Immune Netw.
2012 Oct;12(5):196-206. 10.4110/in.2012.12.5.196.
Glutamine and Leucine Provide Enhanced Protective Immunity Against Mucosal Infection with Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Veterinary Medicine and Bio-Safety Research Institute, Chonbuk National University, Jeonju 561-756, Korea. vetvirus@chonbuk.ac.kr
- 2Department of Immunology, Chonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju 561-756, Korea.
- KMID: 2150749
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4110/in.2012.12.5.196
Abstract
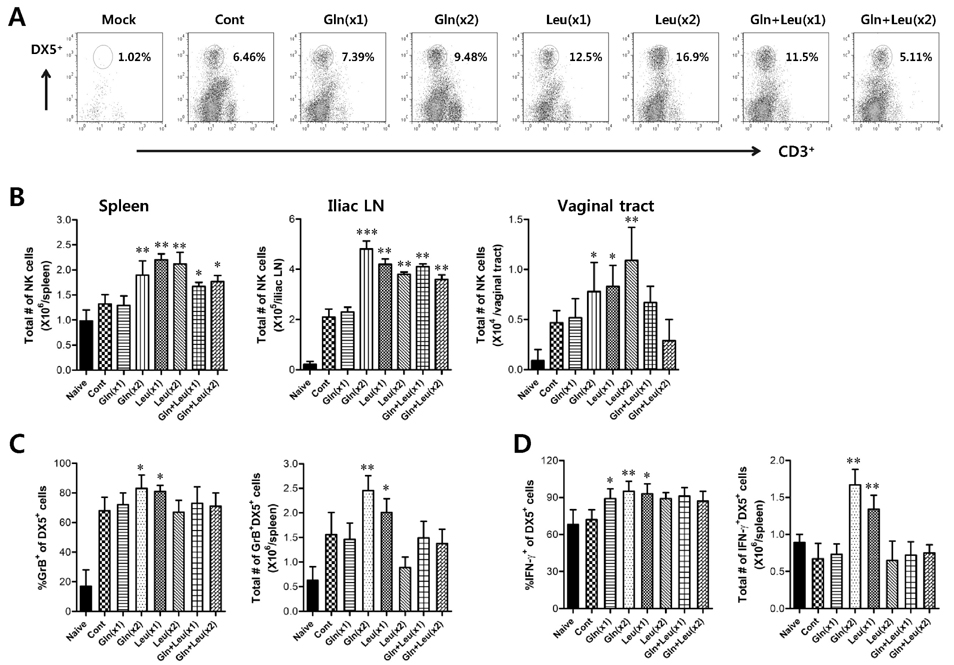
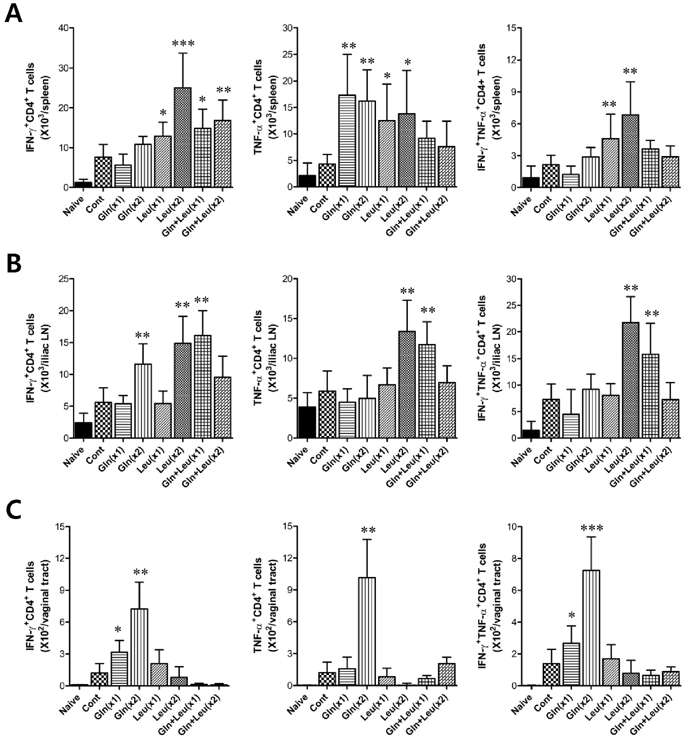
- Besides their role as building blocks of protein, there are growing evidences that some amino acids have roles in regulating key metabolic pathways that are necessary for maintenance, growth, reproduction, and immunity. Here, we evaluated the modulatory functions of several amino acids in protective immunity against mucosal infection of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1). We found that glutamine (Gln) and leucine (Leu) showed enhanced protective immunity to HSV-1 mucosal infection when two administration of Gln and single administration of Leu per day, but not when administered in combinations. Ameliorated clinical signs of HSV-1 challenged mice by the intraperitoneal administration of Gln and Leu were closely associated with viral burden and IFN-gamma production in the vaginal tract at 2 and 4 days post-infection. In addition, the enhanced production of vaginal IFN-gamma appeared to be caused by NK and HSV-1 antigen-specific Th1-type CD4+ T cells recruited into vaginal tract of mice treated with Gln and Leu, which indicates that IFN-gamma, produced by NK and Th1-type CD4+ T cells, may be critical to control the outcome of diseases caused by HSV-1 mucosal infection. Collectively, our results indicate that intraperitoneal administration of Gln and Leu following HSV-1 