Prog Med Phys.
2015 Dec;26(4):273-279. 10.14316/pmp.2015.26.4.273.
The Study of High-functioning Electrodeposition Technology That Pearl-like Feeling Expressed for Medical Devices for Smart Health
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Biomedical Engineering, Daegu Haany University, Daegu, Korea.
- 2Basic Science Institute, Daegu Haany University, Daegu, Korea. lib12@dhu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2151762
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2015.26.4.273
Abstract
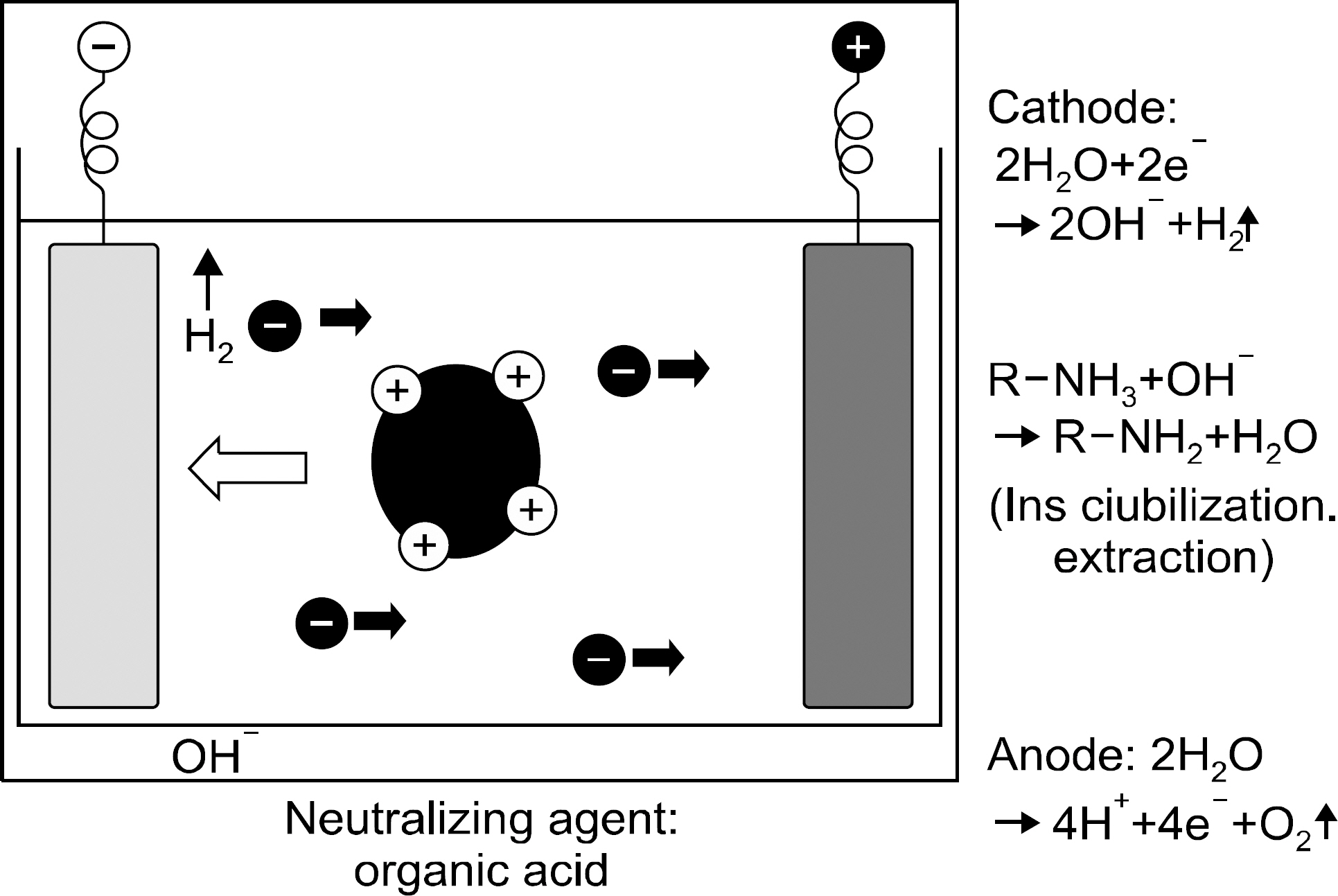
