J Korean Soc Radiol.
2016 Mar;74(3):210-213. 10.3348/jksr.2016.74.3.210.
Persistent Craniopharyngeal Canal with Posterior Pituitary Ectopia: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kimshrad@paik.ac.kr
- KMID: 2155283
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2016.74.3.210
Abstract
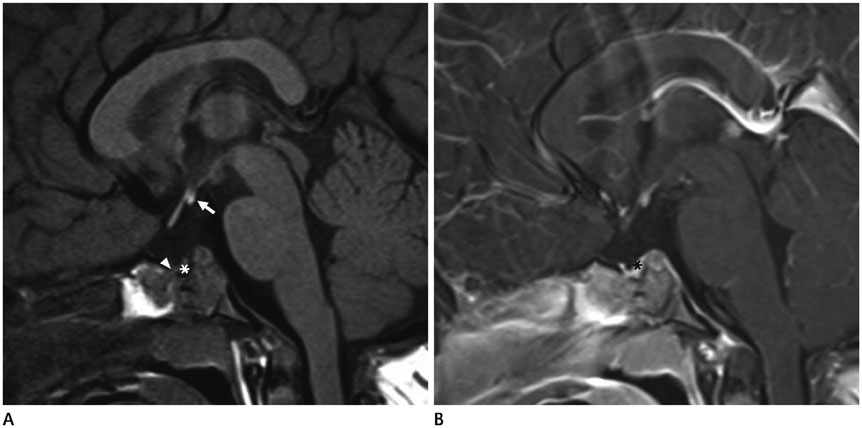
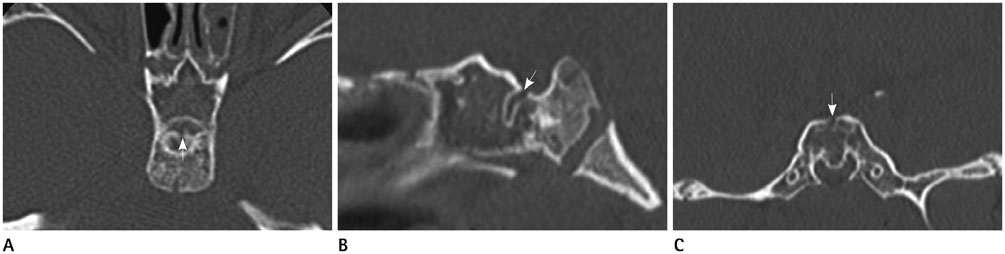
- Persistent craniopharyngeal canal is a congenital defect between sella turcica and nasopharynx. It is considered to develope from incomplete closure of Rathke's pouch, the precursor of adenohypophysis. Persistent craniopharyngeal canal can be associated pituitary anomalies and other central nervous system anomalies. We presented a case of persistent craniopharyngeal canal with posterior pituitary ectopia.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Arey LB. The craniopharyngeal canal reviewed and reinterpreted. Anat Rec. 1950; 106:1–16.2. Ikeda H, Suzuki J, Sasano N, Niizuma H. The development and morphogenesis of the human pituitary gland. Anat Embryol (Berl). 1988; 178:327–336.3. Kjaer I, Fischer-Hansen B. Human fetal pituitary gland in holoprosencephaly and anencephaly. J Craniofac Genet Dev Biol. 1995; 15:222–229.4. Kaushik C, Ramakrishnaiah R, Angtuaco EJ. Ectopic pituitary adenoma in persistent craniopharyngeal canal: case report and literature review. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2010; 34:612–614.5. Currarino G, Maravilla KR, Salyer KE. Transsphenoidal canal (large craniopharyngeal canal) and its pathologic implications. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1985; 6:39–43.6. Hyun SE, Lee BC, Suh BK, Chung SC, Ko CW, Kim HS, et al. Reference values for serum levels of insulin-like growth factor-I and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 in Korean children and adolescents. Clin Biochem. 2012; 45:16–21.7. Yeon KM. Standard bone-age of infants and children in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 1997; 12:9–16.8. Abele TA, Salzman KL, Harnsberger HR, Glastonbury CM. Craniopharyngeal canal and its spectrum of pathology. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2014; 35:772–777.9. Fujisawa I, Kikuchi K, Nishimura K, Togashi K, Itoh K, Noma S, et al. Transection of the pituitary stalk: development of an ectopic posterior lobe assessed with MR imaging. Radiology. 1987; 165:487–489.10. Mitchell LA, Thomas PQ, Zacharin MR, Scheffer IE. Ectopic posterior pituitary lobe and periventricular heterotopia: cerebral malformations with the same underlying mechanism. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002; 23:1475–1481.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Transverse Testicular Ectopia with Incomplete Regression of Mullerian Duct
- Persistent Mullerian Duct Syndrome in a Boy with Transverse Testicular Ectopia: a Case Report
- A Case of Transverse Testicular Ectopia
- A case of crossed renal ectopia with fusion
- Two Cases of Crossed Renal Ectopia with Fusion