J Korean Med Sci.
2015 May;30(5):586-590. 10.3346/jkms.2015.30.5.586.
Association between Serum Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 and Coronary Artery Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea. injkim@pusan.ac.kr
- 2Biomedical Research Institute, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- 3Kim Yong Ki Internal Medicine Clinic, Busan, Korea.
- 4Busan Veterans Hospital, Busan, Korea.
- KMID: 2155471
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2015.30.5.586
Abstract
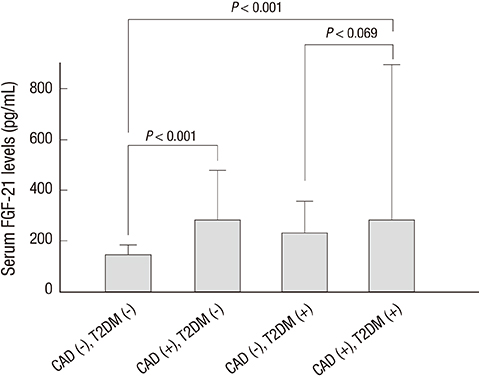
- The aim of this study was to evaluate the association of plasma fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-21 with angiographically significant coronary artery disease (CAD) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Serum FGF-21 was measured in 120 patients undergoing coronary angiography. Patients were divided into 4 groups based on the presence/absence of type 2 diabetes mellitus and of significant CAD. The atherosclerotic burden was obtained by two angiographic scores: Gensini score (GS) and Extent score (ES). FGF-21 levels were higher in type 2 diabetes mellitus than in non-diabetic patients (P = 0.014). FGF-21 levels were significantly correlated with GS (r = 0.358, P < 0.001) and ES (r = 0.324, P < 0.001) in univariate analysis with all patients. After adjusting for several confounding factors, both GS and ES were associated with FGF-21 in all patients (r = 0.271, P = 0.014; r = 0.217, P = 0.041, respectively). However, FGF-21 lost significant correlation with both GS and ES with type 2 diabetes mellitus in the final model. The patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and CAD feature had elevated FGF-21 levels. Despite of a limited role in diabetic patients, FGF-21 levels are independently associated with angiographic severity and extent of CAD.
MeSH Terms
-
Adolescent
Adult
Aged
Aged, 80 and over
Coronary Angiography
Coronary Artery Disease/complications/*diagnosis/pathology
Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2/complications/*diagnosis
Female
Fibroblast Growth Factors/*blood
Humans
Male
Middle Aged
Regression Analysis
Severity of Illness Index
Young Adult
Fibroblast Growth Factors
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Relationship between Circulating FGF21 Concentrations and the Severity of Coronary Artery Damage in Subjects with Cardiovascular Disease
Sung Don Park, Kwi-Hyun Bae, Yeon-Kyung Choi, Jae-Han Jeon, Jung Beom Seo, Namkyun Kim, Chang-Yeon Kim, Sung Woo Kim, Won Kee Lee, Jung Guk Kim, In-Kyu Lee, Jang Hoon Lee, Keun-Gyu Park
J Lipid Atheroscler. 2018;7(1):42-49. doi: 10.12997/jla.2018.7.1.42.
