Ewha Med J.
2016 Jan;39(1):32-35. 10.12771/emj.2016.39.1.32.
Successful Treatment of Prostatic Abscess Accompanied by Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia Using a Percutaneous Fine-Needle Aspiration under the Computed Tomography Guidance
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Nephrology, Department of Internal Medicine, Konyang University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea. hwangwm@kyuh.ac.kr
- KMID: 2152756
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12771/emj.2016.39.1.32
Abstract
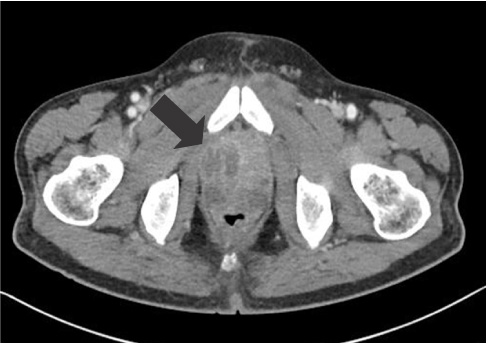
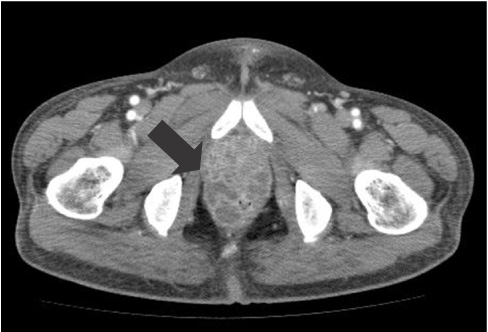
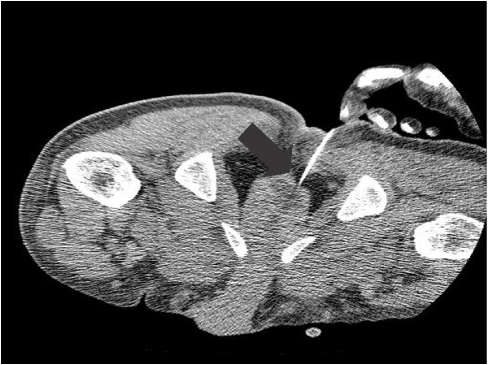
- Prostatic abscess is not a common entity which is characterized by non-specific clinical presentations. This poses a diagnostic challenge for clinicians. Clinicians routinely consider antibiotic treatments concomitantly with drainage for the treatment of prostatic abscess. But there are no established guidelines for its optimal timing, methods and indications. Surgical drainage procedures include transurethral resection of the prostate and perineal incision and drainage. But there is variability in the prognosis of patients between the procedures. We have treated a 48-year-old diabetes patient with prostatic abscess accompanied by MRSA bacteremia using a percutaneous fine-needle aspiration under the computed tomography (CT) guidance. The patient achieved improvement of the symptoms and in follow up CT findings. A percutaneous drainage under the CT guidance is advantageous in that it causes fewer complications. However, Further studies are warranted to establish the optimal timing, methods and indications in patients with prostate abscess.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Oliveira P, Andrade JA, Porto HC, Filho JE, Vinhaes AF. Diagnosis and treatment of prostatic abscess. Int Braz J Urol. 2003; 29:30–34.2. Barozzi L, Pavlica P, Menchi I, De Matteis M, Canepari M. Prostate abscess, Diagnosis and treatment. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1998; 170:753–757.3. Sugao H, Hidekazu T, Sakurai T. Transrectal longitudinal ultrasonography of prostate abscess. J Urol. 1982; 136:1316–1317.4. Rabii R, Rais H, Joual A, el Mrini M, Benjelloun S. Prostate abscess. A review. Ann Urol. 1999; 33:271–273.5. Lim JW, Ko YT, Lee DH, Park SJ, Oh JH, Yoon Y, et al. Treatment of prostate abscess: Value of transrectal ultrasonographically needle aspiration. J Ultrasound Med. 2000; 19:609–617.6. Ludwig M, Schroeder-Printzen I, Schiefer HC, Weidner W. Diagnosis and therapeutic management of 18 patients with prostate abscess. Urology. 1999; 53:340–345.7. Pai MG, Bhat HS. Prostate abscess. J Urol. 1972; 108:599–600.8. Marini AJ, Jacobs LD, Clapp PR, Hariharan A, Stams UK, Hodges CV. Emphysematous prostate abscess: Diagnosis and treatment. J Urol. 1983; 129:385–386.9. Meares EM Jr. Prostate abscess. J Urol. 1986; 136:1281–1282.10. Collado A, Palou J, Garcia-Penit J, Salvador J, De La Torre P, Vincente J. Ultrasound guided needle aspiration in prostate abscess. Urology. 1999; 53:548–552.11. Jang K, Lee DH, Lee SH, Chung BH. Treatment of prostate abscess: case collection and comparison of treatment methods. Korean J Urol. 2012; 53:860–864.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Delayed Diagnosis of Tuberculous Spondylitis Masked by Concomitant Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Infection
- Community-acquired Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia Complicated by Acute Cholecystitis
- A Case of Brain Abscess Complicating Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus Sepsis in a Premature Infant
- Detection of Multidrug Resistant Patterns and Associated - genes of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus ( MRSA ) Isolated from Clinical Specimens
- Microbiological and genotypic factors affecting mortality in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia