Kosin Med J.
2015 Dec;30(2):131-139. 10.7180/kmj.2015.30.2.131.
Mucinous precursor lesions of mucinous carcinoma in breast: Incidence and histopathologic features
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pathology, College of Medicine, Kosin University, Busan, Korea. suajoon@ns.kosinmed.or.kr
- KMID: 2150499
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2015.30.2.131
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Columnar cell lesion (CCL), atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH) and ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) may be premalignant lesion of mammary invasive carcinoma. A few recent investigators reported that the precursor lesions exhibited mucin production and they might be potential precursor lesion for mucinous carcinoma (mCA). This study aims to investigate the incidence and histopathologic characteristics of mucinous precursor lesions, including mucinous DCIS (mDCIS) and mucinous CCL (mCCL).
METHODS
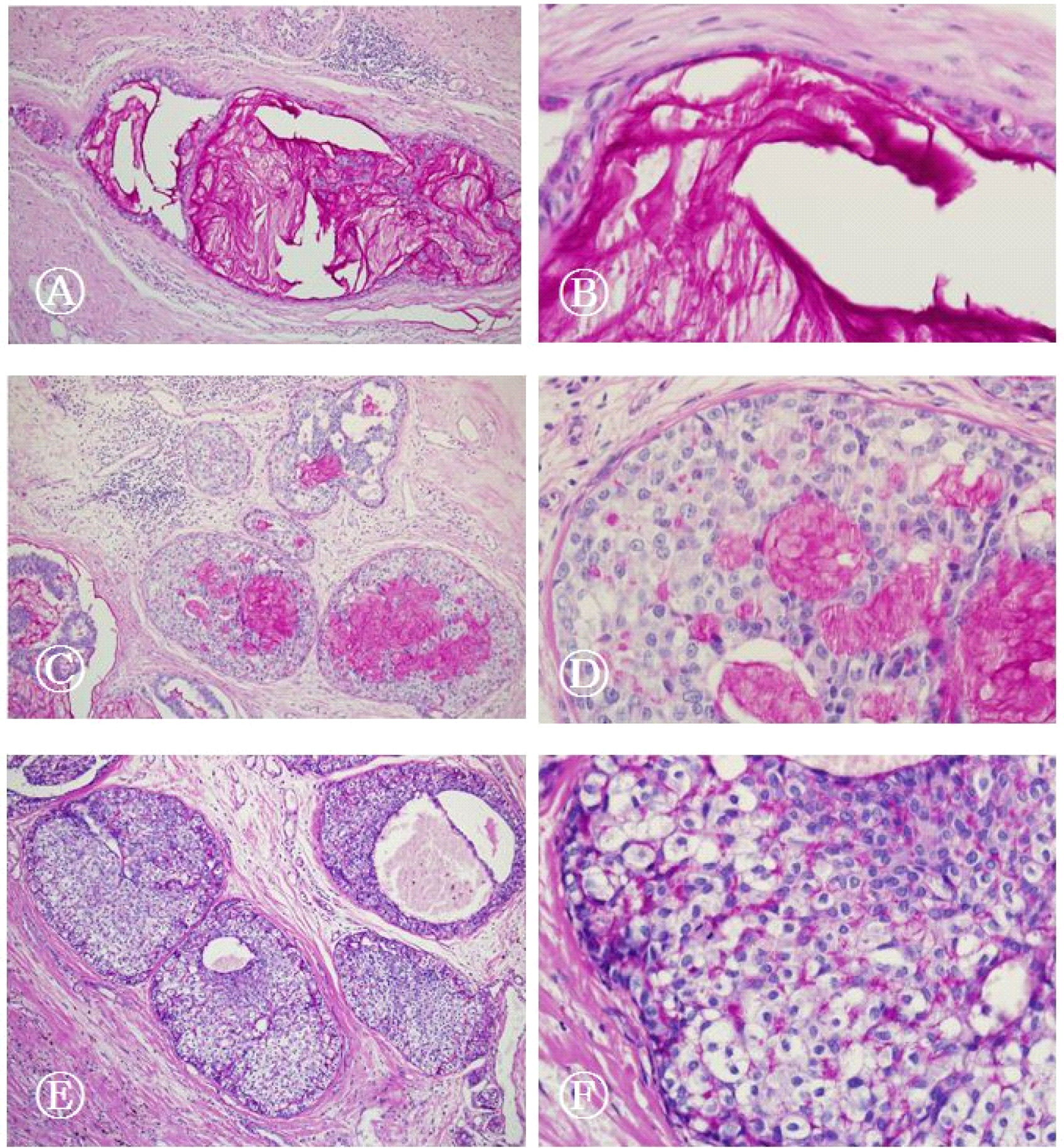
We retrospectively analyzed invasive carcinomas with mucin. Cases were grouped into three subgroups: pure mCA, mixed mCA, and invasive carcinoma of no special type with mucin production (IC of NST-m). Precursor lesions were evaluated with PAS and alcian blue staining.