Reference
-
1. Itoh N, Ornitz DM. Evolution of the Fgf and Fgfr gene families. Trends Genet. 2004; 20:563–569.2. Presta M, Dell'Era P, Mitola S, Moroni E, Ronca R, Rusnati M. Fibroblast growth factor/fibroblast growth factor receptor system in angiogenesis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2005; 16:159–178.3. Nishimura T, Nakatake Y, Konishi M, Itoh N. Identification of a novel FGF, FGF-21, preferentially expressed in the liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2000; 1492:203–206.4. Lin Z, Wu Z, Yin X, Liu Y, Yan X, Lin S, Xiao J, Wang X, Feng W, Li X. Serum levels of FGF-21 are increased in coronary heart disease patients and are independently associated with adverse lipid profile. PLoS One. 2010; 5:e15534.5. Kharitonenkov A, Shiyanova TL, Koester A, Ford AM, Micanovic R, Galbreath EJ, Sandusky GE, Hammond LJ, Moyers JS, Owens RA, et al. FGF-21 as a novel metabolic regulator. J Clin Invest. 2005; 115:1627–1635.6. Hojman P, Pedersen M, Nielsen AR, Krogh-Madsen R, Yfanti C, Akerstrom T, Nielsen S, Pedersen BK. Fibroblast growth factor-21 is induced in human skeletal muscles by hyperinsulinemia. Diabetes. 2009; 58:2797–2801.7. Zhang X, Yeung DC, Karpisek M, Stejskal D, Zhou ZG, Liu F, Wong RL, Chow WS, Tso AW, Lam KS, et al. Serum FGF21 levels are increased in obesity and are independently associated with the metabolic syndrome in humans. Diabetes. 2008; 57:1246–1253.8. Li H, Bao Y, Xu A, Pan X, Lu J, Wu H, Lu H, Xiang K, Jia W. Serum fibroblast growth factor 21 is associated with adverse lipid profiles and gamma-glutamyltransferase but not insulin sensitivity in Chinese subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2009; 94:2151–2156.9. Mraz M, Bartlova M, Lacinova Z, Michalsky D, Kasalicky M, Haluzikova D, Matoulek M, Dostalova I, Humenanska V, Haluzik M. Serum concentrations and tissue expression of a novel endocrine regulator fibroblast growth factor-21 in patients with type 2 diabetes and obesity. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2009; 71:369–375.10. Gensini GG. A more meaningful scoring system for determining the severity of coronary heart disease. Am J Cardiol. 1983; 51:606.11. Sullivan DR, Marwick TH, Freedman SB. A new method of scoring coronary angiograms to reflect extent of coronary atherosclerosis and improve correlation with major risk factors. Am Heart J. 1990; 119:1262–1267.12. Dostálová I, Haluzíková D, Haluzík M. Fibroblast growth factor 21: a novel metabolic regulator with potential therapeutic properties in obesity/type 2 diabetes mellitus. Physiol Res. 2009; 58:1–7.13. Badman MK, Pissios P, Kennedy AR, Koukos G, Flier JS, Maratos-Flier E. Hepatic fibroblast growth factor 21 is regulated by PPARalpha and is a key mediator of hepatic lipid metabolism in ketotic states. Cell Metab. 2007; 5:426–437.14. Inagaki T, Dutchak P, Zhao G, Ding X, Gautron L, Parameswara V, Li Y, Goetz R, Mohammadi M, Esser V, et al. Endocrine regulation of the fasting response by PPARalpha-mediated induction of fibroblast growth factor 21. Cell Metab. 2007; 5:415–425.15. Seo JA, Kim NH. Fibroblast growth factor 21: a novel metabolic regulator. Diabetes Metab J. 2012; 36:26–28.16. An SY, Lee MS, Yi SA, Ha ES, Han SJ, Kim HJ, Kim DJ, Lee KW. Serum fibroblast growth factor 21 was elevated in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus and was associated with the presence of carotid artery plaques. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2012; 96:196–203.17. Chow WS, Xu A, Woo YC, Tso AW, Cheung SC, Fong CH, Tse HF, Chau MT, Cheung BM, Lam KS. Serum fibroblast growth factor-21 levels are associated with carotid atherosclerosis independent of established cardiovascular risk factors. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013; 33:2454–2459.18. Lenart-Lipińska M, Matyjaszek-Matuszek B, Gernand W, Nowakowski A, Solski J. Serum fibroblast growth factor 21 is predictive of combined cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes at a relatively short-term follow-up. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2013; 101:194–200.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Fibroblast Growth Factor 21: A Novel Metabolic Regulator
- Hepatokines as a Link between Obesity and Cardiovascular Diseases
- Letter: Lack of Association between Serum Cystatin C Levels and Coronary Artery Disease in Diabetic Patients (Korean Diabetes J 2010;34:95-100)
- Response: Lack of Association between Serum Cystatin C Levels and Coronary Artery Disease in Diabetic Patients (Korean Diabetes J 2010;34:95-100)
- Association of serum osteoprotegerin with coronary artery calcification scores in patients with asymptomatic type 2 diabetes