- The prevalence, virulence potential, and antibiotic resistance of ophthalmic Staphylococcus pseudintermedius (SP) isolated from dogs were examined. Sixty-seven Staphylococcus species were isolated from ophthalmic samples and surveyed for species-specific sequences in the Staphylococcus intermedius group (SIG) nuclease gene (SInuc), exfoliative toxin gene for SIG (siet), and antibiotic resistance genes (blaZ and mecA). PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of the pta gene was also performed. Fifty isolates were identified as SIG strains, all of which were found to be SP. The blaZ gene was detected in 42 of the 50 SP strains and mecA gene was observed in 18 of the 50 SP strains. The 50 SP strains were most susceptible to amoxicillin/clavulanic acid (94%) and chlorampenicol (70%), and highly resistant to tetracycline (94%) and penicillin (92%). It was also found that 16 (88.9%) mecA-positive SP strains were resistant to oxacillin, tetracycline and penicillin. All mecA-positive SP were resistant to more than four of the eight tested antibiotics and therefore considered SP with multi-drug resistance (MDR). Our results indicate a high prevalence of antibiotic resistance genes in ophthalmic SP along with a close relationship between MDR SP strains and the mecA gene. Based on our findings, judicious administration of antibiotics to companion dogs is necessary.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Animals
Anti-Bacterial Agents/*therapeutic use
Dog Diseases/drug therapy/*microbiology
Dogs
Drug Resistance, Bacterial
Drug Resistance, Multiple, Bacterial
Eye Infections, Bacterial/drug therapy/microbiology/*veterinary
Microbial Sensitivity Tests/veterinary
Multiplex Polymerase Chain Reaction
Staphylococcal Infections/drug therapy/microbiology/*veterinary
Staphylococcus/*drug effects/isolation & purification
Anti-Bacterial Agents
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bannoehr J, Franco A, Iurescia M, Battisti A, Fitzgerald JR. Molecular diagnostic identification of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius. J Clin Microbiol. 2009; 47:469–471.
Article2. Baron F, Cochet MF, Pellerin JL, Ben Zakour N, Lebon A, Navarro A, Proudy I, Le Loir Y, Gautier M. Development of a PCR test to differentiate between Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus intermedius. J Food Prot. 2004; 67:2302–2305.
Article3. Berger-Bächi B, Rohrer S. Factors influencing methicillin resistance in staphylococci. Arch Microbiol. 2002; 178:165–171.
Article4. Broekema NM, Van TT, Monson TA, Marshall SA, Warshauer DM. Comparison of cefoxitin and oxacillin disk diffusion methods for detection of mecA-mediated resistance in Staphylococcus aureus in a large-scale study. J Clin Microbiol. 2009; 47:217–219.
Article5. CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; Twentieth Informational Supplement. CLSI document M100-S20. Wayne: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;2010.6. Descloux S, Rossano A, Perreten V. Characterization of new staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec (SCCmec) and topoisomerase genes in fluoroquinolone- and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius. J Clin Microbiol. 2008; 46:1818–1823.
Article7. García-Álvarez L, Holden MTM, Lindsay H, Webb CR, Brown DFJ, Curran MD, Walpole E, Brooks K, Pickard DJ, Teale C, Parkhill J, Bentley SD, Edwards GF, Girvan EK, Kearns AM, Pichon B, Hill RLR, Larsen AR, Skov RL, Peacock SJ, Maskell DJ, Holmes MA. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus with a novel mecA homologue in human and bovine populations in the UK and Denmark: a descriptive study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2011; 11:595–603.
Article8. Griffeth GC, Morris DO, Abraham JL, Shofer FS, Rankin SC. Screening for skin carriage of methicillin-resistant coagulase-positive staphylococci and Staphylococcus schleiferi in dogs with healthy and inflamed skin. Vet Dermatol. 2008; 19:142–149.
Article9. Ihrke PJ. An overview of bacterial skin disease in the dog. Br Vet J. 1987; 143:112–118.
Article10. Jones RD, Kania SA, Rohrbach BW, Frank LA, Bemis DA. Prevalence of oxacillin- and multidrug-resistant staphylococci in clinical samples from dogs: 1,772 samples (2001-2005). J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2007; 230:221–227.
Article11. Khan AU, Sultan A, Tyagi A, Zahoor S, Akram M, Kaur S, Shahid M, Vaishnavi CV. Amplification of mecA gene in multi-drug resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains from hospital personnel. J Infect Dev Ctries. 2007; 1:289–295.
Article12. Kizerwetter-Swida M, Chrobak D, Rzewuska M, Binek M. Antibiotic resistance patterns and occurrence of mecA gene in Staphylococcus intermedius strains of canine origin. Pol J Vet Sci. 2009; 12:9–13.13. Laurent F, Chardon H, Haenni M, Bes M, Reverdy ME, Madec JY, Lagier E, Vandenesch F, Tristan A. MRSA harboring mecA variant gene mecC, France. Emerg Infect Dis. 2012; 18:1465–1467.14. Lautz S, Kanbar T, Alber J, Lämmler C, Weiss R, Prenger-Berninghoff E, Zschöck M. Dissemination of the gene encoding exfoliative toxin of Staphylococcus intermedius among strains isolated from dogs during routine microbiological diagnostics. J Vet Med B Infect Dis Vet Public Health. 2006; 53:434–438.