RESULTS
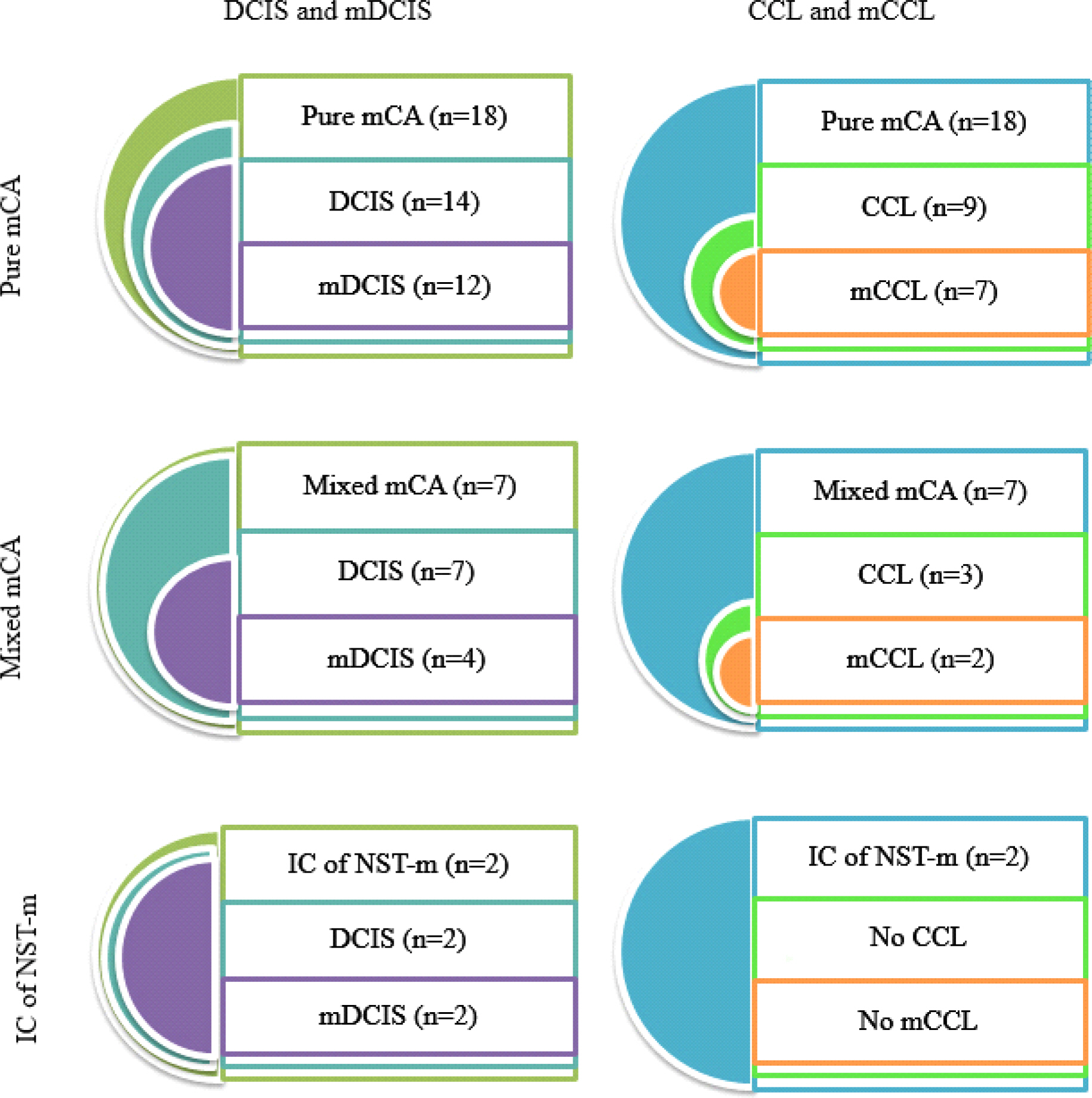
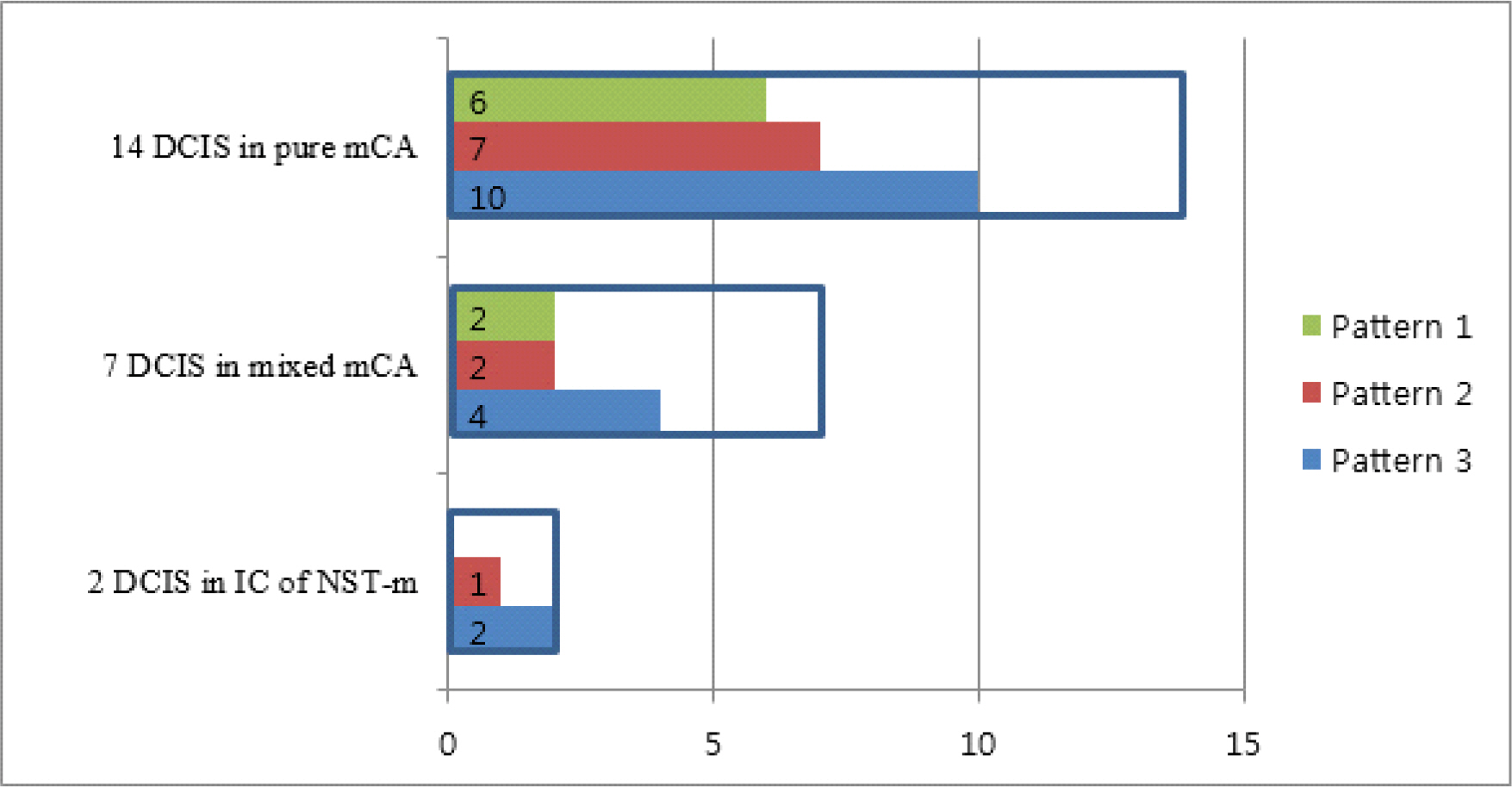
Total 27 cases of invasive carcinoma with mucin were analysed and classified as 18 pure mCA, 7 mixed mCA, and 2 IC of NST-m. mDCISs were found in 12 pure mCA, 4 mixed mCA and 2 IC of NST-m. mCCLs were found in 7 pure mCA and 2 mixed mCA. Majority of mucin was identified in both cytoplasm and ductal lumen, while some tumors exhibited only cytoplasmic mucin. We also observed three patterns of mDCIS classifiable by location of mucin and architecture of tumor cells.