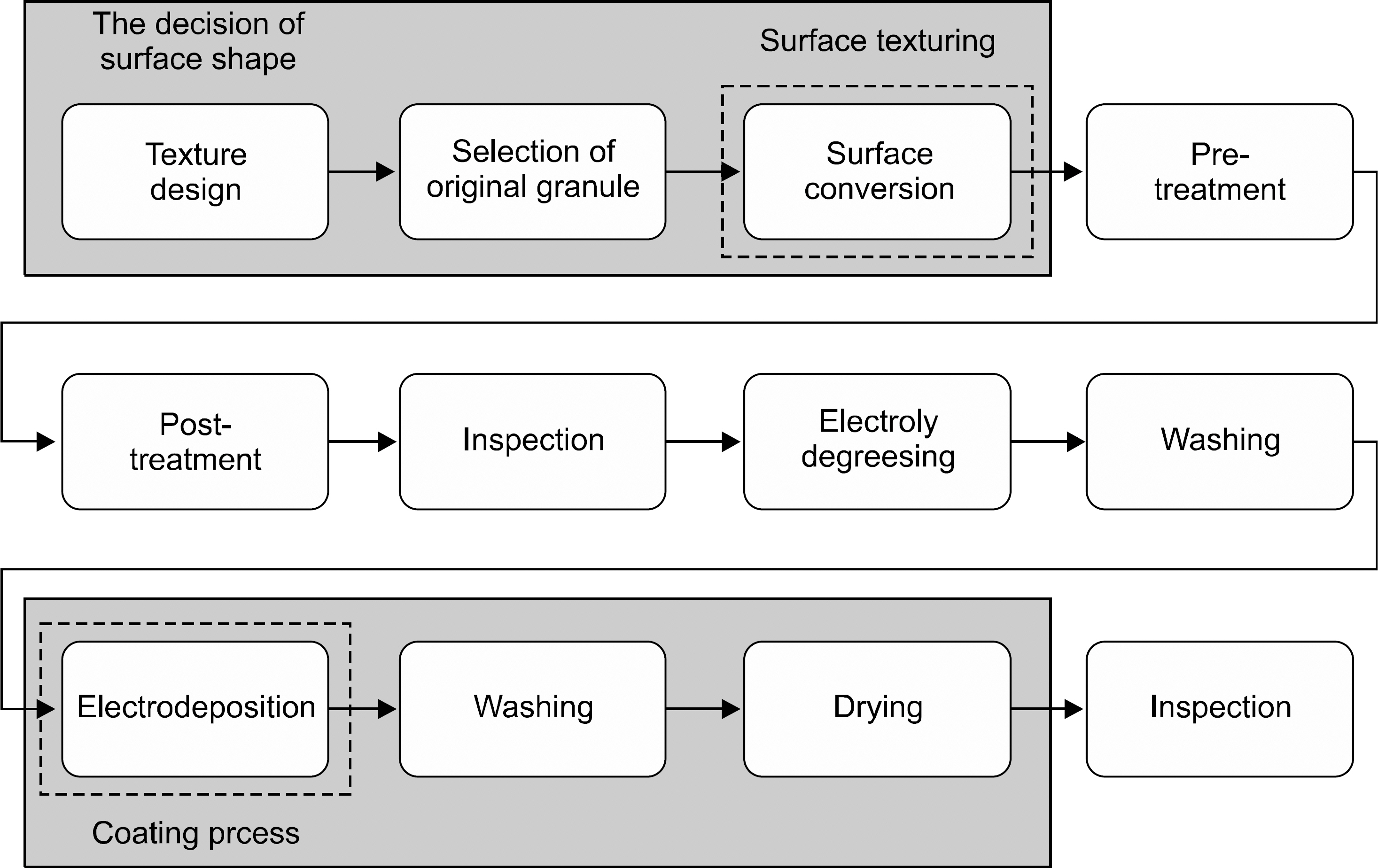
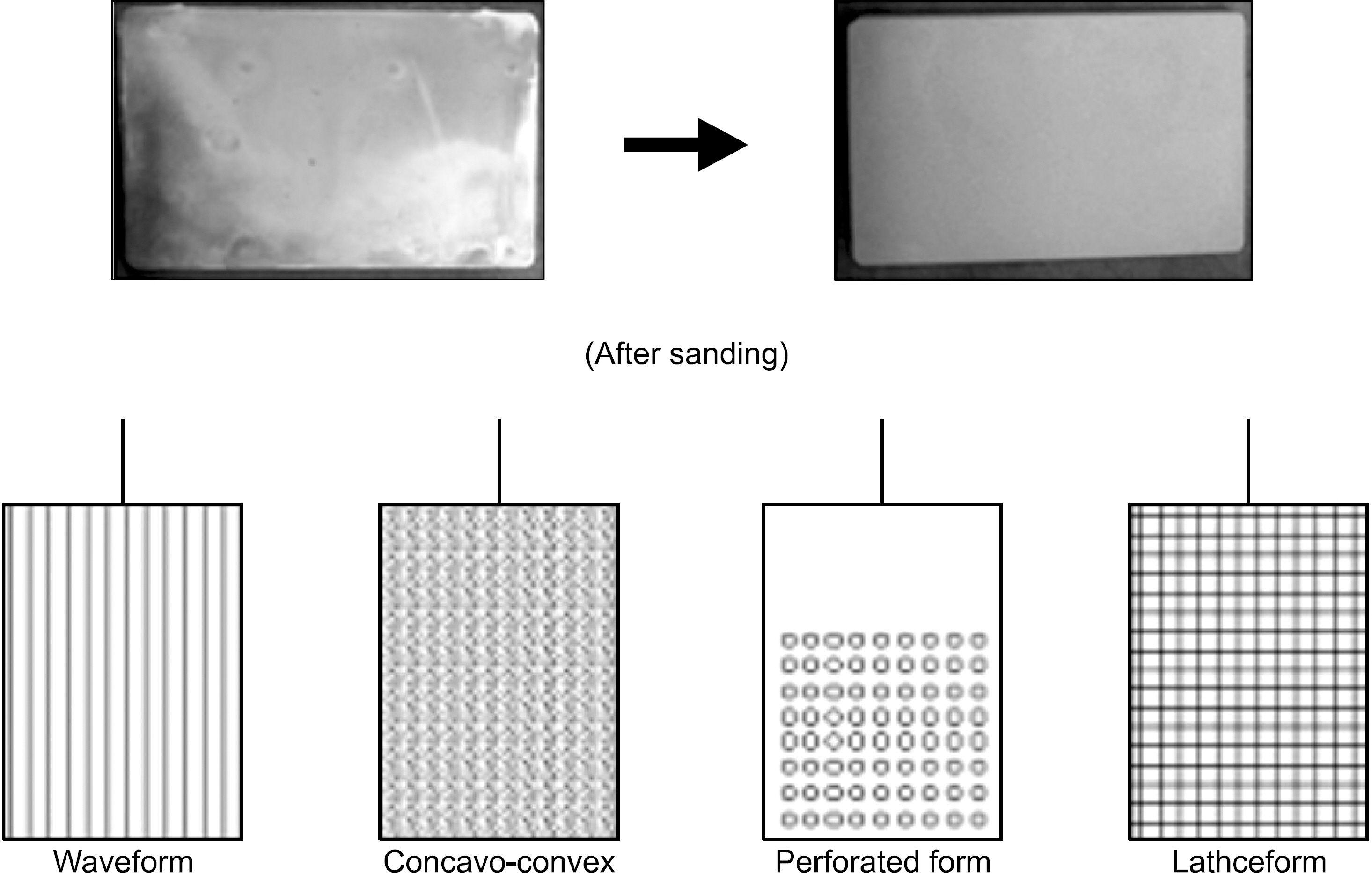
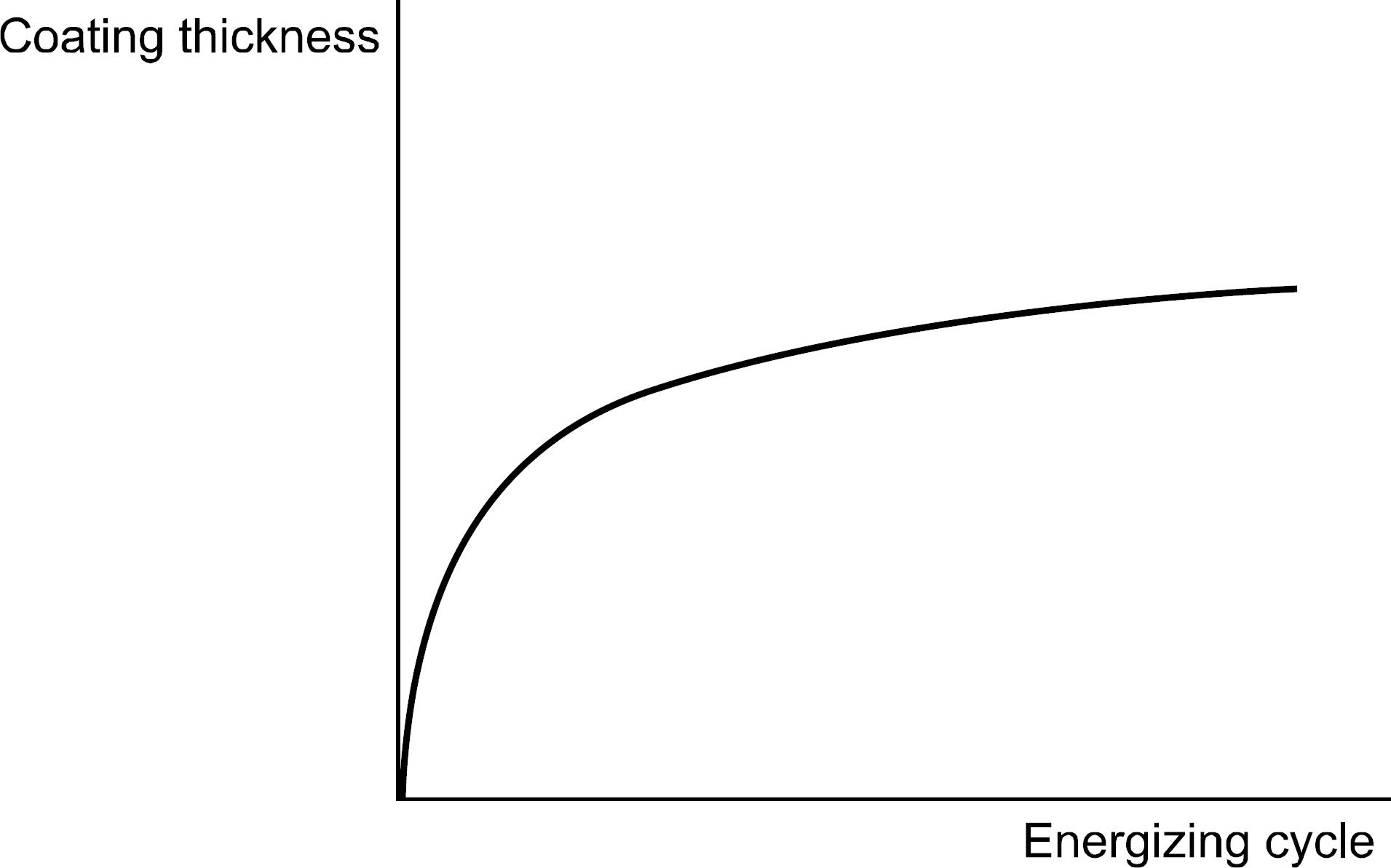
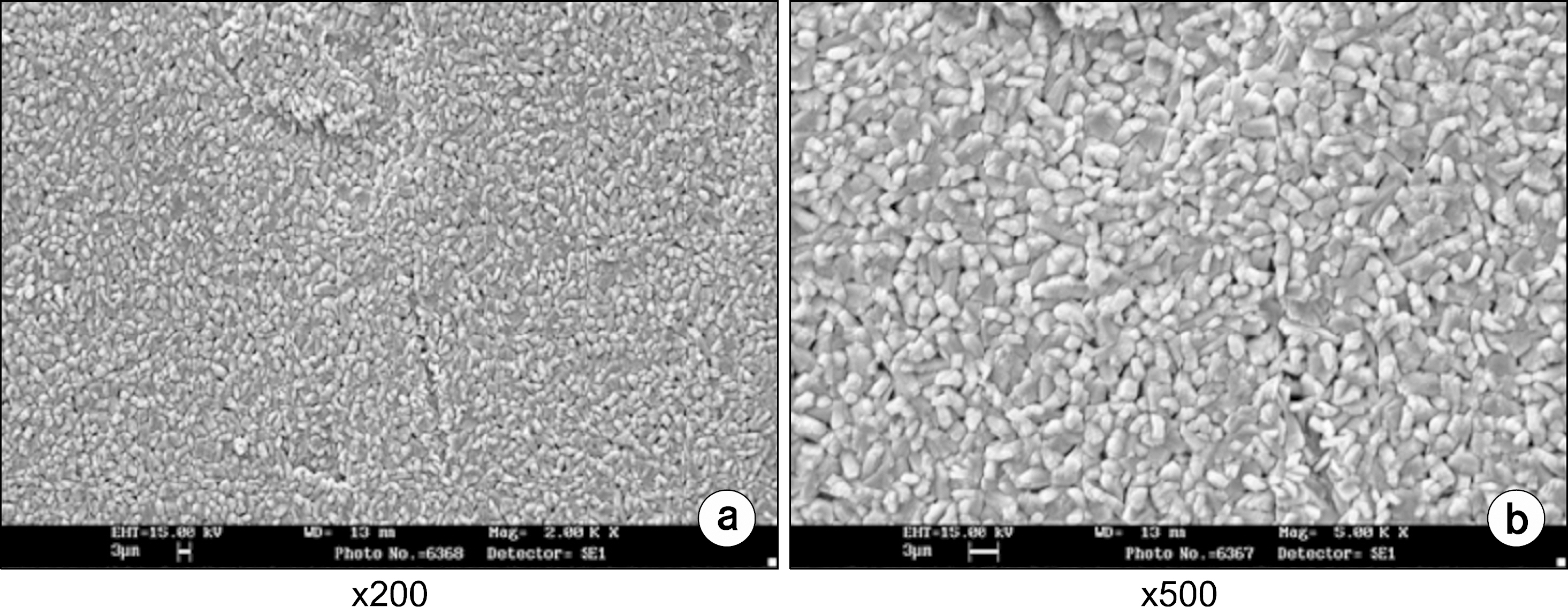
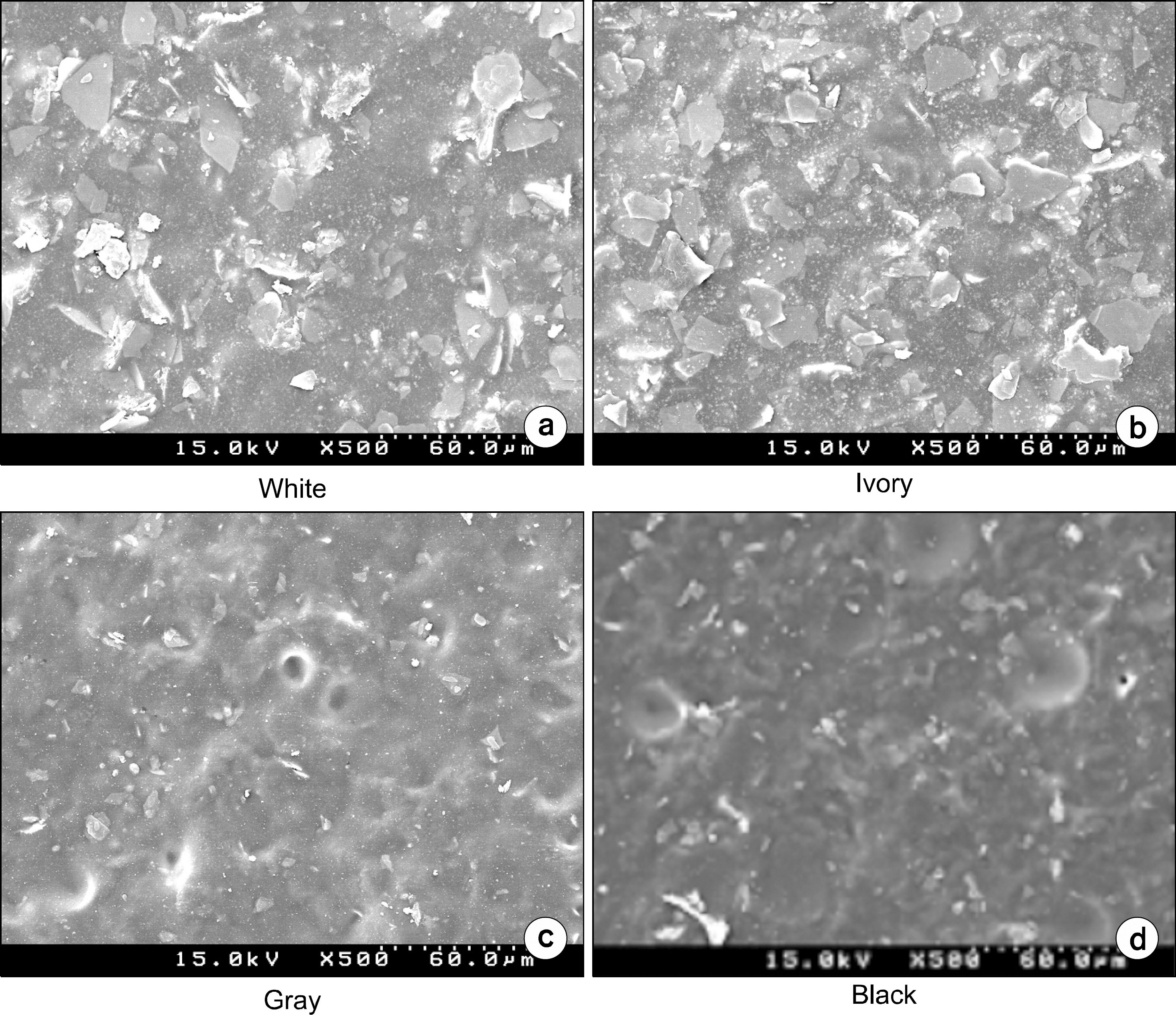
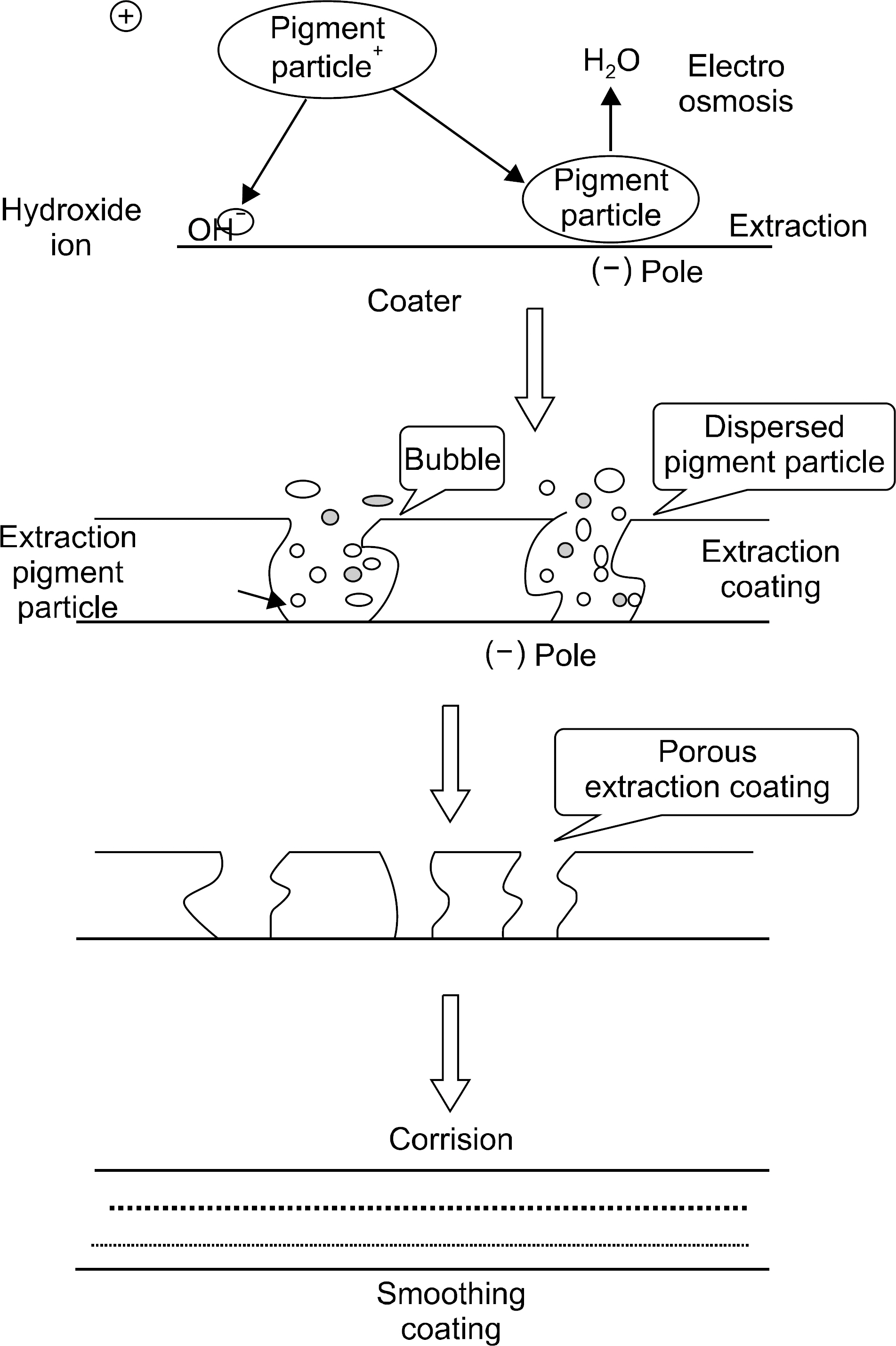
- Recently, medical devices for a smart health development and dissemination are becoming increasingly frequent use of devices and their's thermal stability, durability, the external splendors are required. Industrial demand for smart health medical devices uses high-functioning electrodeposition technology that expressed