J Korean Med Sci.
2015 May;30(5):591-597. 10.3346/jkms.2015.30.5.591.
Radiological Findings and Outcomes of Bronchial Artery Embolization in Cryptogenic Hemoptysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Faculty of Medicine, Gaziantep University, Gaziantep, Turkey. skervancioglu@yahoo.com
- 2Department of Pulmonology, Faculty of Medicine, Gaziantep University, Gaziantep, Turkey.
- 3Department of Thoracic Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, Gaziantep University, Gaziantep, Turkey.
- KMID: 2155472
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2015.30.5.591
Abstract
- Management of cryptogenic massive hemoptysis is difficult, and conservative treatment may be inadequate to stop the hemorrhage. Surgery is not a reasonable option because there is no underlying identifiable pathology. This study aimed to investigate the radiologic findings and bronchial artery embolization outcomes in cryptogenic hemoptysis, and to compare the results with non-cryptogenic hemoptysis. We evaluated 26 patients with cryptogenic hemoptysis and 152 patients with non-cryptogenic hemoptysis. A comparison of the bronchial artery abnormalities between the cryptogenic and non-cryptogenic hemoptysis groups showed that only extravasation was more statistically significant in the cryptogenic hemoptysis group than in the non-cryptogenic hemoptysis group, while the other bronchial artery abnormalities, such as bronchial artery dilatation, hypervascularity, and bronchial-to-pulmonary shunting, showed no significant difference between groups. Involvement of the non-bronchial systemic artery was significantly greater in the non-cryptogenic hemoptysis group than in the cryptogenic hemoptysis group. While 69.2% of patients with cryptogenic hemoptysis also had hypervascularity in the contralateral bronchial arteries and/or ipsilateral bronchial artery branches other than the bleeding lobar branches, this finding was not detected in non-cryptogenic hemoptysis. Embolization was performed on all patients using polyvinyl alcohol particles of 355-500 microm. Hemoptysis ceased in all patients immediately after embolization. While recurrence of hemoptysis showed no statistically significant difference between the cryptogenic and non-cryptogenic hemoptysis groups, it was mild in cryptogenic hemoptysis in contrast to mostly severe in non-cryptogenic hemoptysis. Transarterial embolization is a safe and effective technique to manage cryptogenic hemoptysis.
MeSH Terms
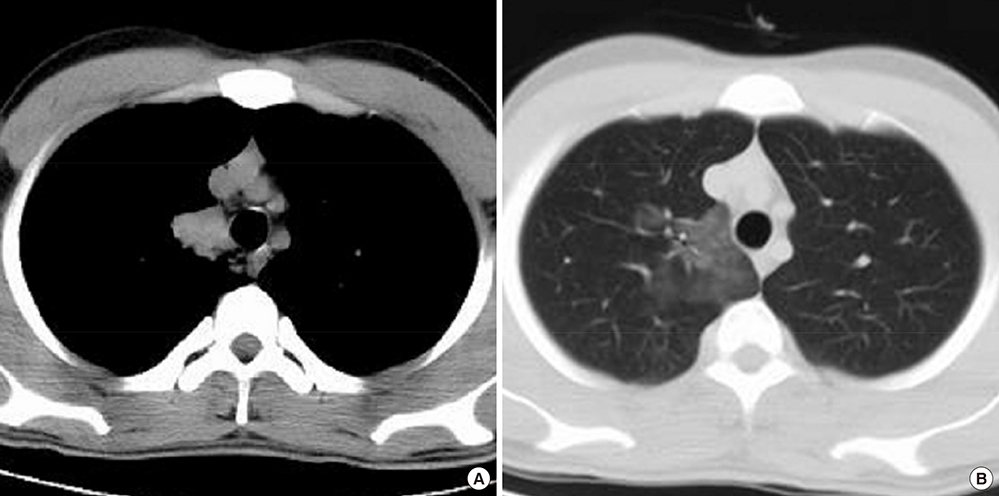
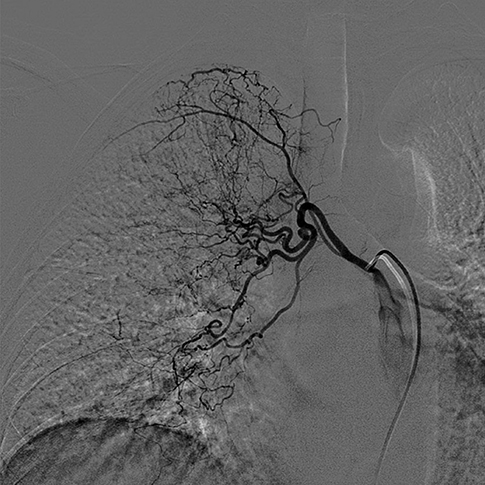
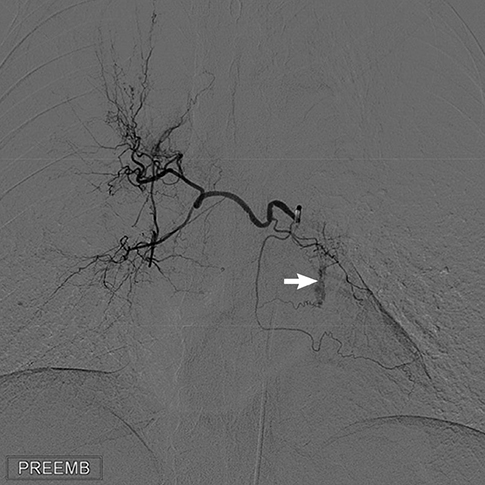
Figure
Reference
-