mucosal infection could provide beneficial effects for the modulation of protective immunity, but dosage and frequency of administration should be carefully considered, because higher frequency and overdose of Gln and Leu, or their combined treatment, showed detrimental effects to protective immunity.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Anti-herpes Activity of Vinegar-processed Daphne genkwa Flos Via Enhancement of Natural Killer Cell Activity
Erdenebileg Uyangaa, Jin Young Choi, Hyung Won Ryu, Sei-Ryang Oh, Seong Kug Eo
Immune Netw. 2015;15(2):91-99. doi: 10.4110/in.2015.15.2.91.Prophylactic and Therapeutic Modulation of Innate and Adaptive Immunity Against Mucosal Infection of Herpes Simplex Virus
Erdenebileg Uyangaa, Ajit Mahadev Patil, Seong Kug Eo
Immune Netw. 2014;14(4):187-200. doi: 10.4110/in.2014.14.4.187.
Reference
-
1. Wu G. Amino acids: metabolism, functions, and nutrition. Amino Acids. 2009. 37:1–17.
Article2. Suenaga R, Tomonaga S, Yamane H, Kurauchi I, Tsuneyoshi Y, Sato H, Denbow DM, Furuse M. Intracerebroventricular injection of L-arginine induces sedative and hypnotic effects under an acute stress in neonatal chicks. Amino Acids. 2008. 35:139–146.
Article3. Wu G, Bazer FW, Davis TA, Jaeger LA, Johnson GA, Kim SW, Knabe DA, Meininger CJ, Spencer TE, Yin YL. Important roles for the arginine family of amino acids in swine nutrition and production. Livest Sci. 2007. 112:8–22.
Article4. Wu G, Bazer FW, Cudd TA, Jobgen WS, Kim SW, Lassala A, Li P, Matis JH, Meininger CJ, Spencer TE. Pharmacokinetics and safety of arginine supplementation in animals. J Nutr. 2007. 137:6 Suppl 2. 1673S–1680S.
Article5. Wu G, Collins JK, Perkins-Veazie P, Siddiq M, Dolan KD, Kelly KA, Heaps CL, Meininger CJ. Dietary supplementation with watermelon pomace juice enhances arginine availability and ameliorates the metabolic syndrome in Zucker diabetic fatty rats. J Nutr. 2007. 137:2680–2685.
