Korean J Radiol.
2015 Jun;16(3):657-661. 10.3348/kjr.2015.16.3.657.
Cryoablation of a Small Pulmonary Nodule with Pure Ground-Glass Opacity: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Research Institute of Clinical Medicine of Chonbuk National University-Biomedical Research Institute of Chonbuk National University Hospital, Institute for Medical Sciences, Jeonju 561-712, Korea. gyjin@chonbuk.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Research Institute of Clinical Medicine of Chonbuk National University-Biomedical Research Institute of Chonbuk National University Hospital, Institute for Medical Sciences, Jeonju 561-712, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Research Institute of Clinical Medicine of Chonbuk National University-Biomedical Research Institute of Chonbuk National University Hospital, Institute for Medical Sciences, Jeonju 561-712, Korea.
- KMID: 2155537
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2015.16.3.657
Abstract
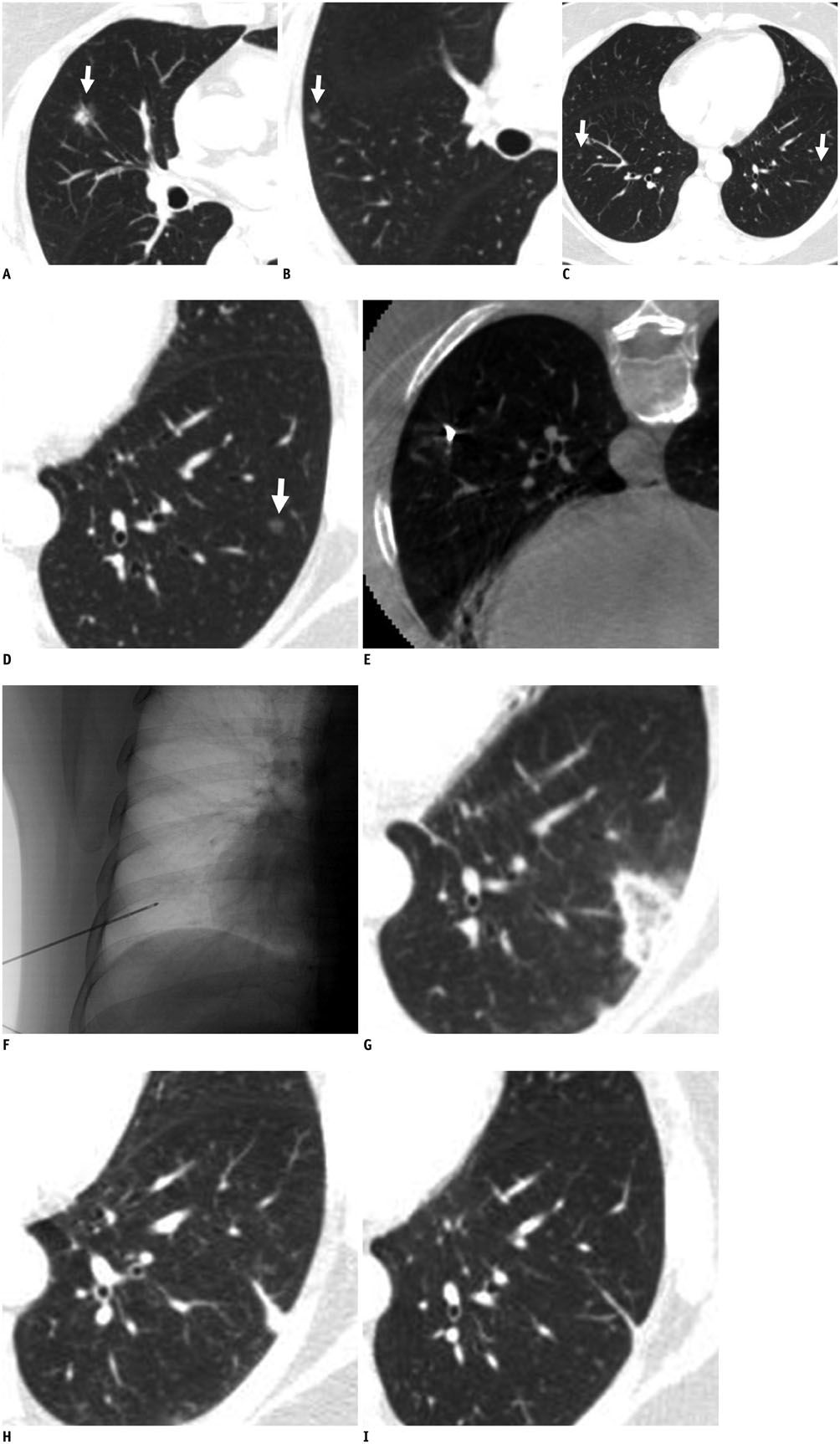
- Treatments for pure ground-glass nodules (GGNs) include limited resection; however, surgery is not always possible in patients with limited pulmonary functional reserve. In such patients, cryoablation may be a suitable alternative to treat a pure GGN. Here, we report our initial experience with cryoablation of a pure GGN that remained after repeated surgical resection in a patient with multiple GGNs. A 5-mm-sized pure GGN in the left lower lobe was cryoablated successfully without recurrence at the 6-month follow-up.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Nakajima R, Yokose T, Kakinuma R, Nagai K, Nishiwaki Y, Ochiai A. Localized pure ground-glass opacity on high-resolution CT: histologic characteristics. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2002; 26:323–329.2. Lim HJ, Ahn S, Lee KS, Han J, Shim YM, Woo S, et al. Persistent pure ground-glass opacity lung nodules ≥ 10 mm in diameter at CT scan: histopathologic comparisons and prognostic implications. Chest. 2013; 144:1291–1299.3. Lee HY, Lee KS. Ground-glass opacity nodules: histopathology, imaging evaluation, and clinical implications. J Thorac Imaging. 2011; 26:106–118.4. Park JH, Lee KS, Kim JH, Shim YM, Kim J, Choi YS, et al. Malignant pure pulmonary ground-glass opacity nodules: prognostic implications. Korean J Radiol. 2009; 10:12–20.5. Bang HJ, Littrup PJ, Currier BP, Goodrich DJ, Aoun HD, Klein LC, et al. Percutaneous cryoablation of metastatic lesions from non-small-cell lung carcinoma: initial survival, local control, and cost observations. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2012; 23:761–769.6. Kim HK, Choi YS, Kim J, Shim YM, Lee KS, Kim K. Management of multiple pure ground-glass opacity lesions in patients with bronchioloalveolar carcinoma. J Thorac Oncol. 