J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2016 Jan;59(1):58-61. 10.3340/jkns.2016.59.1.58.
Sellar-Suprasellar Extraventricular Choroid Plexus Papilloma : A Case Report and Review of the Literature
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Meram Faculty of Medicine, Necmettin Erbakan University, Konya, Turkey. mfatiherdi@hotmail.com
- 2Department of Pathology, Meram Faculty of Medicine, Necmettin Erbakan University, Konya, Turkey.
- KMID: 2152919
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2016.59.1.58
Abstract
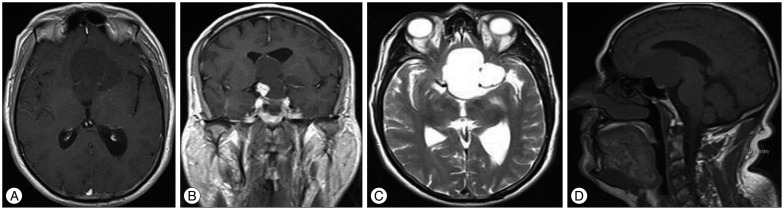
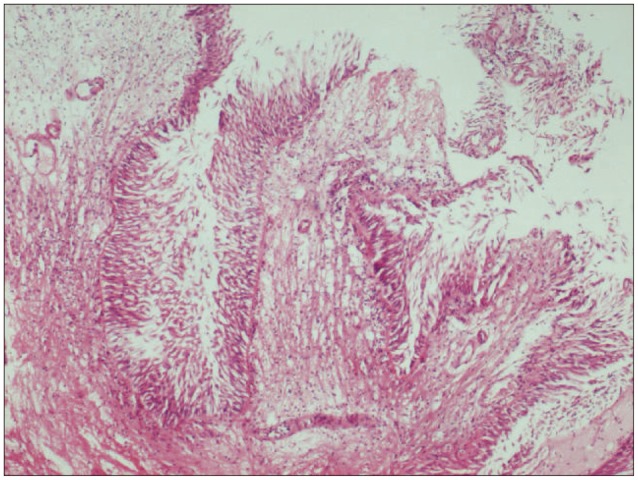
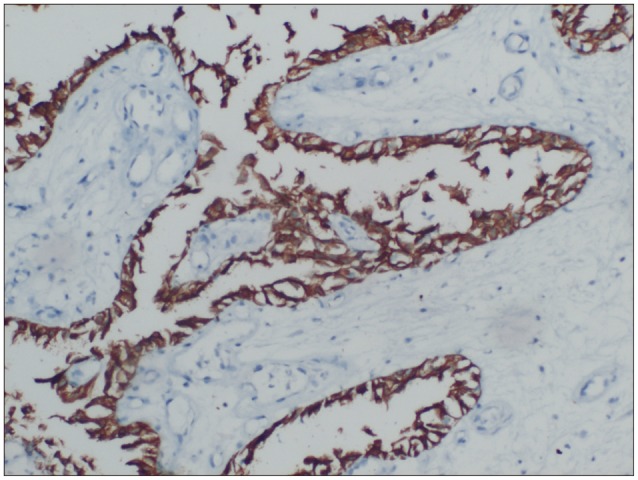
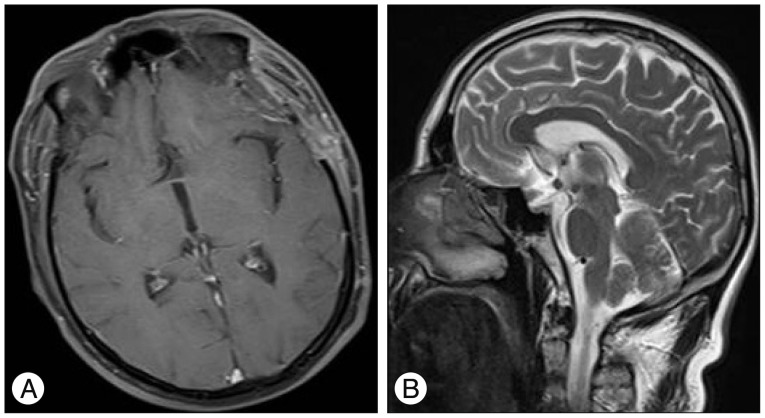
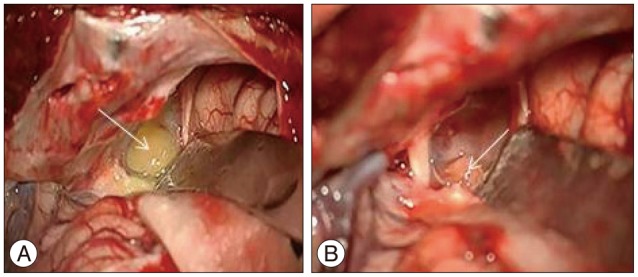
- Choroid plexus papillomas (CPPs) are relatively rare neuroectodermal tumors that develop from choroid plexus epithelial cells and are usually restricted to the ventricles. Extraventricular CPPs are very unusual and can be difficult to diagnose and treat. A 50-year-old male patient was admitted to our clinic complaining of headache and visual deterioration. Neurological examination found no abnormalities except decreased light perception and secondary optic atrophy in the left eye. Endocrine testing revealed normal levels of hormones produced by the pituitary and target glands. Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain revealed a huge regular-shaped lesion in the sellar-suprasellar region occupying the sella turcica and extending into the suprasellar cistern and planum sphenoidale. The lesion was completely excised by microsurgery via an ordinary left-sided pterional approach. Histopathology identified the lesion as a choroid plexus papilloma. Following the case report, literature on the origin, differential diagnosis, and treatment of this rare tumor is reviewed.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Azzam NI, Timperley WR. Intracerebral cyst due to ectopic choroid plexus : case report. J Neurosurg. 1981; 55:651–653. PMID: 7277015.2. Barreto AS, Vassallo J, Queiroz Lde S. Papillomas and carcinomas of the choroid plexus : histological and immunohistochemical studies and comparison with normal fetal choroid plexus. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2004; 62(3A):600–607. PMID: 15334216.