Article6. Fu WJ, Haynes TE, Kohli R, Hu J, Shi W, Spencer TE, Carroll RJ, Meininger CJ, Wu G. Dietary L-arginine supplementation reduces fat mass in Zucker diabetic fatty rats. J Nutr. 2005. 135:714–721.
Article7. Jobgen W, Fu WJ, Gao H, Li P, Meininger CJ, Smith SB, Spencer TE, Wu G. High fat feeding and dietary L-arginine supplementation differentially regulate gene expression in rat white adipose tissue. Amino Acids. 2009. 37:187–198.
Article8. Wang J, Chen L, Li P, Li X, Zhou H, Wang F, Li D, Yin Y, Wu G. Gene expression is altered in piglet small intestine by weaning and dietary glutamine supplementation. J Nutr. 2008. 138:1025–1032.
Article9. Escobar J, Frank JW, Suryawan A, Nguyen HV, Kimball SR, Jefferson LS, Davis TA. Physiological rise in plasma leucine stimulates muscle protein synthesis in neonatal pigs by enhancing translation initiation factor activation. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2005. 288:E914–E921.
Article10. Escobar J, Frank JW, Suryawan A, Nguyen HV, Kimball SR, Jefferson LS, Davis TA. Regulation of cardiac and skeletal muscle protein synthesis by individual branched-chain amino acids in neonatal pigs. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2006. 290:E612–E621.11. Meijer AJ, Dubbelhuis PF. Amino acid signalling and the integration of metabolism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004. 313:397–403.12. Yao K, Yin YL, Chu W, Liu Z, Deng D, Li T, Huang R, Zhang J, Tan B, Wang W, Wu G. Dietary arginine supplementation increases mTOR signaling activity in skeletal muscle of neonatal pigs. J Nutr. 2008. 138:867–872.
Article13. Li P, Yin YL, Li D, Kim SW, Wu G. Amino acids and immune function. Br J Nutr. 2007. 98:237–252.
Article14. Tan B, Li XG, Kong X, Huang R, Ruan Z, Yao K, Deng Z, Xie M, Shinzato I, Yin Y, Wu G. Dietary L-arginine supplementation enhances the immune status in early-weaned piglets. Amino Acids. 2009. 37:323–331.
Article15. Van Brummelen R, du Toit D. L-methionine as immune supportive supplement: a clinical evaluation. Amino Acids. 2007. 33:157–163.
Article16. Macchiarulo A, Camaioni E, Nuti R, Pellicciari R. Highlights at the gate of tryptophan catabolism: a review on the mechanisms of activation and regulation of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), a novel target in cancer disease. Amino Acids. 2009. 37:219–229.
Article17. Platten M, Ho PP, Youssef S, Fontoura P, Garren H, Hur EM, Gupta R, Lee LY, Kidd BA, Robinson WH, Sobel RA, Selley ML, Steinman L. Treatment of autoimmune neuroinflammation with a synthetic tryptophan metabolite. Science. 2005. 310:850–855.
Article18. Lacey JM, Wilmore DW. Is glutamine a conditionally essential amino acid? Nutr Rev. 1990. 48:297–309.
Article19. Roth E, Funovics J, Mühlbacher F, Schemper M, Mauritz W, Sporn P, Fritsch A. Metabolic disorders in severe abdominal sepsis: glutamine deficiency in skeletal muscle. Clin Nutr. 1982. 1:25–41.
Article20. Gamrin L, Essen P, Forsberg AM, Hultman E, Wernerman J. A descriptive study of skeletal muscle metabolism in critically ill patients: free amino acids, energy-rich phosphates, protein, nucleic acids, fat, water, electrolytes. Crit Care Med. 1996. 24:575–583.21. Yeh CL, Hsu CS, Yeh SL, Chen WJ. Dietary glutamine supplementation modulates Th1/Th2 cytokine and interleukin-6 expressions in septic mice. Cytokine. 2005. 31:329–334.22. Peng X, Yan H, You Z, Wang P, Wang S. Glutamine granule-supplemented enteral nutrition maintains immunological function in severely burned patients. Burns. 2006. 32:589–593.
