J Korean Ophthalmol Soc.
2015 Dec;56(12):1913-1920. 10.3341/jkos.2015.56.12.1913.
Diurnal Variation in Intraocular Pressure Measured by Ocular Response Analyzer in Korean Patients with Normal Tension Glaucoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Ophthalmology and The Institute of Ophthalmology and Optometry, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. Ckrey02@ewha.ac.kr
- KMID: 2148754
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3341/jkos.2015.56.12.1913
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To analyze the diurnal change in intraocular pressure (IOP) and corneal biomechanical properties measured using the Ocular Response Analyzer (ORA; Reichert Inc., Depew, NY, USA) in Korean patients with normal tension glaucoma (NTG) patients.
METHODS
Intraocular pressure (Goldmann applanation tonometer IOP [GAT IOP], Goldmann-correlated IOP [IOPg], corneal-compensated IOP [IOPcc]) and corneal hysteresis (CH), corneal resistance factor (CRF) and central corneal thickness (CCT) were measured in 21 eye of NTG patients (12 males, 9 female) at 3 hour intervals for 48 hours using ORA. We recorded the time of each parameter that showed the lowest and the highest values of during the 48 hour testing period (Day 1 and Day 2) and evaluated the change of diurnal variation using Repeated measures analysis of variance (Re-ANOVA).
RESULTS
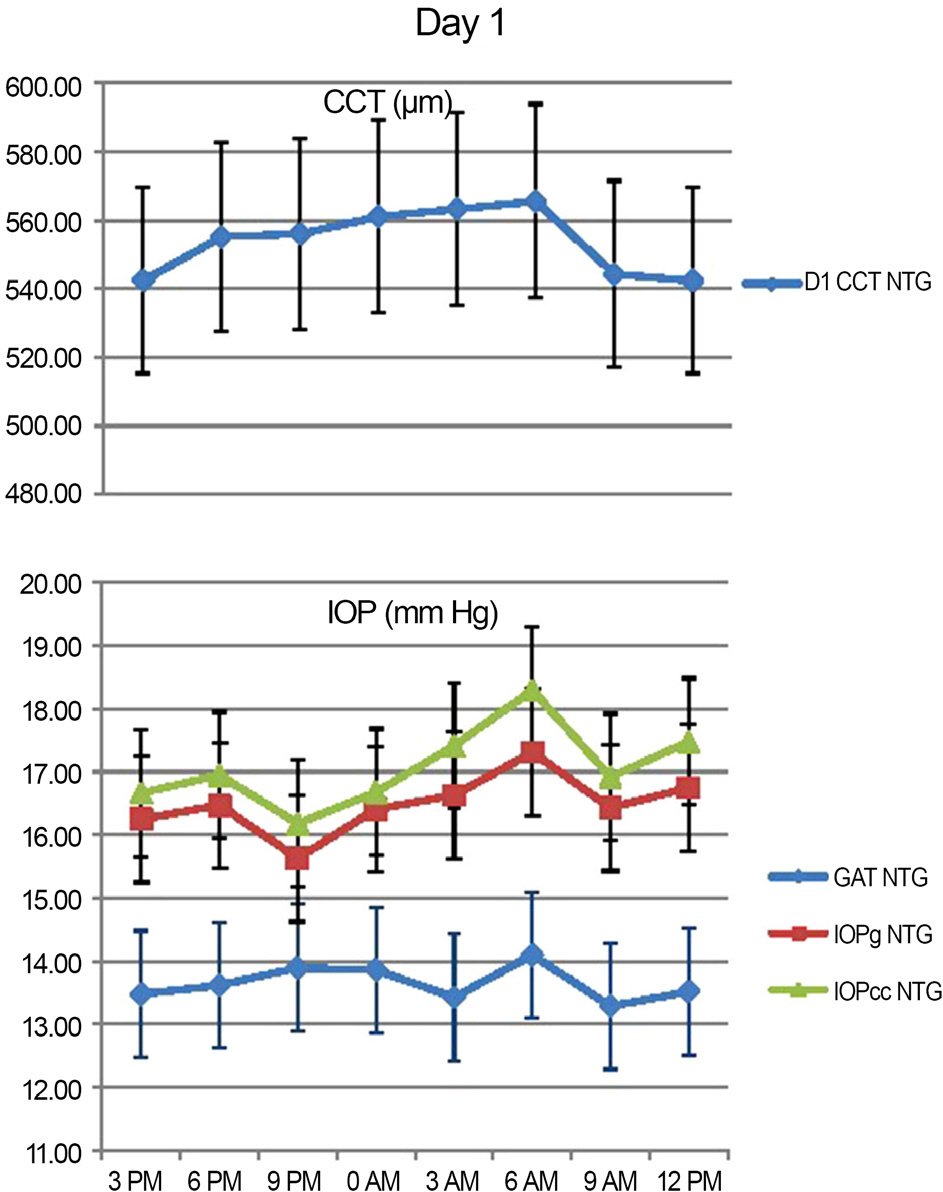
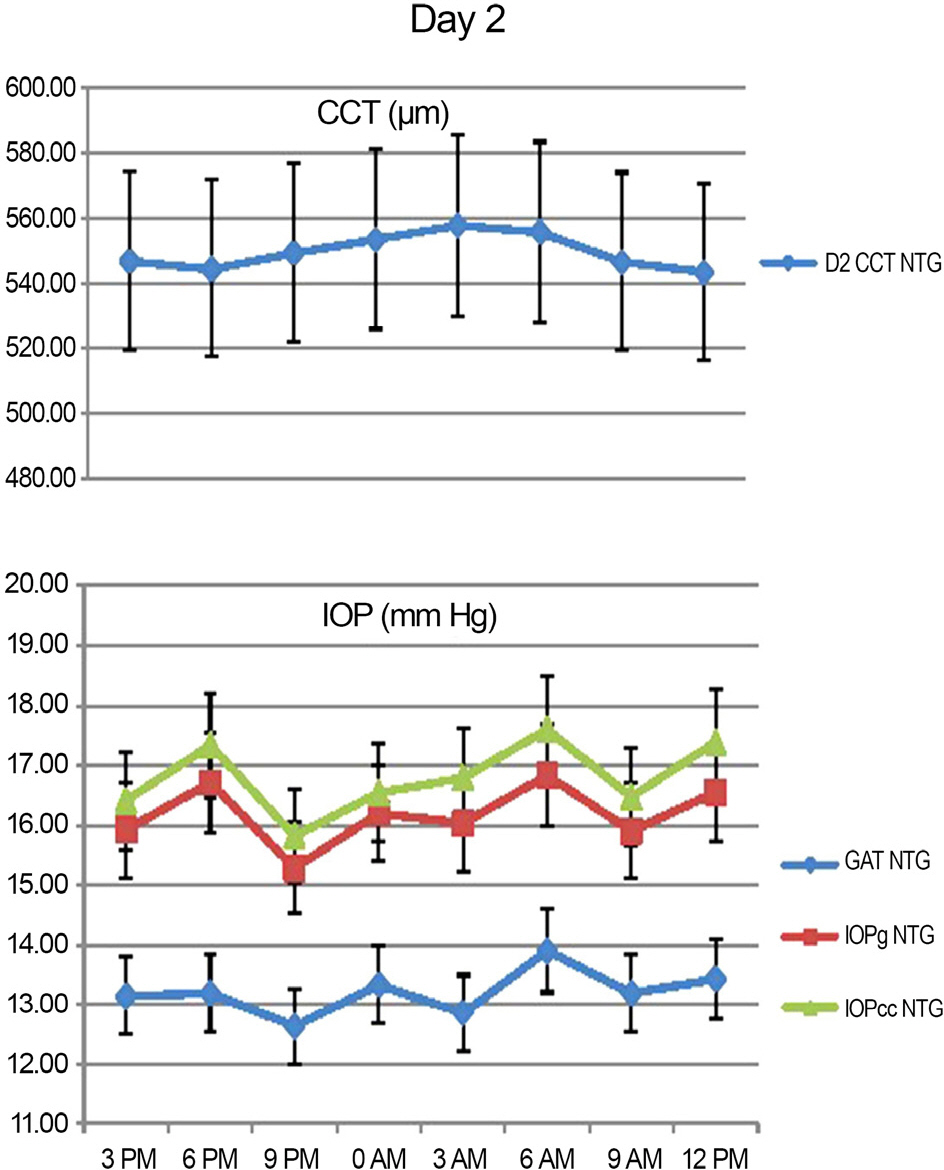
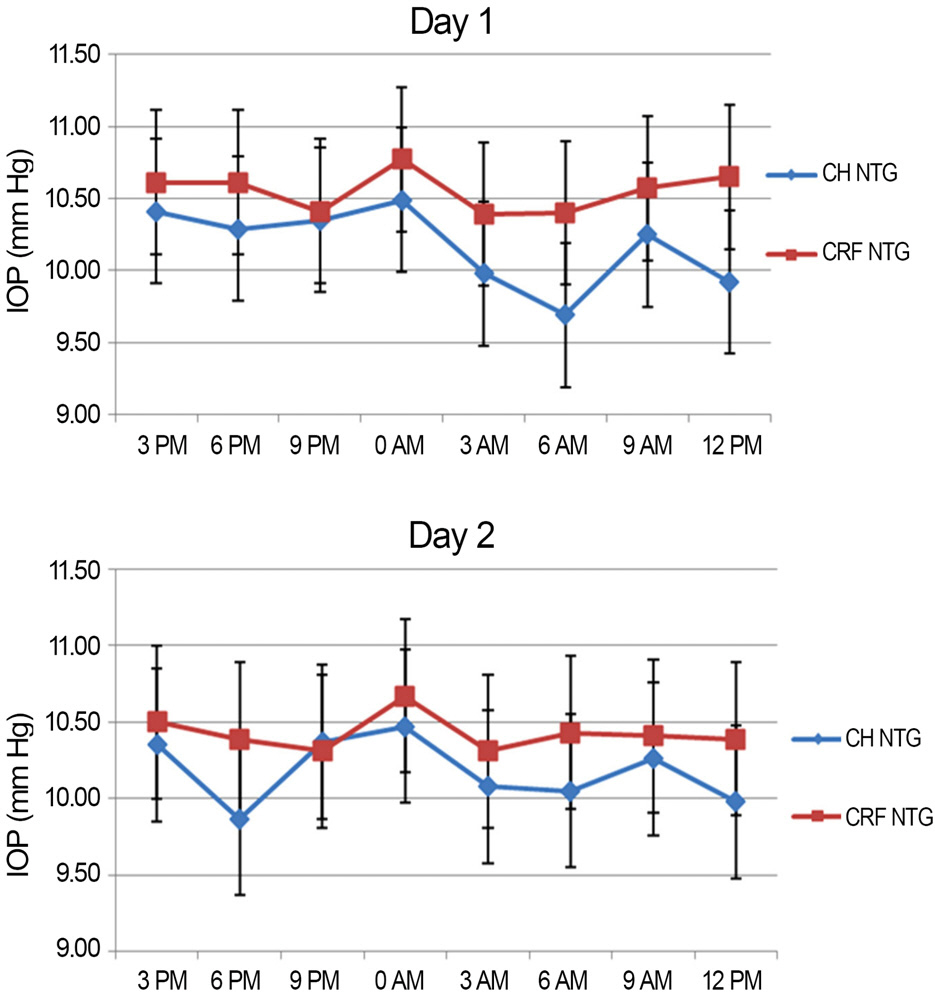
Peak IOP measured with GAT and ORA occurred at 6 AM-9 AM, 3 PM-6 PM and the trough IOP at 9 PM-12 AM during the 48 hour period. CCT, GAT IOP, IOPcc and IOPg measurements showed statistically significant variations (p<0.05). CH and CRF variations were not statistically significant (p>0.05).
CONCLUSIONS
In Korean NTG patients, IOP exhibits significant diurnal variation, with higher values during the dawn and afternoon and lower values before retiring. Clinically, measurements of IOP performed in the afternoon could aid in the detection of relatively elevated IOP.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Sultan MB, Mansberger SL, Lee PP. Understanding the im-portance of IOP variables in glaucoma: a systematic review. Surv Ophthalmol. 2009; 54:643–62.2. Allingham RR, Damji KF, Freedman SF. . Shields’ Textbook of Glaucoma. 6th. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2011. p. 25–9.3. Liu JH. Circadian rhythm of intraocular pressure. J Glaucoma. 1998; 7:141–7.
Article4. Asrani S, Zeimer R, Wilensky J. . Large diurnal fluctuations in intraocular pressure are an independent risk factor in patients with glaucoma. J Glaucoma. 2000; 9:134–42.
Article5. Mertz GW. Overnight swelling of the living human cornea. J Am Optom Assoc. 1980; 51:211–4.6. Fogagnolo P, Rossetti L, Mazzolani F, Orzalesi N. Circadian varia-tions in central corneal thickness and intraocular pressure in pa-tients with glaucoma. Br J Ophthalmol. 2006; 90:24–8.
