Ann Rehabil Med.
2015 Oct;39(5):826-832. 10.5535/arm.2015.39.5.826.
Hypokalemia-Induced Rhabdomyolysis by Primary Aldosteronism Coexistent With Sporadic Inclusion Body Myositis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Physical Education, Korea National Sport University, Seoul, Korea. lkimg@knsu.ac.kr
- 3Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2148215
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2015.39.5.826
Abstract
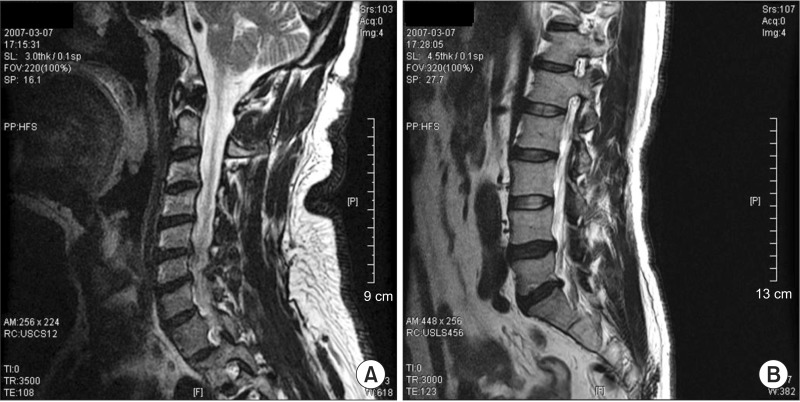
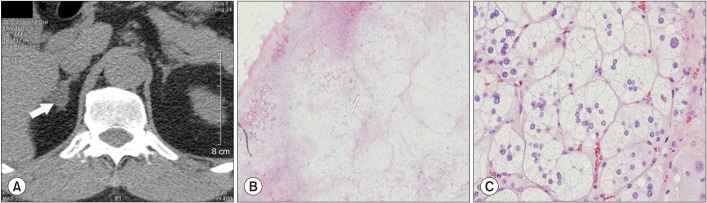
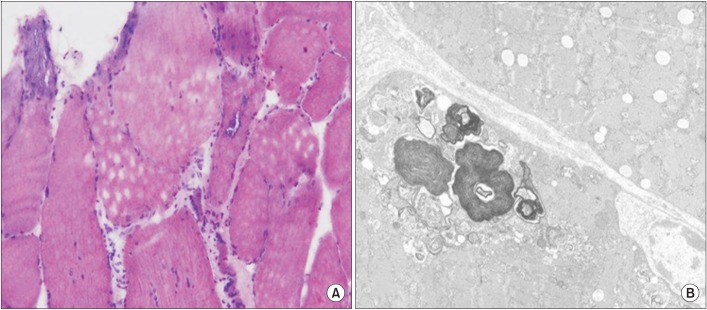
- We describes a patient with hypokalemia-induced rhabdomyolysis due to primary aldosteronism (PA), who suffered from slowly progressive muscle weakness after laparoscopic adrenalectomy, and was later diagnosed with coexisting sporadic inclusion body myositis (sIBM). A 54-year-old Asian male presented with severe muscle weakness of both lower extremities. Laboratory findings showed profound hypokalemia, and extreme elevation of the serum creatine phosphokinase levels, suggestive of hypokalemia-induced rhabdomyolysis. Further evaluation strongly suggested PA by an aldosterone-producing adenoma, which was successfully removed surgically. However, muscle weakness slowly progressed one year after the operation and a muscle biopsy demonstrated findings consistent with sIBM. This case is the first report of hypokalemia-induced rhabdomyolysis by PA coexistent with sIBM, to the best of our knowledge.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Primary Aldosteronism Presenting as Hypokalemia and Rhabdomyolysis
Kee Hong Park, Soo-Kyung Kim, Eun Bin Cho, Heejeong Jeong, Nack-Cheon Choi, Oh-Young Kwon, Byeong Hoon Lim, Jong Ryeal Hahm, Ki-Jong Park
Korean J Clin Neurophysiol. 2016;18(1):21-24. doi: 10.14253/kjcn.2016.18.1.21.
Reference
-
1. Wen Z, Chuanwei L, Chunyu Z, Hui H, Weimin L. Rhabdomyolysis presenting with severe hypokalemia in hypertensive patients: a case series. BMC Res Notes. 2013; 6:155. PMID: 23594380.
Article2. Goto A, Takahashi Y, Kishimoto M, Minowada S, Aibe H, Hasuo K, et al. Primary aldosteronism associated with severe rhabdomyolysis due to profound hypokalemia. Intern Med. 2009; 48:219–223. PMID: 19218772.
Article3. Dimachkie MM, Barohn RJ. Inclusion body myositis. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2013; 13:321. PMID: 23250766.
Article4. Greenberg SA. Inclusion body myositis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2011; 23:574–578. PMID: 21885973.
Article5. Douma S, Petidis K, Doumas M, Papaefthimiou P, Triantafyllou A, Kartali N, et al. Prevalence of primary hyperaldosteronism in resistant hypertension: a retrospective observational study. Lancet. 2008; 371:1921–1926. PMID: 18539224.
Article6. Ma JT, Wang C, Lam KS, Yeung RT, Chan FL, Boey J, et al. Fifty cases of primary hyperaldosteronism in Hong Kong Chinese with a high frequency of periodic paralysis: evaluation of techniques for tumour localisation. Q J Med. 1986; 61:1021–1037. PMID: 3659246.7. Knochel JP, Schlein EM. On the mechanism of rhabdomyolysis in potassium depletion. J Clin Invest. 1972; 51:1750–1758. PMID: 5032523.
Article8. Mattsson C, Young WF Jr. Primary aldosteronism: diagnostic and treatment strategies. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol. 2006; 2:198–208. PMID: 16932426.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Primary Aldosteronism Presenting as Hypokalemia and Rhabdomyolysis
- A Case of Primary Aldosteronism Accompanied by Hypokalemic Rhabdomyolysis
- Two Case of Primary Aldosteronism Induced by Aldosterone Producing Adrenal Adenoma in a Family
- Consumption of an Excessive Amount of Ionic Beverage Can Trigger Adrenal Adenoma - Induced Severe Hypokalemic Rhabdomyolysis
- A Case of Primary Aldosteronism with Rhabdomyolysis