CONCLUSIONS
Cytoplasmic mucin suggested that mucinous feature of precursor lesions in the vicinity of mCA might not be a passive morphologic finding but be involved in development of mCA.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Abdel-Fatah TM, Powe DG, Hodi Z, Reis-Filho JS, Lee AH, Ellis IO. Morphologic and molecular evolutionary pathways of low nuclear grade invasive breast cancers and their putative precursor lesions: further evidence to support the concept of low nuclear grade breast neoplasia family. Am J Surg Pathol. 2008; 32:513–23.
Article2. Simpson PT, Gale T, Reis-Filho JS, Jones C, Parry S, Sloane JP, et al. Columnar cell lesions of the breast: the missing link in breast cancer progression? A morphological and molecular analysis. Am J Surg Pathol. 2005; 29:734–46.3. Sunil R. Lakhani IOE, Stuart J Schinitt, Puay Hoon Tan, Marc J. van de Vijver. WHO classification of tumours of the breast. 4th Edition ed. Fred T. Bosman ESJ, Sunil R. Lakhani, Hiroko Ohgaki, editor. Geneva: International Agency for Research on Cancer;2012.4. Go EM, Tsang JY, Ni YB, Yu AM, Mendoza P, Chan SK, et al. Relationship between columnar cell changes and low-grade carcinoma in situ of the breast–a cytogenetic study. Hum Pathol. 2012; 43:1924–31.
Article5. Moinfar F, Man YG, Bratthauer GL, Ratschek M, Tavassoli FA. Genetic abnormalities in mammary ductal intraepithelial neoplasia-flat type ("clinging ductal carcinoma in situ"): a simulator of normal mammary epithelium. Cancer. 2000; 88:2072–81.6. Schnitt SJ. The diagnosis and management of preinvasive breast disease: flat epithelial atypia–classification, pathologic features and clinical significance. Breast Cancer Res. 2003; 5:263–8.
Article7. Abdel-Fatah TM, Powe DG, Hodi Z, Lee AH, Reis-Filho JS, Ellis IO. High frequency of coexistence of columnar cell lesions, lobular neoplasia, and low grade ductal carcinoma in situ with invasive tubular carcinoma and invasive lobular carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2007; 31:417–26.
Article9. Gadre SA, Perkins GH, Sahin AA, Sneige N, Deavers MT, Middleton LP. Neovascularization in mucinous ductal carcinoma in situ suggests an alternative pathway for invasion. Histopathology. 2008; 53:545–53.
Article10. Kryvenko ON, Chitale DA, Yoon J, Arias-Stella J 3rd, Meier FA, Lee MW. Precursor lesions of mucinous carcinoma of the breast: analysis of 130 cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2013; 37:1076–84.11. O'Connell JT, Shao ZM, Drori E, Basbaum CB, Barsky SH. Altered mucin expression is a field change that accompanies mucinous (colloid) breast carcinoma histogenesis. Hum Pathol. 1998; 29:1517–23.12. Di Saverio S, Gutierrez J, Avisar E. A retrospective review with long term follow up of 11,400 cases of pure mucinous breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2008; 111:541–7.
Article13. Matsukita S, Nomoto M, Kitajima S, Tanaka S, Goto M, Irimura T, et al. Expression of mucins (MUC1, MUC2, MUC5AC and MUC6) in mucinous carcinoma of the breast: comparison with invasive ductal carcinoma. Histopathology. 2003; 42:26–36.
Article14. Komaki K, Sakamoto G, Sugano H, Morimoto T, Monden Y. Mucinous carcinoma of the breast in Japan. A prognostic analysis based on morphologic features. Cancer. 1988; 61:989–96.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Mucinous carcinoma of the breast: distinctive histopathologic and genetic characteristics
- Imaging Features of Mucinous Breast Carcinoma
- Bilateral Mucocele-like Tumors of the Breast Associated with Ductal Carcinoma In Situ and Mucinous Carcinoma: A Case Report
- The Expression of Glut-1, CAIX, and MCT4 in Mucinous Carcinoma
- Clinicopathologic Analysis of 40 Mucinous Breast Carcinomas