pearl-like feeling is rapidly increasing. Generally, pearl powder is added to electrodeposition pigment in order to form a coating which shows pearl-like feeling. On the other hand, the electrodeposition technology for the smart health medical devices uses a new method that can express pearl-like feeling without using pearl powder. In this study, we was tried to find out the most appropriate texture formation, the right dilution recipe. We've tried various ptoportions of pigments (ED-600, ED-600S, ED-MX, ED-M). As a result, we found out that ED-600 and ED-MX (15% solid) in appropriate concentration showed the best adherence rate. By several samples tests and experiments which include washing the fixed pigment in various temperature levels (20~40degrees C) and drying, we were able to get the best results in drying condition of 180+/-10degrees C and 30+/-5 min. The research showed that it is mush more competitive and cost effective to use the new method that produces natural pearl-like feeling on the surface than to add pearl powder to high-functioning electrodeposition pigment, which is a method that has been used for the smart health medical devices so far.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Her Y, Do J.H, Kim H.J: Smart technology trend in healthcare and industry prospect. KEIT Report. 15(4):47–55. 2015.2. Pletcher, Welch. Industrial Electrochemistry. Klackie A&P. Ch.8:146–178. 1993.3. Saito M, Ohashi K. The Electrodeposition Conditions of CoNiFe Films, Crystal Structure, and Evaluation of Magnetic Moments, Proceedings Electrochem. Soc. PV. 27(1):241–248. 2002.4. Saliba-Silva A.M, Oliveira E.T.D, Garcia R.H.L, Durazzo M. Pulse Electrodeposition of Natural Uranium in 2-Propanol Acidic Ionic Solution, ECS Transactions. 