Cancer Res Treat.
2016 Jan;48(1):393-397. 10.4143/crt.2014.209.
Pazopanib for Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: The First Case Report in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Jeju National University Hospital, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea. btfulo@gmail.com
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Incheon, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Jeju National University Hospital, Jeju National University School of Medicine, Jeju, Korea.
- KMID: 2152298
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2014.209
Abstract
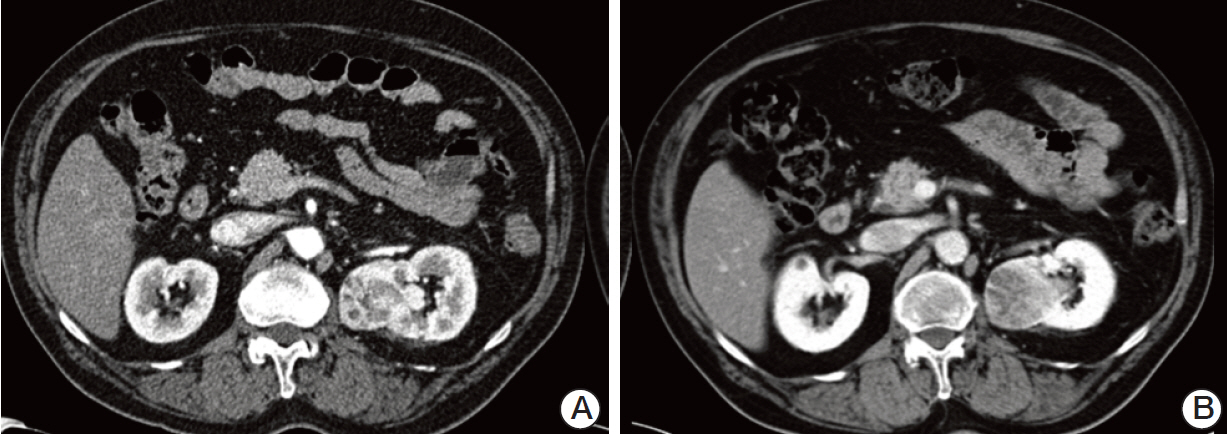
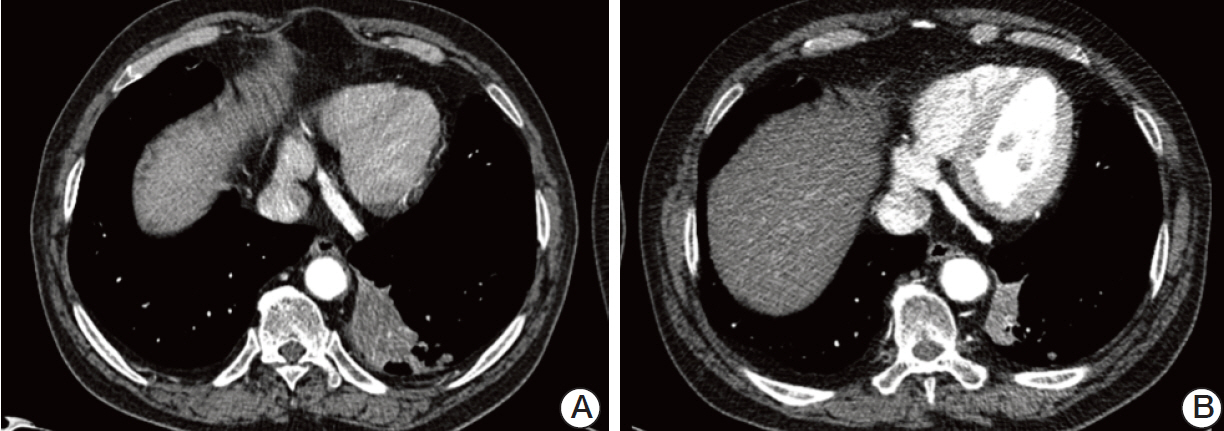
- Pazopanib is a potent multitargeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor that has been shown to have good efficacy in patients with renal cell carcinoma. A previous phase II trial demonstrated that short-term pazopanib administration was generally well tolerated and showed antitumor activity in patients with early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Herein, we report on the case of a 66-year-old man with simultaneous metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the lung and renal cell carcinoma who was treated with pazopanib. The patient showed an unexpected partial response and experienced a 10-month progression-free survival without significant toxicity. To the best of the authors' knowledge, this is the first report of pazopanib treatment in a non-small cell lung cancer patient in Korea. The results in this patient suggest that pazopanib may be a valid treatment option for advanced non-small cell lung cancer.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Mulshine JL, Sullivan DC. Clinical practice. Lung cancer screening. N Engl J Med. 2005; 352:2714–20.2. Sternberg CN, Davis ID, Mardiak J, Szczylik C, Lee E, Wagstaff J, et al. Pazopanib in locally advanced or metastatic renal cell carcinoma: results of a randomized phase III trial. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28:1061–8.