Article15. Nishifuji K, Sugai M, Amagai M. Staphylococcal exfoliative toxins: "molecular scissors" of bacteria that attack the cutaneous defense barrier in mammals. J Dermatol Sci. 2008; 49:21–31.
Article16. Onuma K, Tanabe T, Sato H. Antimicrobial resistance of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius isolates from healthy dogs and dogs affected with pyoderma in Japan. Vet Dermatol. 2012; 23:17–22.17. Sasaki T, Kikuchi K, Tanaka Y, Takahashi N, Kamata S, Hiramatsu K. Reclassification of phenotypically identified Staphylococcus intermedius strains. J Clin Microbiol. 2007; 45:2770–2778.
Article18. Shore AC, Deasy EC, Slickers P, Brennan G, O'Connell B, Monecke S, Ehricht R, Coleman DC. Detection of staphylococcal cassette chromosome mec type XI carrying highly divergent mecA, mecI, mecR1, blaZ, and ccr genes in human clinical isolates of clonal complex 130 methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2011; 55:3765–3773.
Article19. Skov R, Smyth R, Larsen AR, Bolmstrôm A, Karlsson A, Mills K, Frimodt-Moller N, Kahlmeter G. Phenotypic detection of methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus by disk diffusion testing and Etest on Mueller-Hinton agar. J Clin Microbiol. 2006; 44:4395–4399.
Article20. Soedarmanto I, Kanbar T, Ülbegi-Mohyla H, Hijazin M, Alber J, Lämmler C, Akineden Ö, Weiss R, Moritz A, Zschöck M. Genetic relatedness of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius (MRSP) isolated from a dog and the dog owner. Res Vet Sci. 2011; 91:e25–e27.21. Stegmann R, Burnens A, Maranta CA, Perreten V. Human infection associated with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius ST71. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2010; 65:2047–2048.
Article22. Strommenger B, Kettlitz C, Werner G, Witte W. Multiplex PCR assay for simultaneous detection of nine clinically relevant antibiotic resistance genes in Staphylococcus aureus. J Clin Microbiol. 2003; 41:4089–4094.
Article23. Terauchi R, Sato H, Hasegawa T, Yamaguchi T, Aizawa C, Maehara N. Isolation of exfoliative toxin from Staphylococcus intermedius and its local toxicity in dogs. Vet Microbiol. 2003; 94:19–29.
Article24. Tolar EL, Hendrix DV, Rohrbach BW, Plummer CE, Brooks DE, Gelatt KN. Evaluation of clinical characteristics and bacterial isolates in dogs with bacterial keratitis: 97 cases (1993-2003). J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2006; 228:80–85.
Article25. Tomasz A, Drugeon HB, de Lencastre HM, Jabes D, McDougall L, Bille J. New mechanism for methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus: clinical isolates that lack the PBP 2a gene and contain normal penicillin-binding proteins with modified penicillin-binding capacity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1989; 33:1869–1874.
Article26. van Duijkeren E, Catry B, Greko C, Moreno MA, Pomba MC, Pyörälä S, Ruzauskas M, Sanders P, Threlfall EJ, Torren-Edo J, Törneke K. Scientific Advisory Group on Antimicrobials (SAGAM). Review on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2011; 66:2705–2714.27. Varges R, Penna B, Martins G, Martins R, Lilenbaum W. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Staphylococci isolated from naturally occurring canine external ocular diseases. Vet Ophthalmol. 2009; 12:216–220.
Article28. Wang L, Pan Q, Zhang L, Xue Q, Cui J, Qi C. Investigation of bacterial microorganisms in the conjunctival sac of clinically normal dogs and dogs with ulcerative keratitis in Beijing, China. Vet Ophthalmol. 2008; 11:145–149.
Article29. Wang Y, Yang J, Logue CM, Liu K, Cao X, Zhang W, Shen J, Wu C. Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius isolated from canine pyoderma in North China. J Appl Microbiol. 2012; 112:623–630.
Article30. Yoo JH, Yoon JW, Lee SY, Park HM. High prevalence of fluoroquinolone- and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus pseudintermedius isolates from canine pyoderma and otitis externa in veterinary teaching hospital. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010; 20:798–802.31. Yoon JW, Lee KJ, Lee SY, Chae MJ, Park JK, Yoo JH, Park HM. Antibiotic resistance profiles of Staphylococcus pseudintermedius isolates from canine patients in Korea. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2010; 20:1764–1768.32. Zubeir IE, Kanbar T, Alber J, Lämmler C, Akineden O, Weiss R, Zschöck M. Phenotypic and genotypic characteristics of methicillin/oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus intermedius isolated from clinical specimens during routine veterinary microbiological examinations. Vet Microbiol. 2007; 121:170–176.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Detection and characterization of potential virulence determinants in Staphylococcus pseudintermedius and S. schleiferi strains isolated from canine otitis externa in Korea
- Combined antimicrobial effect of two peptide nucleic acids against Staphylococcus aureus and S. pseudintermedius veterinary isolates
- DNA microarray-based characterization and antimicrobial resistance phenotypes of clinical MRSA strains from animal hosts
- Determination of staphylococcal exotoxins, SCCmec types, and genetic relatedness of Staphylococcus intermedius group isolates from veterinary staff, companion animals, and hospital environments in Korea
- Risk Factors for Fluoroquinolone Resistance in Ocular Cultures