Article23. Crawford J, Cohen HJ. The essential role of L-glutamine in lymphocyte differentiation in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 1985. 124:275–282.
Article24. Newsholme P. Why is L-glutamine metabolism important to cells of the immune system in health, postinjury, surgery or infection? J Nutr. 2001. 131:9 Suppl. 2515S–2522S.25. Pithon-Curi TC, Schumacher RI, Freitas JJ, Lagranha C, Newsholme P, Palanch AC, Doi SQ, Curi R. Glutamine delays spontaneous apoptosis in neutrophils. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2003. 284:C1355–C1361.26. Chang WK, Yang KD, Shaio MF. Effect of glutamine on Th1 and Th2 cytokine responses of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Clin Immunol. 1999. 93:294–301.
Article27. Rohde T, MacLean DA, Klarlund Pedersen B. Glutamine, lymphocyte proliferation and cytokine production. Scand J Immunol. 1996. 44:648–650.
Article28. Hörig H, Spagnoli GC, Filgueira L, Babst R, Gallati H, Harder F, Juretic A, Heberer M. Exogenous glutamine requirement is confined to late events of T cell activation. J Cell Biochem. 1993. 53:343–351.
Article29. Klimberg VS, McClellan JL. Claude H. Organ, Jr. Honorary Lectureship. Glutamine, cancer, its therapy. Am J Surg. 1996. 172:418–424.
Article30. Rohde T, Ullum H, Rasmussen JP, Kristensen JH, Newsholme E, Pedersen BK. Effects of glutamine on the immune system: influence of muscular exercise and HIV infection. J Appl Physiol. 1995. 79:146–150.
Article31. Lynch CJ, Patson BJ, Anthony J, Vaval A, Jefferson LS, Vary TC. Leucine is a direct-acting nutrient signal that regulates protein synthesis in adipose tissue. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2002. 283:E503–E513.
Article32. Koelle DM, Corey L. Herpes simplex: insights on pathogenesis and possible vaccines. Annu Rev Med. 2008. 59:381–395.
Article33. Wilson SS, Fakioglu E, Herold BC. Novel approaches in fighting herpes simplex virus infections. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2009. 7:559–568.
Article34. Eo SK, Lee S, Chun S, Rouse BT. Modulation of immunity against herpes simplex virus infection via mucosal genetic transfer of plasmid DNA encoding chemokines. J Virol. 2001. 75:569–578.
Article35. Frentsch M, Arbach O, Kirchhoff D, Moewes B, Worm M, Rothe M, Scheffold A, Thiel A. Direct access to CD4+ T cells specific for defined antigens according to CD154 expression. Nat Med. 2005. 11:1118–1124.
Article36. Sommer MH, Xavier MH, Fialho MB, Wannmacher CM, Wajner M. The influence of amino acids on mitogen-activated proliferation of human lymphocytes in vitro. Int J Immunopharmacol. 1994. 16:865–872.
Article37. Dobbs ME, Strasser JE, Chu CF, Chalk C, Milligan GN. Clearance of herpes simplex virus type 2 by CD8+ T cells requires gamma interferon and either perforin- or Fas-mediated cytolytic mechanisms. J Virol. 2005. 79:14546–14554.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Disseminated Herpes Simplex Virus Infection in Immunocompromised Patient
- A Case of Chronic Herpes Simplex Virus Infection Misdiagnosed as a Perforating Dermatosis
- Clinical Features of Eczema Herpeticum in Comparison with Localized Herpes Simplex Virus Infection
- Prophylactic and Therapeutic Modulation of Innate and Adaptive Immunity Against Mucosal Infection of Herpes Simplex Virus
- A Study of Indirect Immunofluorescence Staining in the Diagnosis of Cutaneous Herpes Simplex Virus Infection