1. Bruzzi JF, Rémy-Jardin M, Delhaye D, Teisseire A, Khalil C, Rémy J. Multidetector row CT of hemoptysis. Radiographics. 2006; 26:3–22.2. Delage A, Tillie-Leblond I, Cavestri B, Wallaert B, Marquette CH. Cryptogenic hemoptysis in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: characteristics and outcome. Respiration. 2010; 80:387–392.3. Samara KD, Tsetis D, Antoniou KM, Protopapadakis C, Maltezakis G, Siafakas NM. Bronchial artery embolization for management of massive cryptogenic hemoptysis: a case series. J Med Case Rep. 2011; 5:58.4. Swanson KL, Johnson CM, Prakash UB, McKusick MA, Andrews JC, Stanson AW. Bronchial artery embolization : experience with 54 patients. Chest. 2002; 121:789–795.5. Shigemura N, Wan IY, Yu SC, Wong RH, Hsin MK, Thung HK, Lee TW, Wan S, Underwood MJ, Yim AP. Multidisciplinary management of life-threatening massive hemoptysis: a 10-year experience. Ann Thorac Surg. 2009; 87:849–853.6. Savale L, Parrot A, Khalil A, Antoine M, Théodore J, Carette MF, Mayaud C, Fartoukh M. Cryptogenic hemoptysis: from a benign to a life-threatening pathologic vascular condition. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007; 175:1181–1185.7. Menchini L, Remy-Jardin M, Faivre JB, Copin MC, Ramon P, Matran R, Deken V, Duhamel A, Remy J. Cryptogenic haemoptysis in smokers: angiography and results of embolisation in 35 patients. Eur Respir J. 2009; 34:1031–1039.8. Yoon W, Kim JK, Kim YH, Chung TW, Kang HK. Bronchial and nonbronchial systemic artery embolization for life-threatening hemoptysis: a comprehensive review. Radiographics. 2002; 22:1395–1409.9. Soejima K, Yamaguchi K, Kohda E, Takeshita K, Ito Y, Mastubara H, Oguma T, Inoue T, Okubo Y, Amakawa K, et al. Longitudinal follow-up study of smoking-induced lung density changes by high-resolution computed tomography. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000; 161:1264–1273.10. Remy-Jardin M, Edme JL, Boulenguez C, Remy J, Mastora I, Sobaszek A. Longitudinal follow-up study of smoker's lung with thin-section CT in correlation with pulmonary function tests. Radiology. 2002; 222:261–270.11. Chun JY, Morgan R, Belli AM. Radiological management of hemoptysis: a comprehensive review of diagnostic imaging and bronchial arterial embolization. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2010; 33:240–250.12. Poyanli A, Acunas B, Rozanes I, Guven K, Yilmaz S, Salmaslioglu A, Terzibasioglu E, Cirpin R. Endovascular therapy in the management of moderate and massive haemoptysis. Br J Radiol. 2007; 80:331–336.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case Report of Aberrant Bronchial Artery from Common Carotid Artery: A Potential Hazard in Bronchial Artery Embolization
- Bronchial artery embolization: clinical analysis of 129 cases
- Left Bronchial Artery Arising from a Replaced Left Hepatic Artery in a Patient with Massive Hemoptysis
- Bronchial artery embolization in the management of hemoptysis
- A Case of Catamenial Hemoptysis Treated by Bronchial Artery Embolization