Article3. Beskonakli E, Cayli S, Bostanci U, Kulaçoglu S, Yalçinlar Y. Choroid plexus papillomas of the posterior fossa : extraventricular extension, intraventricular and primary extraventricular location. Report of four cases. J Neurosurg Sci. 1998; 42:37–40. PMID: 9766271.4. Bian LG, Sun QF, Wu HC, Jiang H, Sun YH, Shen JK. Primary choroid plexus papilloma in the pituitary fossa : case report and literature review. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2011; 153:851–857. PMID: 21140177.
Article5. Furuya K, Sasaki T, Saito N, Atsuchi M, Kirino T. Primary large choroid plexus papillomas in the cerebellopontine angle : radiological manifestations and surgical management. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1995; 135:144–149. PMID: 8748805.
Article6. García-Valtuille R, Abascal F, García-Valtuille AI, Pinto JI, Cerezal L, Sanz F, et al. Adult choroid plexus papilloma of the posterior fossa mimicking a hemangioblastoma. Case report. J Neurosurg. 2000; 92:870–872. PMID: 10794304.
Article7. Imai M, Tominaga J, Matsumae M. Choroid plexus papilloma originating from the cerebrum parenchyma. Surg Neurol Int. 2011; 2:151. PMID: 22059144.
Article8. Jinhu Y, Jianping D, Jun M, Hui S, Yepeng F. Metastasis of a histologically benign choroid plexus papilloma : case report and review of the literature. J Neurooncol. 2007; 83:47–52. PMID: 17387433.
Article9. Kimura M, Takayasu M, Suzuki Y, Negoro M, Nagasaka T, Nakashima N, et al. Primary choroid plexus papilloma located in the suprasellar region : case report. Neurosurgery. 1992; 31:563–566. PMID: 1383866.10. Kurtkaya-Yapicier O, Scheithauer BW, Van Peteghem KP, Sawicki JE. Unusual case of extradural choroid plexus papilloma of the sacral canal. Case report. J Neurosurg. 2002; 97(1 Suppl):102–105. PMID: 12120630.
Article11. Ma YH, Ye K, Zhan RY, Wang LJ. Primary choroid plexus papilloma of the sellar region. J Neurooncol. 2008; 88:51–55. PMID: 18224277.
Article12. McIver JI, Link MJ, Giannini C, Cohen-Gadol AA, Driscoll C. Choroid plexus papilloma and meningioma : coincidental posterior fossa tumors : case report and review of the literature. Surg Neurol. 2003; 60:360–365. PMID: 14505866.
Article13. Mitsuyama T, Ide M, Hagiwara S, Tanaka N, Kawamura H, Aiba M. [Adult choroid plexus papilloma of the posterior fossa : extraventricular location]. No Shinkei Geka. 2005; 33:825–829. PMID: 16095214.14. Nakano I, Kondo A, Iwasaki K. Choroid plexus papilloma in the posterior third ventricle : case report. Neurosurgery. 1997; 40:1279–1282. PMID: 9179902.
Article15. Noguchi A, Shiokawa Y, Kobayashi K, Saito I, Tsuchiya K, McMenomey SO, et al. Choroid plexus papilloma of the third ventricle in the fetus. Case illustration. J Neurosurg. 2004; 100(2 Suppl Pediatrics):224. PMID: 14758957.16. Pillai A, Rajeev K, Chandi S, Unnikrishnan M. Intrinsic brainstem choroid plexus papilloma. Case report. J Neurosurg. 2004; 100:1076–1078. PMID: 15200124.17. Sameshima T, Tanikawa R, Sugimura T, Izumi N, Seki T, Maeda T, et al. Choroid plexus papilloma originating in the sella turcica--case report. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2010; 50:144–146. PMID: 20185881.