2010; 5:206–210.7. Kuriyama K, Seto M, Kasugai T, Higashiyama M, Kido S, Sawai Y, et al. Ground-glass opacity on thin-section CT: value in differentiating subtypes of adenocarcinoma of the lung. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1999; 173:465–469.8. Rapicetta C, Tenconi S, Voltolini L, Luzzi L, Scala V, Gotti G. Impact of lobectomy for non-small-cell lung cancer on respiratory function in octogenarian patients with mild to moderate chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2011; 39:555–559.9. Hiraki T, Gobara H, Mimura H, Matsui Y, Toyooka S, Kanazawa S. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of clinical stage I non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2011; 142:24–30.10. Thanos L, Mylona S, Ptohis N, Tsiouris S, Sotiropoulou E, Pomoni A, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency thermal ablation in the management of lung tumors: presentation of clinical experience on a series of 35 patients. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2009; 15:290–296.11. Zemlyak A, Moore WH, Bilfinger TV. Comparison of survival after sublobar resections and ablative therapies for stage I non-small cell lung cancer. J Am Coll Surg. 2010; 211:68–72.12. Lee JM, Jin GY, Goldberg SN, Lee YC, Chung GH, Han YM, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for inoperable non-small cell lung cancer and metastases: preliminary report. Radiology. 2004; 230:125–134.13. Pereira PL, Masala S. Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiological Society of Europe (CIRSE). Standards of practice: guidelines for thermal ablation of primary and secondary lung tumors. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2012; 35:247–254.14. Jin GY, Han YM, Lee YS, Lee YC. Radiofrequency ablation using a monopolar wet electrode for the treatment of inoperable non-small cell lung cancer: a preliminary report. Korean J Radiol. 2008; 9:140–147.15. Song YS, Park CM, Park SJ, Lee SM, Jeon YK, Goo JM. Volume and mass doubling times of persistent pulmonary subsolid nodules detected in patients without known malignancy. Radiology. 2014; 273:276–284.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Clinical Approach to Nodular Ground Glass Opacity in the Lung
- Ground-Glass Opacity in Lung Metastasis from Adenocarcinoma of the Stomach: A Case Report
- Simple Pulmonary Eosinophilia (Loeffler's Syndrome): Chest Radiographic and CT Findings
- Malignant Pure Pulmonary Ground-Glass Opacity Nodules: Prognostic Implications
- High-resolution CT findings of pleuropulmonary involvement in systemic lupus erythematosus