Article3. van der Graaf WT, Blay JY, Chawla SP, Kim DW, Bui-Nguyen B, Casali PG, et al. Pazopanib for metastatic soft-tissue sarcoma (PALETTE): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2012; 379:1879–86.
Article4. Altorki N, Lane ME, Bauer T, Lee PC, Guarino MJ, Pass H, et al. Phase II proof-of-concept study of pazopanib monotherapy in treatment-naive patients with stage I/II resectable non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2010; 28:3131–7.
Article5. Bible KC, Suman VJ, Molina JR, Smallridge RC, Maples WJ, Menefee ME, et al. A multicenter phase 2 trial of pazopanib in metastatic and progressive medullary thyroid carcinoma: MC057H. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014; 99:1687–93.
Article6. Ettinger DS, Akerley W, Bepler G, Blum MG, Chang A, Cheney RT, et al. Non-small cell lung cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2010; 8:740–801.7. Fukuoka M, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, Sunpaweravong P, Leong SS, Sriuranpong V, et al. Biomarker analyses and final overall survival results from a phase III, randomized, open-label, first-line study of gefitinib versus carboplatin/paclitaxel in clinically selected patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer in Asia (IPASS). J Clin Oncol. 2011; 29:2866–74.
Article8. Cappuzzo F, Ciuleanu T, Stelmakh L, Cicenas S, Szczesna A, Juhasz E, et al. Erlotinib as maintenance treatment in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2010; 11:521–9.
Article9. Santoni M, Conti A, De Giorgi U, Iacovelli R, Pantano F, Burattini L, et al. Risk of gastrointestinal events with sorafenib, sunitinib and pazopanib in patients with solid tumors: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Int J Cancer. 2014; 135:763–73.
Article10. Majem M, Pallares C. An update on molecularly targeted therapies in second- and third-line treatment in non-small cell lung cancer: focus on EGFR inhibitors and anti-angiogenic agents. Clin Transl Oncol. 2013; 15:343–57.
Article11. Barlesi F, Scherpereel A, Rittmeyer A, Pazzola A, Ferrer Tur N, Kim JH, et al. Randomized phase III trial of maintenance bevacizumab with or without pemetrexed after first-line induction with bevacizumab, cisplatin, and pemetrexed in advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer: AVAPERL (MO22089). J Clin Oncol. 2013; 31:3004–11.
Article12. Ganjoo KN, Villalobos VM, Kamaya A, Fisher GA, Butrynski JE, Morgan JA, et al. A multicenter phase II study of pazopanib in patients with advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) following failure of at least imatinib and sunitinib. Ann Oncol. 2014; 25:236–40.
Article13. Ahn HK, Choi JY, Kim KM, Kim H, Choi SH, Park SH, et al. Phase II study of pazopanib monotherapy in metastatic gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumours. Br J Cancer. 2013; 109:1414–9.
Article14. Hurwitz HI, Dowlati A, Saini S, Savage S, Suttle AB, Gibson DM, et al. Phase I trial of pazopanib in patients with advanced cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2009; 15:4220–7.
Article15. Dy GK, Infante JR, Eckhardt SG, Novello S, Ma WW, Jones SF, et al. Phase Ib trial of the oral angiogenesis inhibitor pazopanib administered concurrently with erlotinib. Invest New Drugs. 2013; 31:891–9.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Early Gastric Cancer Associated with Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Durable Response to Pazopanib in a Patient with Metastatic Alveolar Soft Part Sarcoma
- A Case of Iris Metastasis from Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
- A Case of Spontaneous Regression of Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Ovarian Metastasis from Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Responding to Erlotinib