53(11):99–107. 2013.5. Garich H, Taylor E.J.An Electrochemical Cell with Improved Flow for Uniform Current Distribution and Plating Thickness. ECS Transactions. 53(11):3–8. 2013.
Article6. Schwartz M, Yoo B, Nobe K. Aqueous Electrodeposition and Mechanism of Iron Group-Vanadium Ternary Alloys, ECS Transactions. 33(34):19–32. 2010.7. Wurz M, Wagner P, Rissing L, Caro J. Assembly and Embedding of Nanoparticles in a Ni-Matrix, ECS Transactions. 33(34):33–42. 2010.8. Andreae B, Zbiegien J. Barrel Electrocoating of Small Parts, Tech. Papers Soc. Manu. Engineers. 280:1–24. 2002.9. Courval G, Shores S. Elimination of Electrocoating on Aluminum Intensive Vehicles, SAE Technical Papers. 1(352):1. 1999.10. Tsuda T, Nagai T, Asakura S. Cathodic Polarization Conditions for Electrocoating Formation on Carbon Steel in Flowing Tap Water, Corrision Eng. 54(10):655–664. 2005.11. Tsuda T, Nagai T, Suzuki M, Hosaka T, Asakura S. Cathodic Protection and Electrocoating on a Coated Steel Channel in Freshwater, Zairyo to Kankyo. 54(4):146–151. 2005.12. Vadlamani V.K, Chalivendra V.B, Shukla A, Yang S. Electro-mechanical Response of Carbon Nanotube Reinforced Polymer Composites, Bethel Soc. Exp. Mechanics. 2010:365. 2010.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Introduction of Wearable Device in Cardiovascular Field for Monitoring Arrhythmia
- Internet of Things: An Overview and its Applications in Aviation
- Enchanted Life Space: Adding Value to Smart Health by Integrating Human Desires
- Recent Patient Health Monitoring Platforms Incorporating Internet of Things-Enabled Smart Devices
- An Update on the Use of Wearable Devices in Men’s Health