Article7. Hamilton KE, Pye DC, Aggarwala S. . Diurnal variation of central corneal thickness and Goldmann applanation tonometry es-timates of intraocular pressure. J Glaucoma. 2007; 16:29–35.
Article8. Liu JH, Bouligny RP, Kripke DF, Weinreb RN. Nocturnal elevation of intraocular pressure is detectable in the sitting position. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2003; 44:4439–42.
Article9. Kida T, Liu JH, Weinreb RN. Effect of 24-hour corneal bio-mechanical changes on intraocular pressure measurement. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2006; 47:4422–6.
Article10. Kiely PM, Carney LG, Smith G. Diurnal variations of corneal top-ography and thickness. Am J Optom Physiol Opt. 1982; 59:976–82.
Article11. Klyce SD. Stromal lactate accumulation can account for corneal oedema osmotically following epithelial hypoxia in the rabbit. J Physiol. 1981; 321:49–64.
Article12. Liu J, Roberts CJ. Influence of corneal biomechanical properties on intraocular pressure measurement: quantitative analysis. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2005; 31:146–55.13. Detry-Morel M, Jamart J, Hautenauven F, Pourjavan S. Comparison of the corneal biomechanical properties with the Ocular Response Analyzer(R) (ORA) in African and Caucasian normal subjects and patients with glaucoma. Acta Ophthalmol. 2012; 90:e118. 24.14. Rhew JY, Choi KR. Corneal biomechanical properties of normal tension glaucoma in young patients evaluated with the ocular re-sponse analyzer. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2013; 54:280–8.
Article15. Cho AR, Choi YJ, Rhew JY, Choi KR. Diagnostic availability of ocular response analyzer in Korean patients with normal tension glaucoma. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2015; 56:86–92.
Article16. Mosaed S, Chamberlain WD, Liu JH. . Association of central corneal thickness and 24-hour intraocular pressure fluctuation. J Glaucoma. 2008; 17:85–8.
Article17. Villas-Bôas FS, Doi LM, Sousa AK, Melo LA Jr. Correlation be-tween diurnal variation of intraocular pressure, ocular pulse ampli-tude and corneal structural properties. Arq Bras Oftalmol. 2009; 72:296–301.
Article18. Sullivan-Mee M, Billingsley SC, Patel AD. . Ocular response analyzer in subjects with and without glaucoma. Optom Vis Sci. 2008; 85:463–70.
Article19. Shah S, Laiquzzaman M, Mantry S, Cunliffe I. Ocular response an-alyser to assess hysteresis and corneal resistance factor in low ten-sion, open angle glaucoma and ocular hypertension. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. 2008; 36:508–13.
Article20. Nessim M, Mollan SP, Wolffsohn JS. . The relationship be-tween measurement method and corneal structure on apparent in-traocular pressure in glaucoma and ocular hypertension. Cont Lens Anterior Eye. 2013; 36:57–61.
Article21. Shen M, Wang J, Qu J. . Diurnal variation of ocular hysteresis, corneal thickness, and intraocular pressure. Optom Vis Sci. 2008; 85:1185–92.
Article22. Hasegawa K, Ishida K, Sawada A. . Diurnal variation of intra-ocular pressure in suspected normal-tension glaucoma. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2006; 50:449–54.
Article23. Costa VP, Harris A, Anderson D. . Ocular perfusion pressure in glaucoma. Acta Ophthalmol. 2014; 92:e252–66.
Article24. Kong M, Lee JM, Kee C. Repeatability of intraocular pressure pat-terns in glaucomatous patients. J Korean Ophthalmol Soc. 2012; 53:1118–23.
Article25. Lu F, Xu S, Qu J. . Central Corneal thickness and corneal hysteresis during corneal swelling induced by contact lens wear with eye closure. Am J Ophthalmol. 2007; 143:616–22.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Short-Term Effect of Prostaglandin Analog Monotherapy on Corneal Biomechanical Properties in Normal Tension Glaucoma Patients
- A Study on the Diurnal Variation of Intraocular Pressure
- Diagnostic Availability of Ocular Response Analyzer in Korean Patients with Normal Tension Glaucoma
- Corneal Biomechanical Properties of Normal Tension Glaucoma in Young Patients Evaluated with the Ocular Response Analyzer
- Diurnal Variation in the Depth of the Anterior Chamber and Correlation between the Depth of the Anterior Chamber and Intraocular Pressure